《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 the process planning of mechanical manufacturing
Chapter 1 The Process Planning ofmechanical manufacturingAbstractThepurposeofmechanicalmachiningistoturnakind of rawmaterial intothefinished parts that meet the requirement ofthe product. Under given manufactureconditions, howto applyboth aneconomical and efficientmethod,as well asa rational processroutine,to achievethedesiredpartsistheconcernofthischapterThechapterbeginswithsomeimportantconcepts such as working procedure, processtep, cutting in one continuous feed, setup,machiningposition,referencedatummanufacturingprocessandsoon
Chapter 1 The Process Planning of mechanical manufacturing Abstract The purpose of mechanical machining is to turn a kind of raw material into the finished parts that meet the requirement of the product. Under given manufacture conditions, how to apply both an economical and efficient method, as well as a rational process routine, to achieve the desired parts is the concern of this chapter. The chapter begins with some important concepts such as working procedure, process step, cutting in one continuous feed, setup, machining position, reference datum, manufacturing process and so on

1.1Manufacturing Process1.2 The function and design method of process planning file1.3 Selection of positioning reference1.4 Design of process planning1.5 Plan the metal removal1.6 Dimensional Chains1.7 The determination of operational dimensions1.8 Standard machining time and economic analysis
1.1 Manufacturing Process 1.2 The function and design method of process planning file 1.3 Selection of positioning reference 1.4 Design of process planning 1.5 Plan the metal removal 1.7 The determination of operational dimensions 1.6 Dimensional Chains 1.8 Standard machining time and economic analysis

1.1 Process of product1.1.1Processofproduct(生产过程)Manufacturingistheutilizationandmanagement of materials,peopleequipment,and money toproduceproducts.For successful andeconomical manufacturing tobe achieved,planning must start at thedesign stage and continue through the selection of materials, processes.equipment, and the scheduling of production. These related processesconstitutethe so-calledproductionprocessProcess ofproductinvolve:Product design、prepare、transport of raw and processed materials、rough manufacture、mechanical machining、heat treatmentassembly、deburring、test、paintingandpacking.These related processes constitutethe so-calledproduction process.Itisusually completed by the coordinated work of different factories orworkshops
1.1 Process of product 1.1.1 Process of product (生产过程) Manufacturing is the utilization and management of materials, people, equipment, and money to produce products. For successful and economical manufacturing to be achieved, planning must start at the design stage and continue through the selection of materials, processes, equipment, and the scheduling of production. These related processes constitute the so-called production process Process of product involve: Product design 、 prepare、transport of raw and processed materials、 rough manufacture 、 mechanical machining 、 heat treatment 、 assembly、 deburring、test 、painting and packing. These related processes constitute the so-called production process. It is usually completed by the coordinated work of different factories or workshops

1.1.2ProcessofPart(工艺过程)Process of Part:The process by which the shape,dimensions and performance ofraw material or rough casting are changed directly by mechanicalmanufacturing into desired parts is called component manufactured partproduction,orprocessroute.When parts are assembled into a product, it is called the assemblyprocess
1.1.2 Process of Part (工艺过程) Process of Part: The process by which the shape, dimensions and performance of raw material or rough casting are changed directly by mechanical manufacturing into desired parts is called component manufactured part production, or process route. When parts are assembled into a product, it is called the assembly process

1.1.2.1 part productionPartproductionconsistsofoneorseveraloperationsinsequenceA rough casting can be turned into a finished or semi-finished productbytheoperations.(1)operations(工序)When one operator (or a group of operators) works in a definiteposition(one machine tool or clipping table) to achieve the continuousmanufacturingof oneor severalpartssimultaneously.An operation isthe basic element of process procedure as well as of the productionscheduleandofcostestimation
1.1.2.1 part production Part production consists of one or several operations in sequence. A rough casting can be turned into a finished or semi-finished product by the operations. (1) operations (工序) When one operator (or a group of operators) works in a definite position(one machine tool or clipping table) to achieve the continuous manufacturing of one or several parts simultaneously. An operation is the basic element of process procedure as well as of the production schedule and of cost estimation
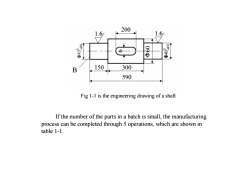
200T00,0009A150300B590Figl-listheengineeringdrawingofashaftIf the number of the parts in a batch is small, the manufacturingprocess can be completed through 5 operations, which are shown intable1-1
If the number of the parts in a batch is small, the manufacturing process can be completed through 5 operations, which are shown in table 1-1. Fig 1-1 is the engineering drawing of a shaft
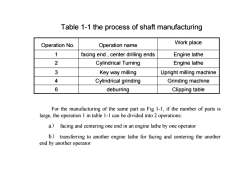
Table 1-1 the process of shaft manufacturingWork placeOperation NoOperationname1facingend,centerdrillingendsEnginelathe2Engine latheCylindrical Turning3Key way millingUpright milling machine4Cylindrical grindingGrinding machine6deburringClipping tableFor the manufacturing of the same part as Fig 1-1, if the number of parts islarge, the operation 1 in table 1-1 can be divided into 2 operations:a)facing and centering one end in an engine lathe by one operatorb) transferring to another engine lathe for facing and centering the anotherend by another operator
Table 1-1 the process of shaft manufacturing 6 deburring Clipping table 4 Cylindrical grinding Grinding machine 3 Key way milling Upright milling machine 2 Cylindrical Turning Engine lathe 1 facing end , center drilling ends Engine lathe Work place Operation No. Operation name For the manufacturing of the same part as Fig 1-1, if the number of parts is large, the operation 1 in table 1-1 can be divided into 2 operations: a) facing and centering one end in an engine lathe by one operator b) transferring to another engine lathe for facing and centering the another end by another operator

