《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy

重庆医科大学儿科学教案讲课题目:Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy(HIE)新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病教师:余加林授课题目TEACHINGTOPICHypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病第几次课TIMES3rd教学方法METHODSClass teaching教学对象OBJECTIVESeven years students学时:TIME40x3minutes教学目标PURPOSEI.master theclinical manifestations and categories2.mastertheprincipleand emphasis accordingtodifferentstageofHIEreatmer3. know the etiology, pathogenesis and assistant tests ofHIE教学重点和难点The clinical manifestations, categories, pathogenesis and assistant tests ofPURPOSE/DIFFICULTIESHIE教学内容的深化与拓宽The advances in mechanism of neural damage, esp.apoptosis, andThedevelopmentsinterventionapproaches ofHIE教学要求的英语单词Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy,consequence,disablementasphyxiaEnglish requirements erebral palsy,antpartminapartmostpartumeenapreancimalposition, placental insufficiency,placental abruption,congenitaanomalie实践性教学安排One teaching hour of clinical demonstrationClinical study教材及参考资料沈晓明,王卫平。儿科学,北京:人民卫生出版社,2008TEXTUSED/2.BOOK杨锡强,易著文儿科学北京:人民卫生出版社,2008REFERENCES3.Taeusch HW, Ballard RA, Gleason CA. Elsevier Saunders: Avery'sdiseases of the newborn, 8thedition, 200教具TEACHINGAIDSPPT教学程序Procedures详细见讲稿主要内容及安排(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配):
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 讲课题目:Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy(HIE)新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 教师: 余加林 授课题目 TEACHING TOPIC Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 第几次课 TIMES 3 rd 教学方法 METHODS Class teaching 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Seven years students 学时: TIME 40×3 minutes 教学目标 PURPOSE 1. master the clinical manifestations and categories 2. master the principle and emphasis according to different stage of HIE treatment 3. know the etiology, pathogenesis and assistant tests of HIE 教学重点和难点 PURPOSE/ DIFFICULTIES The clinical manifestations, categories, pathogenesis and assistant tests of HIE 教学内容的深化与拓宽 The developments The advances in mechanism of neural damage, esp. apoptosis, and intervention approaches of HIE 教学要求的英语单词 English requirements Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, asphyxia, consequence, disablement, cerebral palsy, antepartum, intrapartum,postpartum,teenage pregnancies, malposition, placental insufficiency, placental abruption, congenital anomalies 实践性教学安排 Clinical study One teaching hour of clinical demonstration. 教材及参考资料 TEXT BOOK USED/ REFERENCES 1. 沈晓明,王卫平. 儿科学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008 2. 杨锡强,易著文. 儿科学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008 3.Taeusch HW, Ballard RA, Gleason CA. Elsevier Saunders: Avery’s diseases of the newborn, 8th edition, 2005 教具 TEACHING AIDS PPT 教学程序 Procedures (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配): 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排
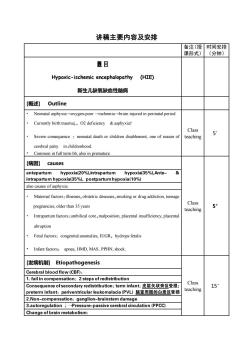
讲稿主要内容及安排备注(授时间安排课形式)(分钟)题目Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病[概述] OutlineNeonatal asphyxia→oxygen-poor -→ischemiabrain injured in perinatal periodCurrently birthtraumal, 02 deficiency& asphyxiatClass5Severe consequenceeonatal death orchildrendisablemer one of reason ofteachingcerebral palsyin childrenhood.Common in full term bb, also in premature[病因] causesantepartumhypoxia(20%),intrapartumhypoxia(35%),Ante-8intrapartum hypoxia(35%), postpartum hypoxia(10%)also causes of asphyxiaMaternal factors: llnesses, obstetric deseases, smoking or drug addiction, teenageClass5'pregnancies, olderthan 35 yearsteachingIntrapartum factors: umbilical core,malposition,placental insufficiency,placentalabruptionFetal factors: congenital anomalies, IUGR, hydrops fetalisInfant factors:apnea, HMD, MAS, PPHN, shock[发病机制] EtiopathogenesisCerebral blood flow (CBF):1. fail in compensation: 2 steps of redistributionClass15'Consequenceofsecondaryredistribution:terminfant:皮层矢状旁区受损;teachingpreterm infant:periventricularleukomalacia(PVL)脑室周围的白质区受损2.Non-compensation:ganglion-brainstem damage3.autoregulationPressure-passive cerebral circulation (PPCC)Change of brain metabolism:
