《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy
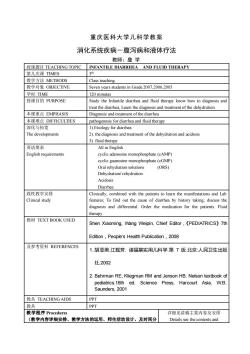
重庆医科大学儿科学教案消化系统疾病一腹泻病和液体疗法教师:詹学授课题目 TEACHING TOPICINFANTILE DIARRHEA AND FLUID THERAPY第几次课TIMES3th教学方法METHODSClass teaching教学对象OBJECTIVESeven years students in Grade 2007,2006,2005学时:TIME120 minutes授课目的PURPOSEStudy the Infantile diarrhea and fluid therapy know how to diagnosis andtreat the diarrhea, Learn the diagnosis and treatment of the dehydration本课重点EMPHASISDiagnosis and treatment of the diarrhea本课难点DIFFICULTIESpathogenesis for diarrhea and fluid therapy深化与拓宽1).Etiology for diarrheaThe developments2).thediagnosisandtreatmentofthedehydrationandacidosis3). fluid therapy英语要求All in EnglishEnglish requirementscyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)cyelic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)Oral rehydration solutions(ORS) Dehydration/rehydrationAcidosisDiarrhea践性教学安排Clinically, combined with the patients to learn the manifestations and Lab Clinical studyfeaturesTofndoutthecauseofdiarheabyhistorytakingdiscussthediagnosis and differential. Order the medication for the patients. Fluidtherapy教材TEXTBOOKUSEDShen Xiaoming, Wang Weipin, Chief Editor ,《PEDIATRICS》 7thEdition,People's Health Publication,2008及参考资料REFERENCES1.胡亚美,江载芳.诸福棠实用儿科学.第7版北京:人民卫生出版社,20022. Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook ofpediatrics.16thed.SciencePress,Harcourt Asia,W.B.Saunders, 2001教具TEACHINGAIDSPPT教具PPT教学程序Procedures详细见讲稿主要内容及安排(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分Details see the contents and
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 消化系统疾病-腹泻病和液体疗法 教师:詹 学 授课题目 TEACHING TOPIC INFANTILE DIARRHEA AND FLUID THERAPY 第几次课 TIMES 3 th 教学方法 METHODS Class teaching 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Seven years students in Grade 2007,2006,2005 学时: TIME 120 minutes 授课目的 PURPOSE Study the Infantile diarrhea and fluid therapy know how to diagnosis and treat the diarrhea, Learn the diagnosis and treatment of the dehydration 本课重点 EMPHASIS Diagnosis and treatment of the diarrhea 本课难点 DIFFICULTIES pathogenesis for diarrhea and fluid therapy 深化与拓宽 The developments 1).Etiology for diarrhea 2). the diagnosis and treatment of the dehydration and acidosis 3). fluid therapy 英语要求 English requirements All in English cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) Dehydration/ rehydration Acidosis Diarrhea 践性教学安排 Clinical study Clinically, combined with the patients to learn the manifestations and Lab features; To find out the cause of diarrhea by history taking; discuss the diagnosis and differential. Order the medication for the patients. Fluid therapy 教材 TEXT BOOK USED Shen Xiaoming, Wang Weipin, Chief Editor,《PEDIATRICS》7th Edition,People’s Health Publication,2008 及参考资料 REFERENCES 1. 胡亚美,江载芳. 诸福棠实用儿科学.第 7 版.北京:人民卫生出版 社,2002 2. Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook of pediatrics.16th ed. Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B. Saunders, 2001 教具 TEACHING AIDS PPT 教具 PPT 教学程序 Procedures (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排 Details see the contents and
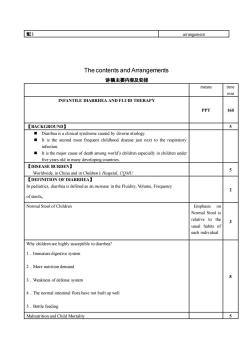
[配)rrangThe contents and Arrangements讲稿主要内容及安排timemeansminINFANTILE DIARRHEA AND FLUID THERAPYPPT160【BACKGROUND】5Darheaisaclinicalsyndrome caused by diverse etiology国It is the second most frequent childhood disease just next to the respiratoryinfectionIt is the major cause of death among world's children especially in children underfiveyears old in manydeveloping countries.[【DISEASE BURDEN】5Worldwide, in China and in Children's Hospital, COMUDEFINITION OF DIARRHEA】In pediatrics,diarrhea is defined as an increasein theFluidity,Volume,Frequency2of stools.Normal Stool of ChildrenEmphasis onNormal Stool isrelative to theusual habits ofeach individualWhy children are highly susceptible to diarrhea?1.Immature digestive system2 . More nutrition demand83. Weakness of defense system4.Thenormal intestinal flora have not built up well5 . Botl feedingMalnutrition and Child Mortality5
