《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis
重庆医科大学儿科学教案感染性疾病一结核性脑膜炎教师:许红梅授课题目TEACHINGTOPICTuberculosis Meningitis第几次课TIMES3rd教学方法METHODSClass teaching教学对象OBJECTIVESeven years students in Grade 2007学时:TIME80minutes授课目的PURPOSEStudy Tuberculosis Meningitis to know how to diagnosis, treat thisdisease and the prognosis本课重点EMPHASISThe clinical manifestations.labs studies, diagnosis and treatment本课难点DIFFICULTIESPathophysiology.pathology.early diagnosis深化与拓宽Characteristics of pediatric TBMThe developments英语要求All in EnglishEnglish requirements践性教学安排Clinically, combined with the patients to leam the manifestationsClinical studyand treatment; To discuss the diagnosis and diferential diagnosisand treatment教材TEXTBOOKUSEDShen Xiaoming, Wang Weipin, Chief Editor,《PEDIATRICS》7thEdition,People's Health Publication,2008及参考资料 REFERENCES1.胡亚美,江载芳.诸福棠实用儿科学.第7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,20022.Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook ofpediatrics.16th ed. Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B.Saunders, 2001PPT教具TEACHINGAIDS教具PPT教学程序Procedures详细见讲稿主要内容及安排(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分Details see the contents and配arrangementThe contents and Arrangements
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 感染性疾病-结核性脑膜炎 教师:许红梅 授课题目TEACHING TOPIC Tuberculosis Meningitis 第几次课 TIMES 3rd 教学方法 METHODS Class teaching 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Seven years students in Grade 2007 学时: TIME 80 minutes 授课目的 PURPOSE Study Tuberculosis Meningitis to know how to diagnosis, treat this disease and the prognosis 本课重点 EMPHASIS The clinical manifestations, labs studies, diagnosis and treatment 本课难点 DIFFICULTIES Pathophysiology, pathology, early diagnosis 深化与拓宽 The developments Characteristics of pediatric TBM 英语要求 English requirements All in English 践性教学安排 Clinical study Clinically, combined with the patients to learn the manifestations and treatment; To discuss the diagnosis and differential diagnosis and treatment. 教材 TEXT BOOK USED Shen Xiaoming, Wang Weipin, Chief Editor,《PEDIATRICS》7th Edition,People’s Health Publication,2008 及参考资料 REFERENCES 1. 胡亚美,江载芳. 诸福棠实用儿科学.第 7 版.北京:人民卫生出版 社,2002 2. Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook of pediatrics.16th ed. Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B. Saunders, 2001 教具 TEACHING AIDS PPT 教具 PPT 教学程序 Procedures (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分 配) 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排 Details see the contents and arrangement The contents and Arrangements
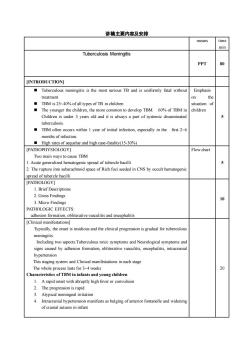
讲稿主要内容及安排timemeanminTuberculosis MeningitisPPT80[INTRODUCTION]Tuberculous meningitis is the most serious TB and is uniformly fatal withoutEmphasisthereatmen0TBM is 25~40% of alltypes of TB in childresituation ofThe younger the chidren, the more common to develop TBM60% of TBM inchildrenChildren is under 3 years old and it is always a part of systemic disseminatedtuberculosisTBM often occurs within 1 year of initial infection, especially in thefirst 2~6onths of infectionHigh rates of sequelae and high case-fatality(15-30%)[PATHOPHYSIOLOGY)Flow chartTwo main ways to cause TBM1. Acute generalized hematogenic spread of tubercle bailli2. The rupture into subarachnoid space of Rich foci seeded in CNS by occult hematogenicspread of tubercle bacill[PATHOLOGY]1.Brief Descriptions2. Gross Findings103. Micro FindingPATHOLOGIC EFFECTSadhesion formation,obliterativevasculitis and encephalitis[Clinical manifestationsTpcallythoetiidoundthincalpgrssinigradualbruouneningitIncludingTuberculous toxic symptoms and Neurological symptoms andsigns caused by adhesion formation, obliterativevasculitis, encephalitis, intracranialhypertensionThis staging system and Clinicalmanifestations ineach stageThe whole process lasts for 3-~4 weeks20Characcteristics of TBM in infants and young childrenArapid onset with abruptly highfever or convulsionThe progression is rapid3Atypical meningeal irritationIntracranial hypertension manifests as bulging of anterior fontanelle and wideningcranial sutuures in infant
讲稿主要内容及安排 means time min Tuberculosis Meningitis PPT 80 [INTRODUCTION] ◼ Tuberculous meningitis is the most serious TB and is uniformly fatal without treatment ◼ TBM is 25~40% of all types of TB in children ◼ The younger the children, the more common to develop TBM. 60% of TBM in Children is under 3 years old and it is always a part of systemic disseminated tuberculosis. ◼ TBM often occurs within 1 year of initial infection, especially in the first 2~6 months of infection. ◼ High rates of sequelae and high case-fatality(15-30%) Emphasis on the situation of children 5 [PATHOPHYSIOLOGY] Two main ways to cause TBM 1. Acute generalized hematogenic spread of tubercle bacilli 2. The rupture into subarachnoid space of Rich foci seeded in CNS by occult hematogenic spread of tubercle bacilli Flow chart 5 [PATHOLOGY] 1. Brief Descriptions 2. Gross Findings 3. Micro Findings PATHOLOGIC EFFECTS: adhesion formation, obliterative vasculitis and encephalitis 10 [Clinical manifestations] Typically, the onset is insidious and the clinical progression is gradual for tuberculous meningitis. Including two aspects:Tuberculous toxic symptoms and Neurological symptoms and signs caused by adhesion formation, obliterative vasculitis, encephalitis, intracranial hypertension This staging system and Clinical manifestations in each stage The whole process lasts for 3~4 weeks Characteristics of TBM in infants and young children 1. A rapid onset with abruptly high fever or convulsion 2. The progression is rapid 3. Atypical meningeal irritation 4. Intracranial hypertension manifests as bulging of anterior fontanelle and widening of cranial sutures in infant 20
