《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism
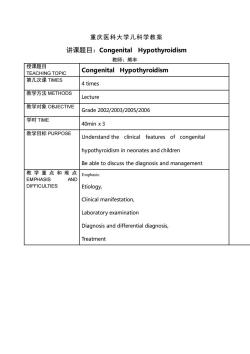
重庆医科大学儿科学教案讲课题目:Congenital Hypothyroidism教师:熊丰授课题目Congenital HypothyroidismTEACHING TOPIC第几次课TIMES4 times教学方法METHODSLecture教学对象OBJECTIVEGrade 2002/2003/2005/2006学时TIME40min x 3教学目标PURPOSEUnderstand the clinical features of congenitalhypothyroidism in neonates and childrenBe able to discuss the diagnosis and management教学重点和难点 EmphasisEMPHASIS ANDDIFFICULTIESEtiology,Clinical manifestation,Laboratory examinationDiagnosis and differential diagnosis,Treatment
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 讲课题目:Congenital Hypothyroidism 教师:熊丰 授课题目 TEACHING TOPIC Congenital Hypothyroidism 第几次课 TIMES 4 times 教学方法 METHODS Lecture 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Grade 2002/2003/2005/2006 学时 TIME 40min x 3 教学目标 PURPOSE Understand the clinical features of congenital hypothyroidism in neonates and children Be able to discuss the diagnosis and management 教学重点和难点 EMPHASIS AND DIFFICULTIES Emphasis: Etiology, Clinical manifestation, Laboratory examination Diagnosis and differential diagnosis, Treatment
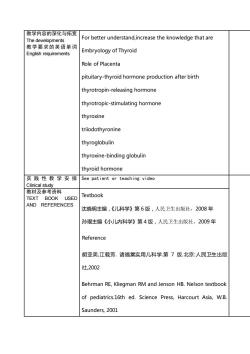
教学内容的深化与拓宽For better understand,increase the knowledge that areThe developments教学要求的英语单词Embryology of ThyroidEnglish requirementsRole of Placentapituitary-thyroid hormone production after birththyrotropin-releasing hormonethyrotropic-stimulating hormonethyroxinetriodothyroninethyroglobulinthyroxine-binding globulinthyroid hormone实践性教学安排See patient or teachingvideoClinical study教材及参考资料TextbookTEXT BOOK USEDAND REFERENCES沈晓明主编,《儿科学》第6版,人民卫生出版社,2008年孙琨主编《小儿内科学》第4版,人民卫生出版社,2009年Reference胡亚美,江载芳.诸福棠实用儿科学.第7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2002Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbookof pediatrics.16th ed. Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B.Saunders, 2001
教学内容的深化与拓宽 The developments 教学要求的英语单词 English requirements For better understand,increase the knowledge that are Embryology of Thyroid Role of Placenta pituitary-thyroid hormone production after birth thyrotropin-releasing hormone thyrotropic-stimulating hormone thyroxine triiodothyronine thyroglobulin thyroxine-binding globulin thyroid hormone 实践性教学安排 Clinical study See patient or teaching video 教材及参考资料 TEXT BOOK USED AND REFERENCES Textbook 沈晓明主编,《儿科学》第 6 版,人民卫生出版社,2008 年 孙琨主编《小儿内科学》第 4 版,人民卫生出版社,2009 年 Reference 胡亚美,江载芳. 诸福棠实用儿科学.第 7 版.北京:人民卫生出版 社,2002 Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook of pediatrics.16th ed. Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B. Saunders, 2001
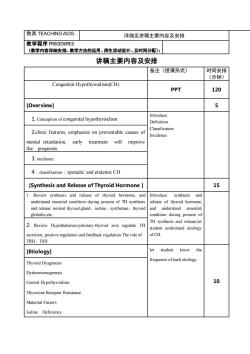
教具TEACHINGAIDS详细见讲稿主要内容及安排教学程序PROCEDURES(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配):讲稿主要内容及安排时间安排备注(授课形式)(分钟)Congenital Hypothyroid ism(CH)PPT1205[Overview]Introduce1. Conception of congenital hypothyroidismDefinitionClassification2.clinic features, emphasize on preventable causes ofIncidence:mental retardation,treatmentwillimproveearlythe prognosis3. incidencesporadic and endemic CH4.classificatio[Synthesis and Release of Thyroid Hormone ] 151.Review synthesis and release of thyroid hormone, andIntroduce:synthesisandunderstand essential condition during process of TH synthesisrelease of thyroid hormone,essentialand release:normal thyroid gland、iodine、synthetase、thyroidunderstandTarcondition during process ofglobulin,etcTH synthesis and release,let2. Review Hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis regulatestudent understand etiologysecreionsitivgulatnnfeedbackgulationoofCHTRH、TSHlet studentknowthe[Etiology]frequenceofeachetiologyThyroid DysgenesisDyshormonogenesis10Central HypothyroidismThyroxine Receptor RssistanceMaternal Factorslodine Defiency
