《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice
重庆医科大学儿科学教案讲课题目:Neonatal Jaundice新生儿黄痘教师:余加林授课题目TEACHINGTOPICNeonatal Jaundice新生儿黄痘第几次课TIMES3r教学方法METHODSClass teaching教学对象OBJECTIVESeven years students学时:TIME40×2 minutes教学目标PURPOSE1.master differentiate diagnosisof physiological jaundice andpathological jaundicehe clinical featuofneonatalhemolyticsorders,neonatalnatehepatitis and biliary atresizknow the features of bilirubin metabolism in neonatesknowtheriskfactors andprophylactic approaches ofkernicterusfamiliar withtheclinicalfeaturesof common disorderscausing2pathological jaundices教学重点和难点1.the features of bilirubinmetabolism in nconatesPURPOSEIDIFFICULTIES2.thefactors aggravating neonatal jaundice3. the maternal and newborn blood types related to isoimmunization教学内容的深化与拓宽Introduce of factors relating to kernicterus.Thedevelopments教学要求的英语单词Jaundice, hyperbilirubinemia, Physiological phenomenon, Pathologic signEnglish requirementsUnconjugated bilirubin, basal ganglia, kernicterus.liver cirrhosis,biliaryatresia, Diagnostic Criteria, TORCHS: toxoplasma, protozoom, rubella,cytomegalovirus,herpes,HIV,syphilis,Hemolytic disorders,ABincompatibility实践性教学安排On teachinghouroelinicalworkshoClinical study教材及参考资料沈晓明,王卫平。儿科学,北京:人民卫生出版社,2008TEXTUSEDI杨锡强,易著文儿科学,北京:人民卫生出版社,2008BOOKREFERENCES3TaeuschHW,BllardRAGleasonAEsevierSaundersAverysdiasthwnditn0教具 TEACHING AIDSPP教学程序Procedures详细见讲稿主要内容及安排(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配):
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 讲课题目:Neonatal Jaundice 新生儿黄疸 教师: 余加林 授课题目 TEACHING TOPIC Neonatal Jaundice 新生儿黄疸 第几次课 TIMES 3 rd 教学方法 METHODS Class teaching 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Seven years students 学时: TIME 40×2 minutes 教学目标 PURPOSE 1. master differentiate diagnosis of physiological jaundice and pathological jaundice 2. mater the clinical features of neonatal hemolytic disorders, neonatal hepatitis and biliary atresia 3. know the features of bilirubin metabolism in neonates 4. know the risk factors and prophylactic approaches of kernicterus 5. familiar with the clinical features of common disorders causing pathological jaundices 教学重点和难点 PURPOSE/ DIFFICULTIES 1. the features of bilirubin metabolism in neonates 2. the factors aggravating neonatal jaundice 3. the maternal and newborn blood types related to isoimmunization 教学内容的深化与拓宽 The developments Introduce of factors relating to kernicterus. 教学要求的英语单词 English requirements Jaundice,hyperbilirubinemia,Physiological phenomenon,Pathologic sign, Unconjugated bilirubin,basal ganglia, kernicterus.liver cirrhosis, biliary atresia,Diagnostic Criteria,TORCHS: toxoplasma,protozoom,rubella, cytomegalovirus , herpes, HIV , syphilis, Hemolytic disorders, ABO incompatibility 实践性教学安排 Clinical study One teaching hour of clinical workshop. 教材及参考资料 TEXT BOOK USED/ REFERENCES 1. 沈晓明,王卫平. 儿科学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008 2. 杨锡强,易著文. 儿科学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008 3.Taeusch HW, Ballard RA, Gleason CA. Elsevier Saunders: Avery’s diseases of the newborn, 8th edition, 2005 教具 TEACHING AIDS PPT 教学程序 Procedures (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配): 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排
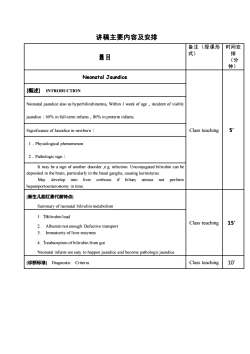
讲稿主要内容及安排备注(授课形时间安式)排题目(分钟)Neonatal Jaundice[概述] NTRODUCTIONNeonatal jaundice also as hyperbilirubinemia, Within 1 week of age , incident of visiblyjaundice :60% infull-term infants80% inpreterm infants5'Class teachingSignificance of Jaundice in newborn :Physiological phermenor2. Pathologic signIt may be a sign of another disorder ,e.g infection. Unconjugated bilirubin can bedositedithe baaruyithe bsagangliaaungkeuMaydevelop intoliver cirhossifbiliay atresianotperformhepatoportoenterostomy in time【新生儿胆红素代谢特点】Summary of neonatal bilirubin metabolism1. Bilirubin loadClass teaching152Abuminnotenoughctivetanspo3.Immaturityof liver enzymes4.Treabsorptionofbilirubinfrom gutNeonatal infants are easy tohappen jaundice and become pathologicjaundiceClass teaching 10°[诊断标准]】 DiagnosticCriteria