讲稿主要内容及安排 备注(授 课形式) 时间安排 (分钟) 题目 Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) 新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病 [概述] Outline • Neonatal asphyxia→oxygen-poor →ischemia→brain injured in perinatal period • Currently birth trauma↓ O2 deficiency & asphyxia↑ • Severe consequence neonatal death or children disablement, one of reason of cerebral palsy in childrenhood. • Common in full term bb, also in premature Class teaching 5’ [病因] causes Class teaching 5’ also causes of asphyxia: • Maternal factors illnesses obstetric deseases smoking or drug addiction, teenage pregnancies, older than 35 years • Intrapartum factors umbilical core malposition, placental insufficiency, placental abruption • Fetal factors congenital anomalies, IUGR hydrops fetalis • Infant factors apnea, HMD, MAS, PPHN, shock. [发病机制] Etiopathogenesis Class teaching 15’

1.oxygen free rsadicalruptureofcellmembranedestroyBBB(1) over production:cytochrome-oxydasel;reperfusion:xanthine oxidaset→ urea +oxyradicalshypoxanthine(2)remove not enough:超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)2.imbalance ofNa&Ca:anaerobic glycolysis-→lactic acid,ATPlpump out oforder→ Cat inflow→chaos of signalNa++ inflow→intra-cellular edema3.excitable neurotransmitter:glutamic acid ; β-opioid peptideneuropathology :Edema,ncrosisand apoptosis obraincells[临床表现] Clinical manifestationhistory: asphyxianervous system:basic:conscious disturbance,tension ofmuscle,primitivereflexsr:onulsion,bulgonanelrrgularrpiratonpupilClass10'teachingdisordeMild: alert, rritable,but has normal tone and no seizuresModerate:lethargic,hypotonic,often seizuresSevere:stuporous or coma, flaccid or limp,often apneic,persistent seizures[实验室检查] investigationsElectroencephalogram (EEG):-- may be normal during first few dayClasssuppressed or frequent seizure activity- poor prognosis:10'teachingImaging assessment--cranial ultrasound-- brain CT scan-- MRI and spectroscopyClass[诊断] diagnose 5'teaching
1.oxygen free rsadical → rupture of cell membrane destroy BBB (1) over production cytochrome-oxydase↓ reperfusion xanthine oxidase↑ hypoxanthine-→ urea +oxyradicals (2) remove not enough SOD ↓ 2.imbalance of Na & Ca:anaerobic glycolysis→lactic acid↑,ATP↓→ pump out of order → Ca++ inflow→chaos of signal →Na++ inflow→intra-cellular edema 3.excitable neurotransmitter: glutamic acid;β-opioid peptide neuropathology: Edema,necrosis and apoptosis of brain cells [临床表现] Clinical manifestation Class teaching 10’ • history asphyxia • nervous system basic: conscious disturbance, tension of muscle, primitive reflex severe convulsions, bulge fontanel, irregular respiration, pupils disorder • Mild alert, irritable,but has normal tone and no seizures • Moderate lethargic, hypotonic, often seizures • Severe stuporous or coma, flaccid or limp, often apneic, persistent seizures [实验室检查] investigations Class teaching 10’ Electroencephalogram (EEG): - may be normal during first few day - poor prognosis: suppressed or frequent seizure activity Imaging assessment: - cranial ultrasound - brain CT scan - MRI and spectroscopy [诊断] diagnose Class teaching 5’
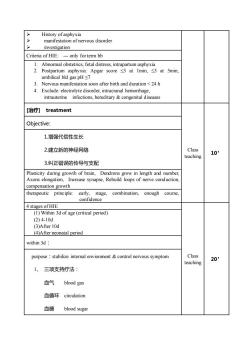
NHistory of asphyxiaYmanifestation of nervous disorderYinvestigationCriteria ofHIE:-- only forterm bb1Abnormal obstetrics, fetal distress, intrapartum asphyxia2. Postpartum asphyxia: Apgar score ≤3 at 1min, ≤5 at 5min,umbilical bld gas pH ≤73.Nervous manifestation soon after birth and duration24h4.Exclude: electrolyte disorder, intracranal hemorrhage,intrauterineinfections, hereditary&congenital diseases[治疗] treatmentObjective:1.增强代偿性生长Class2.建立新的神经网络10'teaching3.纠正错误的传导与支配Plastity during growth of brain, Dendrons grow in length and number,Axonselongation,Increasesynapse,Rebuild loops of nerve conduction,compensation growththerapeutic principle: early,stage, combination, enough course,confidence4 stages of HIE(I) Within 3d of age (critical period)(2) 4-10d(3)After 10d(4)After neonatal periodwithin 3d :Classpurpose : stabilize intermalenvionment &control nervous symptom20'teaching1、三项支持疗法:血气 blood gas血循环circulation血糖blood sugar