配) arrangement The contents and Arrangements 讲稿主要内容及安排 means time min INFANTILE DIARRHEA AND FLUID THERAPY PPT 160 【BACKGROUND】 5 ◼ Diarrhea is a clinical syndrome caused by diverse etiology. ◼ It is the second most frequent childhood disease just next to the respiratory infection. ◼ It is the major cause of death among world’s children especially in children under five years old in many developing countries. 【DISEASE BURDEN】 Worldwide, in China and in Children’s Hospital, CQMU 5 【DEFINITION OF DIARRHEA】 In pediatrics, diarrhea is defined as an increase in the Fluidity, Volume, Frequency of stools。 2 Normal Stool of Children Emphasis on Normal Stool is relative to the usual habits of each individual 3 Why children are highly susceptible to diarrhea? 1.Immature digestive system 2.More nutrition demand 3.Weakness of defense system 4.The normal intestinal flora have not built up well 5.Bottle feeding 8 Malnutrition and Child Mortality 5
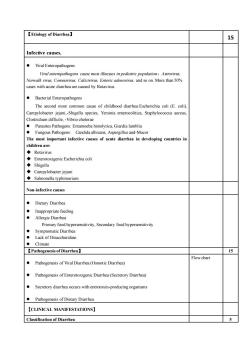
【Etiologyof Diarrhea】15Infective causesViral EnteropathogeniralathogeipeoropuNonwalk virus, Coronavirus, Calicivirus, Enteric adenovirus, and so on. More than 5%cases with acute diarrhea are caused by RotavirusBacterial EnteropathogensThe second most common cause of childhood diarrhea:Escherichia coli (E. coli)Campylobacter jejuniShigella species, Yersinia enterocolitica, Staphylococcus aureus,Clostridium difficile, -Vibrio choleraeParasites Pathogens: Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lambliaFungous PathogensCandida albicans, Aspergillus and-MucorThe most important infective causes of acute diarrhea in developing countries inchildren are: RotavirusEnterotoxigenic Escherichia coli· Shigella Campylobacter jejuni Salmonella typhimuriunNon-infectivecauseDietaryDiarrhea.Inappropriate feedingAllergic DiarrhePrmaryoodhypersensitivityeondaryoodhyerensitiviySymptomatic Diarrhea.Lack of Disaccharidase·Climate15【Pathogenesis ofDiarrhea】Flow charts of Viral Diarrhea (Osmotic Diarhea)PathogPathogenesis of Enterotoxigenic Diarrhea (SecretoryDiarrhea)Secretory diarrhea occurs with entrotoxin-producing organisms.Pathogenesis of Dietary Diarrhea[CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS]Classification of Diarrhe5
【Etiology of Diarrhea】 15 Infective causes. ⚫ Viral Enteropathogens Viral enteropathogens cause most illnesses in pediatric population:Astrovirus, Norwalk virus, Coronavirus, Calicivirus, Enteric adenovirus, and so on. More than 50% cases with acute diarrhea are caused by Rotavirus. ⚫ Bacterial Enteropathogens The second most common cause of childhood diarrhea:Escherichia coli (E. coli), Campylobacter jejuni,-Shigella species, Yersinia enterocolitica, Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium difficile, -Vibrio cholerae ⚫ Parasites Pathogens: Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia lamblia ⚫ Fungous Pathogens: Candida albicans, Aspergillus and-Mucor The most important infective causes of acute diarrhea in developing countries in children are: ◆ Rotavirus ◆ Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli ◆ Shigella ◆ Campylobacter jejuni ◆ Salmonella typhimurium Non-infective causes ⚫ Dietary Diarrhea ⚫ Inappropriate feeding ⚫ Allergic Diarrhea Primary food hypersensitivity, Secondary food hypersensitivity ⚫ Symptomatic Diarrhea ⚫ Lack of Disaccharidase ⚫ Climate 【Pathogenesis of Diarrhea】 15 ⚫ Pathogenesis of Viral Diarrhea (Osmotic Diarrhea) ⚫ Pathogenesis of Enterotoxigenic Diarrhea (Secretory Diarrhea) ⚫ Secretory diarrhea occurs with entrotoxin-producing organisms ⚫ Pathogenesis of Dietary Diarrhea Flow chart 【CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS】 Classification of Diarrhea 5
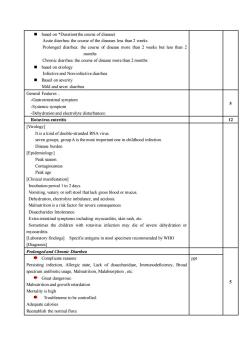
