《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia
重庆医科大学儿科学教案讲课题目:Neonatal Septicemia 新生儿败血症教师:余加林授课题目TEACHINGTOPICNeonatalSepticemia新生儿败血症第几次课TIMES3rd教学方法METHODSClass teaching教学对象OBJECTIVESeven years students学时:TIME40x1minutes教学目标PURPOSEmaster the definitionand clinical manifestationsofneonatal septicemialearn principle of antibiotics selection教学重点和难点.clinical manifestationsPURPOSE/DIFFICULTIES2. key points of treatmentlaborratorytests4. principle of antibiotics selection教学内容的深化与拓宽1.Septicemia isthechiefcauseofneonatal death indevelopingcountries.The developmentsFurther study: the new conception of septicemia, and therelationshipandfndsepticem教学要求的英语单词SisspmiaPathgnacteriastaphylcci&oliGrouEnglish requirementsStreptococcus, GBS, Infectious gateway, Descending infection, Ascendinginn,iacboobranbr,pall,thay,judfhypothermia,temperature instability,poorhandling,hypoglycemiahyperglycemia, blood gas derangements, increased respiratory rate, apneagrunting, cyanosis实践性教学安排One teaching hourofclinical workshopClinical study 教材及参考资料沈晓明,王卫平。儿科学北京:人民卫生出版社,2008USED/2.TEXTBOOK杨锡强,易著文.儿科学。北京:人民卫生出版社,2008REFERENCESTaeusch HW, Ballard RA, Gleason CA. Elsevier Saunders: Avery'sdiseases of the newborn,8th edition,2005教具 TEACHING AIDSop教学程序Procedures详细见讲稿主要内容及安排(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配):
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 讲课题目:Neonatal Septicemia 新生儿败血症 教师: 余加林 授课题目 TEACHING TOPIC Neonatal Septicemia 新生儿败血症 第几次课 TIMES 3 rd 教学方法 METHODS Class teaching 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Seven years students 学时: TIME 40×1 minutes 教学目标 PURPOSE 1. master the definition and clinical manifestations of neonatal septicemia 2. learn principle of antibiotics selection 教学重点和难点 PURPOSE/ DIFFICULTIES 1.clinical manifestations 2.key points of treatment 3.laboratory tests 4.principle of antibiotics selection 教学内容的深化与拓宽 The developments 1.Septicemia is the chief cause of neonatal death in developing countries. 2.Further study: the new conception of septicemia, and the relationship and differences between sepsis and septicemia. 教学要求的英语单词 English requirements Sepsis, septicemia, Pathogenic Bacteria, staphylococci & E coli, Group B Streptococcus, GBS, Infectious gateway, Descending infection, Ascending infection, iatrogenic, blood-brain barrier, pallor, lethargy, jaundice, fever, hypothermia, temperature instability, poor handling, hypoglycemia / hyperglycemia, blood gas derangements, increased respiratory rate, apnea, grunting, cyanosis 实践性教学安排 Clinical study One teaching hour of clinical workshop. 教材及参考资料 TEXT BOOK USED/ REFERENCES 1. 沈晓明,王卫平. 儿科学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008 2. 杨锡强,易著文. 儿科学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008 3. Taeusch HW, Ballard RA, Gleason CA. Elsevier Saunders: Avery’s diseases of the newborn, 8th edition, 2005 教具 TEACHING AIDS ppt 教学程序 Procedures (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配): 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排
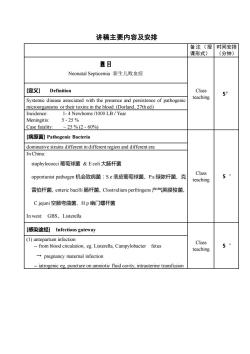
讲稿主要内容及安排备注(授时间安排课形式)(分钟)题目Neonatal Septicemia 新生儿败血症[定义]ClassDefinition5'teachingSystemic disease associated with the presence and persistence of pathogenicmicroorganisms or their toxins in the blood.(Dorland, 27th ed)Incidence:1-4Newborns/1000LB/YearMeningitis:5-25%Case fatality:25% (2 - 60%)[病原菌] Pathogenic Bacteriadominative strains dfferent in different region and diferent eraIn China:staphylococci葡萄球菌&Ecoli 大肠杆菌Class5opportunist pathogen 机会致病菌:S.e表皮葡萄球菌、P.a绿脓杆菌、克teaching雷伯杆菌、entericbacilli肠杆菌、Clostridium perfringens产气英膜梭菌、Cjejuni空肠弯曲菌、H.p 幽门螺杆菌Inwest: GBS、Listerella[感染途经 Infectiousgateway() antepartum infection Class5--from blood circulation, eg Listerella, Campylobacterfetusteaching+ pregnancy maternal infectiondcavatro