教具 TEACHING AIDS 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排 教学程序 PROCEDURES (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分配): 讲稿主要内容及安排 备注(授课形式) 时间安排 (分钟) Congenital Hypothyroidism(CH) PPT 120 [Overview] 5 1. Conception of congenital hypothyroidism Introduce: Definition Classification Incidence 2.clinic features, emphasize on preventable causes of mental retardation, early treatment will improve the prognosis. 3. incidence 4.classification:sporadic and endemic CH [Synthesis and Release of Thyroid Hormone ] 15 1. Review synthesis and release of thyroid hormone, and understand essential condition during process of TH synthesis and release: normal thyroid gland、iodine、synthetase、thyroid globulin,etc. Introduce: synthesis and release of thyroid hormone, and understand essential condition during process of TH synthesis and release,let student understand etiology of CH. 2. Review Hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis regulate TH secretion, positive regulation and feedback regulation.The role of TRH、TSH. [Etiology] let student know the frequence of each etiology. 10 Thyroid Dysgenesis Dyshormonogenesis Central Hypothyroidism Thyroxine Receptor Rssistance Maternal Factors Iodine Deficiency
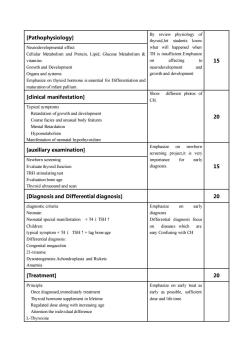
Byreview physiology[Pathophysiology]thyroid,letstudentsknowWhat will happened whenNeurodevelopmental effectTH is insufficient.EmphasizeCellular Metabolism and Protein, Lipid, Glucose Metabolism &vitaminaffecting15Growth and Developmentneurodevelopmentancgrowthand developmentOrgans and systemsEmphasizeon thyroidhormone isessentialforDifferentiationandmaturation of infant palliumShowdifferent photos of[clinical manifestation]CH.Typical symptomsRetardation of growth and development20Coarse facies and unusual body featuresMental RetardationHypometabolismManifestation of neonatal hypothyroidismEmphasize on newborn[auxiliary examination]seceening projetit is veryNewborn screeningimportanceearlyfor15Evaluate thyroid functiondiagnosis.TRH stimulating testEvaluation bone ageThyroid ultrasound and scan[Diagnosis and Differential diagnosis]20diagnostic criteriaEmphasizeonearlyNeonate:diagnosisNeonatal special manifestation +T4 ↓TSHtDifferential diagnosis focusChildren:on diseases whicharetypical symptom + T4 ↓ TSH t + lag bone ageeasy Confusing with CHDifferential diagnosis:Congenital megacolon21-trisomeDysosteogenesis:Achondroplasia and RicketsAnaemi20[Treatment]PrincipleEmphasize on early treat asOnce diagnosed,immediately treatmentearly as possible, sufficientThyroid hormone supplement in lifetimedose and lifetimeRegulated dose along with increasing ageAttentiontheindividualdifferenceL-Thyroxine
[Pathophysiology] By review physiology of thyroid,let students know what will happened when TH is insufficient.Emphasize on affecting to neurodevelopment and growth and development 15 Neurodevelopmental effect Cellular Metabolism and Protein, Lipid, Glucose Metabolism & vitamins Growth and Development Organs and systems Emphasize on thyroid hormone is essential for Differentiation and maturation of infant pallium. [clinical manifestation] Show different photos of CH. 20 Typical symptoms Retardation of growth and development Coarse facies and unusual body features Mental Retardation Hypometabolism Manifestation of neonatal hypothyroidism [auxiliary examination] Emphasize on newborn screening project,it is very importance for early diagnosis. 15 Newborn screening Evaluate thyroid function TRH stimulating test Evaluation bone age Thyroid ultrasound and scan [Diagnosis and Differential diagnosis] 20 diagnostic criteria Neonate: Neonatal special manifestation + T4↓TSH↑ Children: typical symptom + T4↓ TSH↑+ lag bone age Differential diagnosis: Congenital megacolon 21-trisome Dysosteogenesis:Achondroplasia and Rickets Anaemia Emphasize on early diagnosis Differential diagnosis focus on diseases which are easy Confusing with CH [Treatment] 20 Principle Once diagnosed,immediately treatment Thyroid hormone supplement in lifetime Regulated dose along with increasing age Attention the individual difference L-Thyroxine Emphasize on early treat as early as possible, sufficient dose and life time