n *Duration(the coseofdiseaseAcute diarrhea:the course ofthe diseases less than 2 weeksProlonged diarhea: the course of disease more than 2 weeks but lessthan 2monthsChronic diarrhea the course of disease more than 2 monthsbasedonetiologInfective and Non-infective dirrheaBased on severityMild and sever dirrheaGeneral FeaturesGastrointestinal symptom5Systemic symptomDehydration and electrolyte disturbancesRotavirus enteritis12[VirologyIt is a kind of doub!ndedRNAviruseven groups, groupA is the most important one in childhood infectionDisease burden[Epidemiology] Peak season.ContagiousnessPeak age[Clinical manifestatiorIncubation period Ito 2 daysVomiting,watery or soft stool that lack gross blood ormucusDehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and acidosisMalnutritionon is ariskfactorfor severe consequencesDisaccharides Intolerance.Extra-intestinal symptoms including myocarditis skinrash, etc.Sometimes the children with rotavirus infection may die of severe dehydration ormyocarditis[Laboratory findings] Specific antigens in stool specimen recommended by WHO[DiagnosisProlonged and Chronic DirrheaComplicatereasonsPptPersisting infection, Allergic state, Lack of disaccharidase, Immunodeficiency, Broadusage, Malnutrition, Malabsorption,etc.spectribiotlGreatdangerouMalnutrition and growth retardationMortality is highTroublesome to be controlledAdequate caloriesReestablish the normal flora
◼ based on *Duration(the course of disease) Acute diarrhea: the course of the diseases less than 2 weeks Prolonged diarrhea: the course of disease more than 2 weeks but less than 2 months Chronic diarrhea: the course of disease more than 2 months ◼ based on etiology Infective and Non-infective diarrhea ◼ Based on severity Mild and sever diarrhea General Features :. -Gastrointestinal symptom -Systemic symptom -Dehydration and electrolyte disturbances: 5 Rotavirus enteritis 12 [Virology] It is a kind of double-stranded RNA virus. seven groups, group A is the most important one in childhood infection. Disease burden [Epidemiology] Peak season. Contagiousness Peak age [Clinical manifestation] Incubation period 1 to 2 days. Vomiting, watery or soft stool that lack gross blood or mucus. Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and acidosis. Malnutrition is a risk factor for severe consequences. Disaccharides Intolerance. Extra-intestinal symptoms including: myocarditis, skin rash, etc. Sometimes the children with rotavirus infection may die of severe dehydration or myocarditis. [Laboratory findings] Specific antigens in stool specimen recommended by WHO [Diagnosis] Prolonged and Chronic Diarrhea 5 Complicate reasons: Persisting infection, Allergic state, Lack of disaccharidase, Immunodeficiency, Broad spectrum antibiotic usage, Malnutrition, Malabsorption , etc. Great dangerous: Malnutrition and growth retardation Mortality is high Troublesome to be controlled: Adequate calories Reestablish the normal flora ppt
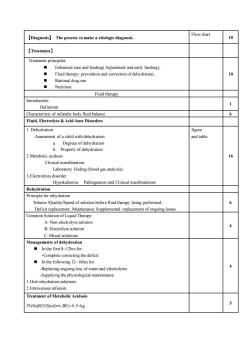
Flow chart[Dianosis]Theprocestomakeaetiologicdiagnosis10[Treatment)Treatment principlesEnhanced care and feeding( Adiustmenand early feeding)10Fluid therapy: prevention and correction of dehydration,-Rational drug useNutritionFluid therapyIntroductior1DefinitionCharacteristic of infantile body fluid balance6Fluid, Electrolyte & Acid-base Disorders1. DehydrationfigureAsssment ofa child with dehydrationand tableDegrees of dehydration0.Propertyof dehydration162 Metabolic acidosisClinical manifestationcaboratoryfinding (blood gas analysis):3.Electrolytes disorderHypokaliemia:Pathogenesis and Clinical manifestationsRehydrationPrinciple for rehydrationVolume/Quality/Speedof solution beforefluid therapy being performed6Dfitrplament; Maintenance Supplementalrplaemnt of ongoing lseCommon Solution of Liquid TherapyA. Non-electrolyte solution4B. Electrolyte solutionC.Mixed solutionManagements of dehydration In the first 8~12hrs for:-Complete correcting the deficit In the following 12-16hrs for:4Replacing ongoing loss of water and electrolytesSupplying the physiological maintenance.1.Oral rehydration solutions2.Intravenous infusion:Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis35%NaHCO3(ml)=(-BE)0.5×kg
