《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Machining Accuracy

Chapter 6 Machining AccuracyAbstractThemachiningaccuracyofmachinepartsisthequalityfoundation of thewholemachine.It is usually measured withtwo indices:machining accuracy and surface quality and theirvaluesizewill directlyaffecttheperformanceandlifeofthewholemachine.ThischaptermainlyinvolvesthemachiningaccuracyThebasicconcepts,factorsthatarerelatedwiththemachiningaccuracy,thecomprehensiveanalysis ofmachining errors, and the methods of raising the machiningaccuracyarediscussed inthischapter
Chapter 6 Machining Accuracy Abstract The machining accuracy of machine parts is the quality foundation of the whole machine. It is usually measured with two indices: machining accuracy and surface quality and their value size will directly affect the performance and life of the whole machine. This chapter mainly involves the machining accuracy. The basic concepts,factors that are related with the machining accuracy, the comprehensive analysis of machining errors, and the methods of raising the machining accuracy are discussed in this chapter
Index3.1Basicconceptsof machiningaccuracy3.2factorsaffectingthemachiningaccuracy3.3statisticanalysisofmachining errors/methods of raising the machining accuracy
Index 3.1 Basic concepts of machining accuracy 3.2 factors affecting the machining accuracy 3.3 statistic analysis of machining errors 3.4 methods of raising the machining accuracy

3.1Basic concept of machining accuracy3.1.1 Machining accuracy and machining errorMachining accuracy:The degree of the practical dimensions aftermachining conforms to the desired geometrical parameters.The higher thedegree conforms, the higher the machining accuracy.Machining error: The degree of the practical dimensions after machiningdeviatesfrom thedesired geometrical parameters.The size ofthe machiningerror denotes the size of the machining accuracy.“Machining accuracy"and"Machining error"are two different conceptsto evaluate the accurate degree of the part geometries. In productionpractice, the accuracy is ensured by controlling the machining error or activeadapting method
3.1 Basic concept of machining accuracy 3.1.1 Machining accuracy and machining error Machining accuracy:The degree of the practical dimensions after machining conforms to the desired geometrical parameters.The higher the degree conforms, the higher the machining accuracy. Machining error:The degree of the practical dimensions after machining deviates from the desired geometrical parameters. The size of the machining error denotes the size of the machining accuracy. “Machining accuracy”and“Machining error” are two different concepts to evaluate the accurate degree of the part geometries. In production practice, the accuracy is ensured by controlling the machining error or active adapting method

3.1.2 The method to study the machining accuracyThere are two methods to study the machining accuracy. One is thesingle factor analysis method, in which the machining accuracy is analyzedby calculation, experiment or inspection so as to decide the single factor'sinfluencing law to the single error. Another one is the statistic method, inwhich the statistical theory is used to process the inspected data of a batch ofworkpiecefromthepractice soastocontroltheprocessrunning innormalcondition.These two methods are often used together in practice. Generally, thestatistic method is first used to find out the law of the error, and judge thecauses, then factoranalysis method is used tofind outthekeyfactors whichinfluencethemachiningaccuracy
3.1.2 The method to study the machining accuracy There are two methods to study the machining accuracy. One is the single factor analysis method, in which the machining accuracy is analyzed by calculation, experiment or inspection so as to decide the single factor’s influencing law to the single error. Another one is the statistic method, in which the statistical theory is used to process the inspected data of a batch of workpiece from the practice so as to control the process running in normal condition. These two methods are often used together in practice. Generally, the statistic method is first used to find out the law of the error, and judge the causes, then factor analysis method is used to find out the key factors which influence the machining accuracy

3.21Factors affecting the machining accuracyPart machining happens in the processing system composed ofmachine tools, fixtures, cutting tool and workpiece. All the factors in thesystem that may cause machining errors are called the original errors.Theexistence of the original errors makes the positional or motional relationshipdeviated from its desired state, and brings about the machining error. If theoriginal errors existed before machining,or in another word, it is causedwithout the cutting force, it is called the static processing error, otherwise,itiscalledthedynamicprocesserror
3.2 Factors affecting the machining accuracy Part machining happens in the processing system composed of machine tools, fixtures, cutting tool and workpiece. All the factors in the system that may cause machining errors are called the original errors. The existence of the original errors makes the positional or motional relationship deviated from its desired state, and brings about the machining error. If the original errors existed before machining,or in another word, it is caused without the cutting force, it is called the static processing error, otherwise, it is called the dynamic process error
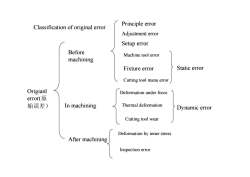
Principle errorClassification oforiginal erronAdjustmenterrorSetup errorBeforeMachinetoolerrormachiningStaticerrorFixture errorCutting tool manu errorOrigianlDeformationunderforceerror(原Thermaldeformation始误差In machiningDynamic errorCutting tool wearDeformationbyinnerstressAftermachiningInspection error
Classification of original error Origianl error(原 始误差) Before machining In machining After machining Principle error Adjustment error Setup error Machine tool error Fixture error Cutting tool manu error Deformation under force Thermal deformation Cutting tool wear Deformation by inner stress Inspection error Dynamic error Static error
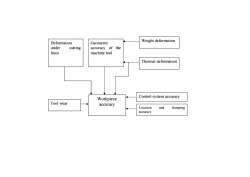
WeightdeformationDeformationGeometricunderaccuracyofthecuttingforcemachinetoolThermaldeformationControl system accuracyWorkpieceTool wearaccuracyandLocationclampingaccuracy
Deformation under cutting force Geometric accuracy of the machine tool Tool wear Workpiece accuracy Control system accuracy Location and clamping accuracy Weight deformation Thermal deformation