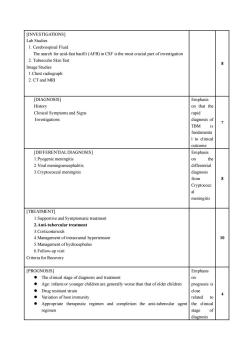
[INVESTIGATIONSLab Studies1. Cerebrospinal FluidThe search for acid-fast bacilli (AFB) in CSF is the most crucial part of investigation2. Tuberculin Skin Test8Image Studies1.Chest radiograph:2. CT and MRI [DIAGNOSIS]EmphasisHistoryon that theClinical Symptoms and SignsrapidInvestigationsdiagnosis ofTBMisfundamentaI to clinicaloutcome[DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS]Emphasis1.Pyogenic meningitisothe2.Viral meningoencephalitisdifferential3.Cryptococcal meningitisdiagnosisfromCryptococoalmeningitis[TREATMENT]1.Supportive and Symptomatic treatment2.Anti-tubercular treatment3.Corticosteriods4.Management ofintracranial hypertension105.Management ofhydrocephalus6.Follow-up visitCriteria for Recovery[PROGNOSIS]EmphasisoTheclinicAge: infants or younger children are generally worsethan that ofolder childrenprognosis isDrug resistant straincloserelatedtoVariation of host immunityagent the clinical.Appropriate therapeutic regimen and completion the anti-tubercularregimenstagediagnosis
[INVESTIGATIONS] Lab Studies 1. Cerebrospinal Fluid The search for acid-fast bacilli (AFB) in CSF is the most crucial part of investigation 2. Tuberculin Skin Test Image Studies 1.Chest radiograph: 2. CT and MRI 8 [DIAGNOSIS] History Clinical Symptoms and Signs Investigations Emphasis on that the rapid diagnosis of TBM is fundamenta l to clinical outcome 7 [DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS] 1.Pyogenic meningitis 2.Viral meningoencephalitis 3.Cryptococcal meningitis Emphasis on the differential diagnosis from Cryptococc al meningitis 8 [TREATMENT] 1.Supportive and Symptomatic treatment 2.Anti-tubercular treatment 3.Corticosteriods 4.Management of intracranial hypertension 5.Management of hydrocephalus 6.Follow-up visit Criteria for Recovery 10 [PROGNOSIS] ⚫ The clinical stage of diagnosis and treatment ⚫ Age: infants or younger children are generally worse than that of older children ⚫ Drug resistant strain ⚫ Variation of host immunity ⚫ Appropriate therapeutic regimen and completion the anti-tubercular agent regimen Emphasis on prognosis is close related to the clinical stage of diagnosis 4
andtreatment[结课]3回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容,布置见习的内容和要求Review QAWhofTubteristicsofTuberculosis Meningitis ininfants and youngchildrenWhat aretheclinical charaoWhat is the characteristics ofCSF changes in Tuberculosis Meningitis?总结及补充修正授课年级总结及修正补充内容备注2005级增加病理改变图片2006级增加发病机理的流程图2007级增加脑脊液循环图及我院结核性脑膜炎的资料
and treatment [结课] 3 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容, 布置见习的内容和要求 Review QA: 1. What are the clinical features of stage 1 of Tuberculosis Meningitis? 2. What are the clinical characteristics of Tuberculosis Meningitis in infants and young children? 3. What is the characteristics of CSF changes in Tuberculosis Meningitis? 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注 2005 级 增加病理改变图片 2006 级 增加发病机理的流程图 2007 级 增加脑脊液循环图及我院结核性脑膜炎的资料
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十九章 自动临床生物化学分析仪的应用及评价.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 治疗药物浓度监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 妊娠的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 Immunodeficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 Acute Convulsion in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)08 questions of immune system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)07 questions of urinological system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)09 questions of endocrine disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)10 questions of infectious diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)06 questions of nervous system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)03 questions of respiratory diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)04 questions of circulatory system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)05 questions of blood disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)02 questions of neonatal diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)01 questions of children healthcare.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 nephrotic syndrome-2.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 anute nepheritis-1.doc