➢ History of asphyxia ➢ manifestation of nervous disorder ➢ investigation Criteria of HIE: - only for term bb 1. Abnormal obstetrics, fetal distress, intrapartum asphyxia 2. Postpartum asphyxia: Apgar score ≤3 at 1min, ≤5 at 5min, umbilical bld gas pH ≤7 3. Nervous manifestation soon after birth and duration < 24 h 4. Exclude: electrolyte disorder, intracranal hemorrhage, intrauterine infections, hereditary & congenital diseases [治疗] treatment Class teaching 10’ Objective: 1.增强代偿性生长 2.建立新的神经网络 3.纠正错误的传导与支配 Plasticity during growth of brain, Dendrons grow in length and number, Axons elongation, Increase synapse, Rebuild loops of nerve conduction, compensation growth therapeutic principle: early, stage, combination, enough course, confidence 4 stages of HIE Class teaching 20’ (1) Within 3d of age (critical period) (2) 4-10d (3)After 10d (4)After neonatal period within 3d: purpose:stabilize internal envionment & control nervous symptom 1、 三项支持疗法: 血气 blood gas 血循环 circulation 血糖 blood sugar

2、三项对症处理:控制惊蕨:phenobarbital,diazepam降颅压:furosemide,mannitol消除脑干症状:纳络酮naloxone指征 indication :① severe HIE pupil disorder@ shock@ frequent convulsion3 . improve metabolism of cells :cerebrolysin,胞磷胆碱 citicoline,复方丹参Salvia miltiorrhizahyperbaric oxygenation (HBO)4-10d of age :purpose:4-5d开始好转,7-9d明显好转method:improve metabolism of cellsAfter10d purpose:Consolidate therapeuticeffect&prevente sequelaemethod: if neonatal behavior nervous assessment (NBNA)<351.促神经细胞代谢2.新生儿期干预 interventionAfterneonatal period:NBNA<35,DQ<85,继续治疗3-6月[结课回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容布置见习的内容和要求QUESTIONS:
2、 三项对症处理 : 控制惊厥:phenobarbital, diazepam 降颅压:furosemide, mannitol 消除脑干症状:纳络酮 naloxone 指征 indication:① severe HIE ② pupil disorder ③ shock ④ frequent convulsion 3.improve metabolism of cells: cerebrolysin, 胞磷胆碱 citicoline, 复方丹参 Salvia miltiorrhiza hyperbaric oxygenation (HBO) 4-10d of age: purpose: 4-5d 开始好转,7-9d 明显好转 method: improve metabolism of cells After 10d: purpose: Consolidate therapeutic effect & prevente sequelae method: if neonatal behavior nervous assessment (NBNA)<35 1.促神经细胞代谢 2.新生儿期干预 intervention After neonatal period: NBNA<35, DQ<85, 继续治疗 3-6 月 [结课] 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容 布置见习的内容和要求 QUESTIONS:
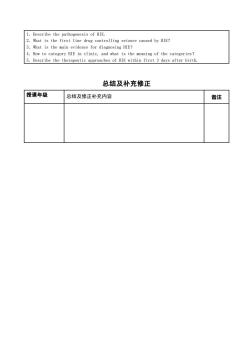
1. Describe the pathogenesis of HIE2. What is the first line drug controlling seizure caused by HIE?3. What is the main evidence for diagnosing HIE?4. How to category HIE in clinic, and what is the meaning of the categories?Describe the therapeutic approaches of HIE within first 3 days after birth总结及补充修正授课年级总结及修正补充内容备注
1.Describe the pathogenesis of HIE. 2.What is the first line drug controlling seizure caused by HIE? 3.What is the main evidence for diagnosing HIE? 4.How to category HIE in clinic, and what is the meaning of the categories? 5.Describe the therapeutic approaches of HIE within first 3 days after birth. 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十九章 自动临床生物化学分析仪的应用及评价.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 治疗药物浓度监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 妊娠的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 肿瘤标志物的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 神经系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 消化系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 内分泌疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 心血管系统疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 肾功能损伤的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 肝胆疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 营养状况的评估及的生物化学监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微量元素与维生素异常的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 骨代谢紊乱及相关元素的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 电解质和酸碱平衡紊乱的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 血浆脂蛋白代谢紊乱的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 糖代谢紊乱的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 血浆蛋白质与含氮化合物的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 生物化学检验中的诊断酶学.ppt
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