讲稿主要内容及安排 题目 备注(授课形 式) 时间安 排 (分 钟) Neonatal Jaundice Class teaching 5’ [概述] INTRODUCTION Neonatal jaundice also as hyperbilirubinemia, Within 1 week of age,incident of visibly jaundice:60% in full-term infants,80% in preterm infants. Significance of Jaundice in newborn: 1.Physiological phenomenon 2.Pathologic sign: It may be a sign of another disorder ,e.g. infection. Unconjugated bilirubin can be deposited in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia, causing kernicterus. May develop into liver cirrhosis if biliary atresia not perform hepatoportoenterostomy in time. [新生儿胆红素代谢特点] Summary of neonatal bilirubin metabolism Class teaching 15’ 1. ↑Bilirubin load 2. Albumin not enough: Defective transport 3. Immaturity of liver enzymes 4. ↑reabsorption of bilirubin from gut Neonatal infants are easy to happen jaundice and become pathologic jaundice. [诊断标准] Diagnostic Criteria Class teaching 10’
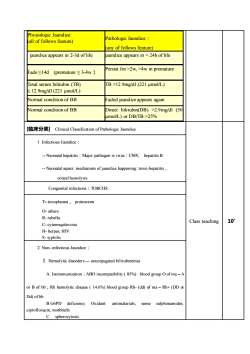
Physiologic JaundicePathologic Jaundice :alloffollowsfeature)(any offollows feature)jaundice appears in2-3d oflifejaundice appears in2w,>4w in prematureFade≤14d (premature≤3-4w)Total serum bilirubin (TB)TB>12.9mg/dl (221 μmol/L)12.9mg/dl (221 μmol/L)Normal cond ition of BBFaded jaundiceappears againDirect bilirubin(DB) >2.9mg/dl (50Normal condition of BBumol/L)orDB/IB>25%[临床分类] Clinical Classification of Pathologic JaundiceI. Infectious Jaundice : Neonatal hepatitis : Major pathogen is virus : CMV, hepatitis B-- Neonatal sepsis: mechanism of jaundice happening: toxic-hepatitis ,or/and hemolysisCongenital infections : TORCHS:T-toxoplasma, protozoomO- othersR- rubella10'Class teachingC- cytomegalovirusH- herpes, HIVS- syphilis2. Non- infectious Jaundice :I.Hemolytic disorders--- unconjugated bilirubinemiaA. Isoimmunization : ABO incompatibility ( 85%) : blood group O of ma -Aor B of bb ; Rh hemolytic disease (14.6%) blood group Rh-(dd) of ma -Rh+ (DD oDd) of bBGPD deficieney Oxidant:antimalarials,some sulphonamidesciprofloxacin, mothballsC.spherocytosis
Physiologic Jaundice: (all of follows feature) Pathologic Jaundice: (any of follows feature) jaundice appears in 2-3d of life jaundice appears in 2w, >4w in premature Total serum bilirubin (TB) ≤ 12.9mg/dl (221 µmol/L) TB >12.9mg/dl (221 µmol/L) Normal condition of BB Faded jaundice appears again Normal condition of BB Direct bilirubin(DB) >2.9mg/dl (50 µmol/L) or DB/TB >25% [临床分类] Clinical Classification of Pathologic Jaundice Class teaching 10’ 1. Infectious Jaundice: - Neonatal hepatitis:Major pathogen is virus:CMV, hepatitis B - Neonatal sepsis: mechanism of jaundice happening: toxic-hepatitis, or/and hemolysis Congenital infections:TORCHS: T– toxoplasma, protozoom O- others R- rubella C- cytomegalovirus H- herpes, HIV S- syphilis 2. Non- infectious Jaundice: Ⅰ. Hemolytic disorders - unconjugated bilirubinemia A. Isoimmunization:ABO incompatibility ( 85%) : blood group O of ma – A or B of bb;Rh hemolytic disease ( 14.6%) blood group Rh- (dd) of ma – Rh+ (DD or Dd) of bb B.G6PD deficiency Oxidant: antimalarials, some sulphonamides, ciprofloxacin, mothballs C. spherocytosis

[溶血病发病机制]Pathogenesy:lala M20 Class teaching 5O8-9Wsecondst ↑firstst(Primary stimulus)-Pregnancy mother-(After 8-9wBlood-groupantigensproduce) Blood-group antibody (IgG)Same blood-group antigens (again stimulus) Same pregnancy mother-anamnesticreaction-→Blood-group antibody ↑↑ (IgG)(cross placenta)Fetal or neonatalcirculation-hemolysisHemolytie disordes--- athogenesisABO incompatibility:Commonly Otype blood in the motheA or B type in fetus (AB?)Similar A or B antigen in natureNo AB type in mothes.noOtypeininfant50%of invasion in first pregnancyRh immunization-Rh antigen only in rhesus & human being-6 kinds of antigen, antigenicity in order D>E>C>c>e15'Class teaching- definition of Rh+ taking D antigen, eg DD.Ddthe overwhelming majority of Han people belong to Rh(+)- Frequency of Rh(-) varies in different racial groups-Usually not happen in first pregnancy involving Rh+ fetus:primary sensitization only need 0.5-1ml blood, when end stage pregnancy or ruptureof placenta-Rh(-)mother ,producing IgM and a little IgG, then delivery.When onceagain pregnancy Rh+fetus only 0.05-0.1ml blood anamnestic reactionMother with Rh+ also causes: DDee or Ddee in mothe+DdEeorDDEe ilinfants