(2)Operation Step(工步)Anoperationstepisthebasicelementofanoperation.Oneoperation step is defined as an operation that is completed under thecondition when the surface to be manufactured, the cutting parameters(including cutting speed and feed) and cutting tool remain the same.When any of the cutting parameters is changed, it will become anotheroperation step.When several surfaces of a part aremanufacturedsimultaneously, it is called a composite operation step.The purpose of classifying an operationinto steps istomake a complex operationmore convenient and easy to analyze anddescribe,andtomakeitmore efficient toorganize the manufacturing and calculate theoperationtime
(2)Operation Step (工步) An operation step is the basic element of an operation. One operation step is defined as an operation that is completed under the condition when the surface to be manufactured, the cutting parameters (including cutting speed and feed) and cutting tool remain the same. When any of the cutting parameters is changed, it will become another operation step. When several surfaces of a part are manufactured simultaneously, it is called a composite operation step. The purpose of classifying an operation into steps is to make a complex operation more convenient and easy to analyze and describe, and to make it more efficient to organize the manufacturing and calculate the operation time
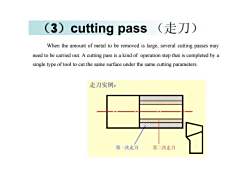
(走刀)(3) cuttingpassWhen the amountof metal tobe removed is large, several cutting passes mayneed to be carried out. A cutting pass is a kind of operation step that is completed by asingle type oftool to cut the same surface under the same cuttingparameters走刀实例:第一次走刀第二次走刀
(3)cutting pass (走刀) When the amount of metal to be removed is large, several cutting passes may need to be carried out. A cutting pass is a kind of operation step that is completed by a single type of tool to cut the same surface under the same cutting parameters

(4)setup(安装)Before it can be machined,thepart musthave a proper positionrelative to the cutting tool, and be clamped by a fixture in the machinetool. This procedure is called the fixturing(clamping). The operationcompleted through one fixturing is called single setupEachoperationmayhaveeithersinglesetuporseveral setupsIn the same operation, the number of setups should be arranged to beas few as possible. If this is done, not only can the production efficiencyberaised,butalsotheproductionerrorcausedbysetupscanbereduced
(4) setup (安装) Before it can be machined, the part must have a proper position relative to the cutting tool, and be clamped by a fixture in the machine tool. This procedure is called the fixturing(clamping). The operation completed through one fixturing is called single setup. Each operation may have either single setup or several setups. In the same operation, the number of setups should be arranged to be as few as possible. If this is done, not only can the production efficiency be raised, but also the production error caused by setups can be reduced
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第02章 机床夹具设计原理.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第01章 机械加工工艺规程的制订.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第00章 基本概念(石河子大学:葛云).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第06章 机械制造技术的发展.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第03章 机械加工精度.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第05章 机械装配工艺.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第04章 机械加工表面质量.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 1 The Process Planning of mechanical manufacturing.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 3 Machining Accuracy.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程授课教案(石河子大学:葛云).doc
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程考试大纲.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2 机床夹具设计原理(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)1 工艺规程(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)3 机械加工精度(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)机械制造工艺学习题集(部分有解答).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)4 机械加工质量分析与控制(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)5 机器装配工艺过程设计(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)6 机械制造技术的发展(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Machining Accuracy.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 机械制造技术的发展.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 机械加工表面质量.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 机器装配工艺过程设计 Machine Assembling.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 机械加工精度.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 机床夹具设计.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论 Mechanical Manufacturing Technology(石河子大学:葛云).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 机械加工工艺规程设计.pdf
- 《汽车设计》课程教学大纲 Automobile Design.pdf
- 《汽车设计》课程授课教案(文字版).docx
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学大纲 Technology of Machinery Manufacture.pdf
- 《汽车构造》课程授课教案 Brief Introduction of Automobile.pdf
- 《机械原理》课程教学大纲及基本要求(机械原理课程设计).doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学大纲 Theory of Machines and Mechanisms.doc
- 《机械原理》课程实验教学大纲.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)10.1-10.2机械的平衡.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)11.2机械的等效动力学模型和机器运动方程式.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)11.3周期性速度波动及其调节.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)9.1其他常用机构.doc