讲稿主要内容及安排 备注(授 课形式) 时间安排 (分钟) 题目 Neonatal Septicemia 新生儿败血症 Class teaching 5’ [定义] Definition Systemic disease associated with the presence and persistence of pathogenic microorganisms or their toxins in the blood. (Dorland, 27th ed) Incidence: 1- 4 Newborns /1000 LB / Year Meningitis: 5 - 25 % Case fatality: ~ 25 % (2 - 60%) [病原菌] Pathogenic Bacteria Class teaching 5‘ dominative strains different in different region and different era In China: staphylococci 葡萄球菌 & E coli 大肠杆菌 opportunist pathogen 机会致病菌:S.e 表皮葡萄球菌、P.a 绿脓杆菌、克 雷伯杆菌、enteric bacilli 肠杆菌、Clostridium perfringens 产气荚膜梭菌、 C.jejuni 空肠弯曲菌、H.p 幽门螺杆菌 In west: GBS、Listerella [感染途经] Infectious gateway Class teaching 5‘ (1) antepartum infection - from blood circulation, eg. Listerella, Campylobacter fetus → pregnancy maternal infection - iatrogenic eg, puncture on amniotic fluid cavity, intrauterine transfusion
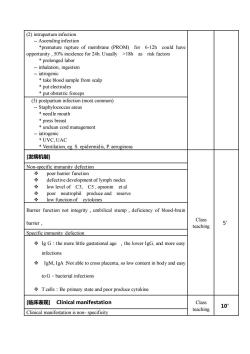
(2) intrapnfectio-- Ascending infection*premature rupture of membrane (PROM) for 6-12h could haveopportunity,50%incidencefor24h.Usually>18hasriskfactors* prolonged labor-- inhalation, ingestioniatrogenic* take blood sample from scalp* put electrodes* put obstetric forceps(3) postpartum infection (most common)Staphylococcus areus* needle mouth*pressbreasordmanagemenlatrogen* UVC,UAC* Ventilation, eg. S. epidermidis, P. aeruginosa[发病机制]Non-specific immunity defectionpoor barrier functiondefective development of lymph nodes+low level of C3, C5,opsonin et alneutrophil produce andreserve000low function of cytokinesBarrier function not integrity , umbilical stump , deficiency of blood-brainClassbarrier,5teachingSpecific immunity defection+ Ig G : the more ltle gastational age , the lower IgG, and more easyinfections*IgM、IgA Not able to cross placenta, so low content in body and easytoG- bacterial infections+ Tcells : Be primary state and poor produce cytokine[临床表现] Clinical manifestationClass10teachingClinical manifestation is non- specificity
(2) intrapartum infection - Ascending infection *premature rupture of membrane (PROM) for 6-12h could have opportunity , 50% incidence for 24h. Usually >18h as risk factors * prolonged labor - inhalation, ingestion - iatrogenic * take blood sample from scalp * put electrodes * put obstetric forceps (3) postpartum infection (most common) - Staphylococcus areus * needle mouth * press breast * unclean cord management - iatrogenic * UVC, UAC * Ventilation, eg. S. epidermidis, P. aeruginosa [发病机制] Class teaching 5’ Non-specific immunity defection ❖ poor barrier function ❖ defective development of lymph nodes ❖ low level of C3, C5 , opsonin et al ❖ poor neutrophil produce and reserve ❖ low function of cytokines Barrier function not integrity,umbilical stump,deficiency of blood-brain barrier, Specific immunity defection ❖ Ig G:the more little gastational age ,the lower IgG, and more easy infections ❖ IgM、IgA:Not able to cross placenta, so low content in body and easy to G-bacterial infections ❖ T cells:Be primary state and poor produce cytokine [临床表现] Clinical manifestation Class teaching 10’ Clinical manifestation is non- specificity