[溶血病发病机制] Pathogenesy: Class teaching 5’ Blood-group antigens →(Primary stimulus)→ Pregnancy mother→(After 8-9w produce)→ Blood-group antibody (IgG) Same blood-group antigens →(again stimulus)→ Same pregnancy mother→anamnestic reaction→Blood-group antibody ↑↑ (IgG)→(cross placenta)→ Fetal or neonatal circulation→hemolysis Hemolytic disorders - pathogenesis Class teaching 15’ ABO incompatibility: Commonly O type blood in the mother A or B type in fetus (AB?) Similar A or B antigen in nature No AB type in mothers, no O type in infants 50% of invasion in first pregnancy Rh immunization: - Rh antigen only in rhesus & human being - 6 kinds of antigen, antigenicity in order D>E>C>c>e - definition of Rh+ : taking D antigen, eg DD.Dd - the overwhelming majority of Han people belong to Rh(+) - Frequency of Rh(-) varies in different racial groups - Usually not happen in first pregnancy involving Rh+ fetus: primary sensitization only need 0.5-1ml blood, when end stage pregnancy or rupture of placenta→Rh(-)mother,producing IgM and a little IgG, then delivery.When once again pregnancy Rh+ fetus only 0.05-0.1ml blood→ anamnestic reaction - Mother with Rh+ also causes: DDee or Ddee in mother → DdEe or DDEe in infants first st ↑ 8-9W second st ↑ time antibody Level of Ig M Ig G
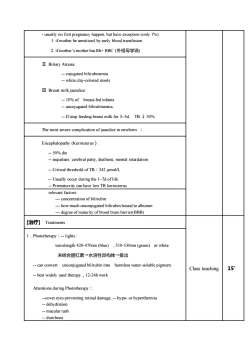
, but have exception (only1%)isuallynofirstpregnancy1.if motherbe sensitized byearlybloodtransfusior2. if mother's mother has Rh+ RBC (外祖母学说)II. Biliary Atresia-- cojugated bilirubinemia-whiteclay-colored stoolsI. Breast milk jaundice:-- 10% ofbreast-fed infants- uncojugated bilirubinemia-Ifstopfeedingbreastmilkfor3~5d,TB↓50%The most severe complication ofjaundice in newbornEncephalopathy (Kernicterus ) :-- 50% die--sequelaes:cerebralpalsy,dafssmentalretadatCritical threshold of TB : 342 μmol/L-- Usually occur during the 1-7d oflife-- Prematurrity can have low TB kernicterusrelevant factors-- concentration of bilirubin- how much unconjugated bilirubin bound to albumindegree of maturity of blood brain barrier(BBB)[治疗] Treatments1. Phototherapy : --lightswavelength 420-470nm (blue),510-530nm(green)or white未结合胆红素→水溶性异构体一排出canconvertunconjugated bilirubin intoharmless water-soluble pigment.15'Class teaching-- best widely used therapy , 12-24h workAttentions during Phototherapy-cover eyes preventing retinal damage, -- hypo-or hyperthermia--dehydration-- macular rashlarrhoea
- usually no first pregnancy happen, but have exception (only 1%) 1. if mother be sensitized by early blood transfusion 2. if mother’s mother has Rh+ RBC (外祖母学说) Ⅱ. Biliary Atresia: - cojugated bilirubinemia - white clay-colored stools Ⅲ. Breast milk jaundice: - 10% of breast-fed infants - uncojugated bilirubinemia. - If stop feeding breast milk for 3~5d, TB ↓ 50% The most severe complication of jaundice in newborn : Encephalopathy (Kernicterus): - 50% die - sequelaes: cerebral palsy, deafness, mental retardation - Critical threshold of TB:342 µmol/L - Usually occur during the 1~7d of life - Prematurrity can have low TB kernicterus relevant factors: - concentration of bilirubin - how much unconjugated bilirubin bound to albumin - degree of maturity of blood brain barrier(BBB) [治疗] Treatments Class teaching 15’ 1.Phototherapy:- lights : wavelength 420-470nm (blue) , 510-530nm (green) or white 未结合胆红素→水溶性异构体→排出 - can convert unconjugated bilirubin into harmless water-soluble pigment. - best widely used therapy,12-24h work Attentions during Phototherapy: -cover eyes preventing retinal damage, - hypo- or hyperthermia - dehydration - macular rash - diarrhoea
2 . Drugs therapy:(1) IVIG (intravenous immunoglobulin): may seal offthe combining of antigenand antibody, and prevent isoimmunization, may avoid the development of exchangetransfusio(2).glucose: provide enough raw material of conjugating bilirubin(3)albuminor plasma: increase binding decrease free bilirubin3. Exchange transfusionIndications :-- fetal hydropsy-- severe anemia--TB>20mg/dl (full-terrnfants)-at-riskinfantofkernicterusyolumof:-- wiceth ifant's volume (85m/kg)transfusion channel!via an umbilical venousvia a peripheral vein and an arterial line[病例及讨论] Case and discussiorGirl,3d12hofage,jaundicefor3d,becomemoreseriousgradually,G1P1full-termdelivered smoothly, 3. 2 kgof birthweightbilirubin (TB)level wasserumtotal22mg/dl (373 μmol/L), Hb180 g/L, urobilinogen(+) ,urobilirubin(-), normal stoolmother's blood type: O, DdEEccDiscussion5'father's blood type: A,DDEeccI , the best possible diagnosis?2. still what clinical symptoms and signs need to atention?3.further laboratory investigation for definite diagnose?4. how to treat ?