3.2.1 Error of machining principleMachining principle refers to the forming principle of the surface on theworkpiece. The error of machining principle is caused by similar cuttingmotion of forming or similar cutting edge geometry. The purpose is tosimplify the design and manufacturing of the machine tool and cuttingtool, reduce the manufacturing cost, raise the production efficiency andfacilitatetheuse
3.2.1 Error of machining principle Machining principle refers to the forming principle of the surface on the workpiece. The error of machining principle is caused by similar cutting motion of forming or similar cutting edge geometry. The purpose is to simplify the design and manufacturing of the machine tool and cutting tool, reduce the manufacturing cost, raise the production efficiency and facilitate the use

3.2.2 Error of the machine toolErrorofthemachinetoolreferstothemanufactureerror,setuperrorandwearcomefromthemachinetoolwithoutcuttingforce.3.2.2.1 spindlerotational error(1)conceptof spindlerotational errorTheoretically,thepositionoftherotational axisofthespindleinthespace is fixed, or in another word, the instant speed is zero. But inpractice,there are a lot of factors influence the position of the spindle andmakethe spindleposition changeinstantly.Wecallthemaximumfloatingvalueinthesensitivedirectionoftheerrortherotationalerrorofthespindle
3.2.2 Error of the machine tool Error of the machine tool refers to the manufacture error, setup error and wear come from the machine tool without cutting force. 3.2.2.1 spindle rotational error (1)concept of spindle rotational error Theoretically,the position of the rotational axis of the spindle in the space is fixed, or in another word, the instant speed is zero. But in practice,there are a lot of factors influence the position of the spindle and make the spindle position change instantly. We call the maximum floating value in the sensitive direction of the error the rotational error of the spindle

movieTherearethreetypes ofspindlerotational error,shown below:()Fig.1 the threetypes of the spindle error of themachinetool(a)Pureradial jump (b)pureaxial jump(c)pureangularmovePure radial jump :Thepractical axis is parallel to the desired axis, butjumpinconstantamplitudePure axial jump :The practical axis moves along the desired axis withconstantamplitude.Pure angular move:The practical axis moves inclined to the desired axis with aconstant amplitude,and the jointpoint keeps constant
Pure angular move:The practical axis moves inclined to the desired axis with a constant amplitude , and the joint point keeps constant. Pure radial jump :The practical axis is parallel to the desired axis, but jump in constant amplitude Pure axial jump : The practical axis moves along the desired axis with constant amplitude. There are three types of spindle rotational error, shown below:movie Fig.1 the three types of the spindle error of the machine tool (a) Pure radial jump (b) pure axial jump (c) pure angular move
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 the process planning of mechanical manufacturing.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第02章 机床夹具设计原理.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第01章 机械加工工艺规程的制订.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第00章 基本概念(石河子大学:葛云).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第06章 机械制造技术的发展.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第03章 机械加工精度.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第05章 机械装配工艺.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(中文讲稿)第04章 机械加工表面质量.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 1 The Process Planning of mechanical manufacturing.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(英文讲稿)Chapter 3 Machining Accuracy.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程授课教案(石河子大学:葛云).doc
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程考试大纲.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)2 机床夹具设计原理(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)1 工艺规程(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)3 机械加工精度(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(书籍文献)机械制造工艺学习题集(部分有解答).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)4 机械加工质量分析与控制(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)5 机器装配工艺过程设计(无答案).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 The design principle of jigs and fixtures.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 机械制造技术的发展.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 机械加工表面质量.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 机器装配工艺过程设计 Machine Assembling.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 机械加工精度.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 机床夹具设计.pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第0章 绪论 Mechanical Manufacturing Technology(石河子大学:葛云).pdf
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 机械加工工艺规程设计.pdf
- 《汽车设计》课程教学大纲 Automobile Design.pdf
- 《汽车设计》课程授课教案(文字版).docx
- 《机械制造工艺学》课程教学大纲 Technology of Machinery Manufacture.pdf
- 《汽车构造》课程授课教案 Brief Introduction of Automobile.pdf
- 《机械原理》课程教学大纲及基本要求(机械原理课程设计).doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学大纲 Theory of Machines and Mechanisms.doc
- 《机械原理》课程实验教学大纲.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)10.1-10.2机械的平衡.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)11.2机械的等效动力学模型和机器运动方程式.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)11.3周期性速度波动及其调节.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)9.1其他常用机构.doc
- 《机械原理》课程教学资源(授课教案)8.1齿轮系分类定轴轮系传动比计算.doc