【Diagnosis】 The process to make a etiologic diagnosis Flow chart 10 【Treatment】 Treatment principles: ◼ Enhanced care and feeding( Adjustment and early feeding); ◼ Fluid therapy: prevention and correction of dehydration; ◼ Rational drug use ◼ Nutrition 10 Fluid therapy Introduction Definition 1 Characteristic of infantile body fluid balance 6 Fluid, Electrolyte & Acid-base Disorders 1. Dehydration Assessment of a child with dehydration a. Degrees of dehydration b. Property of dehydration 2 Metabolic acidosis Clinical manifestation: Laboratory finding (blood gas analysis): 3.Electrolytes disorder Hypokaliemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical manifestations figure and table 16 Rehydration Principle for rehydration Volume /Quality/Speed of solution before fluid therapy being performed. Deficit replacement; Maintenance Supplemental; replacement of ongoing losses. 6 Common Solution of Liquid Therapy A. Non-electrolyte solution B. Electrolyte solution C. Mixed solutions: 4 Managements of dehydration ◼ In the first 8~12hrs for: -Complete correcting the deficit ◼ In the following 12~16hrs for: -Replacing ongoing loss of water and electrolytes -Supplying the physiological maintenance. 1.Oral rehydration solutions 2.Intravenous infusion: 4 Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis 5%NaHCO3(ml)=(-BE)×0.5×kg 3

Treatment of Kaliopenia5potassium chloride injection (10% KCI) needs to be added to the infusion ([KCI) ≤0.3%),once urine output is establishedSeveral special conditions neonatal diarrheapneumonia with dirhea:malnutrition with diarrhea[结课]5回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容布置见习的内容和要求ReviewQA :1) What is the diarrhea?2) Why diarrhea is highly susceptible to children?3) Why diarrheais more dangerous for children?4) What arethe main causes ofdirrhea in children?5) What are the common diarrhea manifestations?6)How to diagnose the dehydration in children?7) How to diagnose diarrhea inchildren?8) How to manage dehydration in children with diarrhea?总结及补充修正授课年级总结及修正补充内容备注2005级增加细菌图片2006级增加提问2007级增加我院的腹泻资料
Treatment of Kaliopenia potassium chloride injection (10% KCl) needs to be added to the infusion ([KCl] ≤ 0.3%), once urine output is established. 5 Several special conditions ⚫ neonatal diarrhea ⚫ pneumonia with diarrhea: ⚫ malnutrition with diarrhea: 5 [结课] 5 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容, 布置见习的内容和要求 Review QA: 1) What is the diarrhea? 2) Why diarrhea is highly susceptible to children? 3) Why diarrhea is more dangerous for children? 4) What are the main causes of diarrhea in children? 5) What are the common diarrhea manifestations? 6) How to diagnose the dehydration in children? 7) How to diagnose diarrhea in children? 8) How to manage dehydration in children with diarrhea? 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注 2005 级 增加细菌图片 2006 级 增加提问 2007 级 增加我院的腹泻资料
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十九章 自动临床生物化学分析仪的应用及评价.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 治疗药物浓度监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 妊娠的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 肿瘤标志物的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 神经系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 消化系统疾病的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 内分泌疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 心血管系统疾病的生物化学检测.ppt
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 Immunodeficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 Acute Convulsion in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)08 questions of immune system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)07 questions of urinological system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)09 questions of endocrine disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)10 questions of infectious diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)06 questions of nervous system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)03 questions of respiratory diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)04 questions of circulatory system.doc