2.Drugs therapy: (1). IVIG (intravenous immunoglobulin): may seal off the combining of antigen and antibody, and prevent isoimmunization, may avoid the development of exchange transfusion. (2). glucose: provide enough raw material of conjugating bilirubin. (3). albumin or plasma: increase binding decrease free bilirubin 3.Exchange transfusion: Indications: - fetal hydropsy - severe anemia - TB>20mg/dl (full-term infants) - at-risk infant of kernicterus volume of donor blood needed: - twice the infant’s volume (85ml/kg) - transfusion channels: 1. via an umbilical venous 2. via a peripheral vein and an arterial line [病例及讨论] Case and discussion Discussion Girl, 3d12h of age,jaundice for 3d,become more serious gradually,G1P1,full-term, delivered smoothly, 3.2kg of birthweight,serum total bilirubin (TB) level was 22mg/dl (373 µmol/L), Hb180 g/L, urobilinogen(+),urobilirubin(-), normal stool. mother’s blood type: O,DdEEcc father’s blood type: A,DDEecc 1.the best possible diagnosis? 2.still what clinical symptoms and signs need to attention? 3.further laboratory investigation for definite diagnose? 4.how to treat? 5’
[结课】回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容布置见习的内容和要求QUESTIONS :What is the incidence of neonatal jaundice within I week after birth ?What are the features of bilirubin metabolism in neonates?What are the factors aggravating neonatal jaundice?3.What are differentiation points of physiological and pathological jaund ice?What are the main causes of infectious jaundice? Describe the individual characteristics?What are the main causes of non-infectious jaundice? Describe the individual characteristics?6Describe the clinical features of ABO incompatibility and Rh hemolysis.8What are the risk factors and clinical manifestations ofkermnicterusWhat are the serologic tests of hemolvtic disorders newborn. and how to analyze the results ?10. Describe the main approaches treating neonatal jaundice总结及补充修正授课年级备注总结及修正补充内容
[结课] 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容 布置见习的内容和要求 QUESTIONS: 1. What is the incidence of neonatal jaundice within 1 week after birth? 2. What are the features of bilirubin metabolism in neonates? 3. What are the factors aggravating neonatal jaundice? 4. What are differentiation points of physiological and pathological jaundice? 5. What are the main causes of infectious jaundice? Describe the individual characteristics? 6. What are the main causes of non-infectious jaundice? Describe the individual characteristics? 7. Describe the clinical features of ABO incompatibility and Rh hemolysis. 8. What are the risk factors and clinical manifestations of kernicterus. 9. What are the serologic tests of hemolytic disorders newborn, and how to analyze the results? 10. Describe the main approaches treating neonatal jaundice. 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十九章 自动临床生物化学分析仪的应用及评价.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 治疗药物浓度监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 妊娠的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 肿瘤标志物的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 神经系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 消化系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 内分泌疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 心血管系统疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 肾功能损伤的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 肝胆疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 营养状况的评估及的生物化学监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微量元素与维生素异常的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 Immunodeficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 Acute Convulsion in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)08 questions of immune system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)07 questions of urinological system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)09 questions of endocrine disorders.doc