General featurespallor, lethargy jaundicefever, hypothermia, temperature instability (note 1/3 of confirmed sepsiscases are normothermic)poor handlinghypoglycaemia /hyperglycaemiablood gas derangements(including acidosis and lactate accumulation)Respiratory : increased respiratory rate, apnoea , grunting , cyanosisCVS : tachycardia , bradycardic episodes , poor perfusion, hypotensionCutaneous : petechiae , bruising , bleeding from puncture sitesGIT : poor feeding , vomiting , abdominal distension , feed intolerance ,bilious aspirates /vomits , loose stoolsCNS : lethargy, irritability , seizures[实验室检查]InvestigationsI. bacteriology study1.Blood culture (mandatory)Classtake sample underaseptic techniquebeforeadministration of antibiotics10'as soon as possibleteaching- anaerobic culture p.r.n if GI perforation-L-type bacterial culture p.rn if penicillins or cephalosporins exposuresamplefromgastric juice&external auditorycanal for smear orculturewithin 1 hour of life if antepartum infection suspected- samples for culture include CSE, serous cavityfluid,catherter engBlood culture , CSF culture from Lumber puncture , supper pubicaspiation,SPA,Swab fromextemalauditory canals2. special antigen & DNA-forGBS andKantigen ofE colicounter immunoelectrophoresislatex agglutination test, ELISA- polymerase chain reaction(PCR) →16S rRNADNAprobe
General features: pallor, lethargy, jaundice fever, hypothermia, temperature instability (note 1/3 of confirmed sepsis cases are normothermic) poor handling hypoglycaemia / hyperglycaemia blood gas derangements(including acidosis and lactate accumulation) Respiratory:increased respiratory rate,apnoea ,grunting,cyanosis CVS:tachycardia ,bradycardic episodes,poor perfusion,hypotension Cutaneous:petechiae ,bruising,bleeding from puncture sites GIT:poor feeding,vomiting,abdominal distension,feed intolerance, bilious aspirates /vomits,loose stools CNS:lethargy,irritability,seizures [实验室检查] Investigations Class teaching 10’ Ⅰ. bacteriology study 1. Blood culture (mandatory) - take sample under aseptic technique before administration of antibiotics as soon as possible - anaerobic culture p.r.n if GI perforation - L-type bacterial culture p.r.n if penicillins or cephalosporins exposure - sample from gastric juice & external auditory canal for smear or culture within 1 hour of life if antepartum infection suspected - samples for culture include CSF, serous cavity fluid, catherter end Blood culture , CSF culture from Lumber puncture , supper pubic aspiration, SPA,Swab from external auditory canals 2. special antigen & DNA - for GBS and K1 antigen of E coli →counter immunoelectrophoresis, latex agglutination test, ELISA - polymerase chain reaction(PCR) →16S rRNA - DNA probe
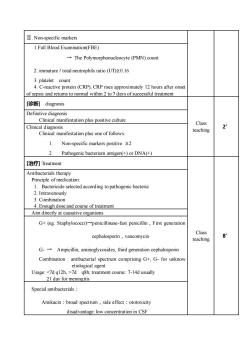
II. Non-specific markers1.Full Blood Examination(FBE)→ The Polymorphonucleocyte (PMN) count2. immature / total neutrophils ratio (1/1)≥0.163. platelet count4. C-reactive protein (CRP), CRP rises approximately 12 hours after onsetof sepsis and returns to normal within 2 to 7 days of successful treatment[诊断] diagnosisDefinitive diagnosisClinical manifestation plus positive cultureClass2'Clinical diagnosisteachingClinical manifestation plus one of follows:Non-specific markers positive ≥2Pathogenic bacterium antigen(+) or DNA(+)[治疗] TreatmentAntibacterials therapyPrinciple of medicationBactericide selected accord ing to pathogenic bacteria2. Intravenously3. Combination4. Enough dose and course of treatmentAim directly at causative organismsG+ (eg. Staphylococci)penicillinase-fast penicillin,First generationClass8'cephalosporin,vancomycinteachingG- -→Ampicillin, aminoglycosides, third generation cephalosporinCombination : antibacterial spectrum comprising G+, G-for unknowetiological agent Usage: 7d q8h; treatment course: 7-14d usually21dayformeningitisSpecial antibacterials :Amikacin : broad spectrum , side effect : ototoxicitydisadvantage: low concentration in CSF