Replacement as soon as possibleDose ofT4 changes with age:newborn 10 to15 μg/kg.d,bid orqdInfant: 6-8ug/kg.d, bid or qdlater in childhood 3-5 μg/kg, bid orqdGoal: serum T4 upper half of normal rangeDo NOT give with Iron, soy or fibreFollow-upFollow-up initially:2/52 w-4/52w:Every 1-2 mo during the first 6 mo:Every 3-4 mo between 6 mo and 3 y of age;Every 6-12 mo from 3y of age to end of growth[结课]Summarize the content of this lesson , repeat the emphasis.Give the content of review after the lessonReview points :1)Etiology and pathophysiology of CH ?2)Clinic feature of CH in children and neonate3)Why we must do neonatal screening? And howto do that? How to evaluation?4Diagnosis and dfferent diagnosis ofCH5) Treatment ofCH总结及补充修正授课年级总结及修正补充内容备注Grade 2002Increase the anaemia as differential diagnosisGrade 2003increase the knowledge ofEmbryology of ThyroidGrade 2005Increase the role of PlacentaGrade2006Increase pituitary-thyroid hormone production after birth
Replacement as soon as possible Dose of T4 changes with age: newborn 10 to 15 μg/kg.d , bid or qd Infant: 6-8ug/kg.d, bid or qd later in childhood 3-5 μg/kg, bid or qd Goal: serum T4 upper half of normal range Do NOT give with Iron, soy or fibre Follow-up Follow-up initially: 2/52 w-4/52 w; Every 1-2 mo during the first 6 mo; Every 3-4 mo between 6 mo and 3 y of age; Every 6-12 mo from 3y of age to end of growth. [结课] Summarize the content of this lesson,repeat the emphasis. Give the content of review after the lesson Review points: 1) Etiology and pathophysiology of CH ? 2) Clinic feature of CH in children and neonate 3) Why we must do neonatal screening? And how to do that? How to evaluation? 4) Diagnosis and different diagnosis of CH. 5) Treatment of CH. 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注 Grade 2002 Increase the anaemia as differential diagnosis. Grade 2003 increase the knowledge of Embryology of Thyroid, Grade 2005 Increase the role of Placenta Grade 2006 Increase pituitary-thyroid hormone production after birth
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 Immunodeficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 Acute Convulsion in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)08 questions of immune system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)07 questions of urinological system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)09 questions of endocrine disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)10 questions of infectious diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)06 questions of nervous system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)03 questions of respiratory diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)04 questions of circulatory system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)05 questions of blood disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)02 questions of neonatal diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)01 questions of children healthcare.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 nephrotic syndrome-2.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 anute nepheritis-1.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)08 diarrhea.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)03 congenital heart disease-VSD.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)04 iron deficiency anemia.doc