Ⅱ. Non-specific markers 1.Full Blood Examination(FBE) → The Polymorphonucleocyte (PMN) count 2. immature / total neutrophils ratio (I/T)≥0.16 3. platelet count 4. C-reactive protein (CRP), CRP rises approximately 12 hours after onset of sepsis and returns to normal within 2 to 7 days of successful treatment [诊断] diagnosis Class teaching 2’ Definitive diagnosis Clinical manifestation plus positive culture Clinical diagnosis Clinical manifestation plus one of follows: 1. Non-specific markers positive ≥2 2. Pathogenic bacterium antigen(+) or DNA(+) [治疗] Treatment Class teaching 8’ Antibacterials therapy Principle of medication: 1. Bactericide selected according to pathogenic bacteria 2. Intravenously 3. Combination 4. Enough dose and course of treatment Aim directly at causative organisms G+ (eg. Staphylococci)→penicillinase-fast penicillin,First generation cephalosporin,vancomycin G- → Ampicillin, aminoglycosides, third generation cephalosporin Combination : antibacterial spectrum comprising G+, G- for unknow etiological agent Usage: 7d q8h; treatment course: 7-14d usually 21 day for meningitis Special antibacterials: Amikacin:broad spectrum,side effect:ototoxicity disadvantage: low concentration in CSF

CeftazidimeP. aeruginosa meningitis Metronidazole -anaerobicbacteriumImipenem+Cilastatin (Tienam) : broad spectrummaintenance therapyIntravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) mainly forprematuresevere infectionMaintain homeostasis: -correct acidosis- electrolyte balance- smooth microcirculation[结课 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容布置见习的内容和要求QUESTIONS :What atoptwo bacteria causing neonatal septicemia in our country?What is the first line of antibiotics treating septicemia complicated with pyocyanic meningitis?Whapathogenscausing neonatalsepticemiacaused byprepartum infectionWhat is the mfneonatal septicemia?licationWhat is the antibiotics principle of neonatal septicemia?What arethe infetiopathways inolvingnonatal septicmia?总结及补充修正授课年级总结及修正补充内容备注
Ceftazidime→P. aeruginosa meningitis Metronidazole →anaerobic bacterium Imipenem+Cilastatin (Tienam) : broad spectrum maintenance therapy Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) mainly for - premature - severe infection Maintain homeostasis: - correct acidosis - electrolyte balance - smooth microcirculation [结课] 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容 布置见习的内容和要求 QUESTIONS: What are the top two bacteria causing neonatal septicemia in our country? What is the first line of antibiotics treating septicemia complicated with pyocyanic meningitis? What are the two common pathogens causing neonatal septicemia caused by prepartum infection? What is the most common complication of neonatal septicemia? What is the antibiotics principle of neonatal septicemia? What are the infection pathways involving neonatal septicemia? 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十九章 自动临床生物化学分析仪的应用及评价.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 治疗药物浓度监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 妊娠的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 肿瘤标志物的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 神经系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 消化系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 内分泌疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 心血管系统疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 肾功能损伤的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 肝胆疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 营养状况的评估及的生物化学监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微量元素与维生素异常的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 骨代谢紊乱及相关元素的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 Immunodeficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 Acute Convulsion in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)08 questions of immune system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)07 questions of urinological system.doc
