《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)20 Toxic Bacillary Dysentery
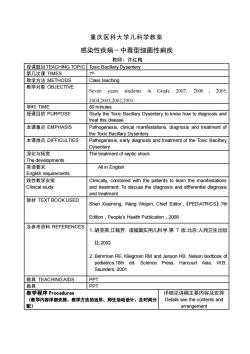
重庆医科大学儿科学教案感染性疾病一中毒型细菌性痫疾教师:许红梅授课题目TEACHINGTOPICToxic BacillaryDysentery第几次课TIMES7th教学方法METHODSClass teaching教学对象OBJECTIVESevenstudentsGrade2007,20062005,years2004.2003.2002.2001学时:TIME80 minutesStudy the Toxic Bacillary Dysentery to.know how to diagnosis and授课目的PURPOStreat this diseasePathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of本课重点EMPHASISthe Toxic Bacillary Dysentery本课难点DIFFICULTIESPathogenesis, early diagnosis and treatment of the Toxic BacillaryDysentery深化与拓宽ThetreatmentofsepticshockThe developments英语要求All in EnglishEnglish requirements践性教学安排Clinicaly,combined with the patients to learn the manifestatonsand treatment; To discuss the diagnosis and dfferential diagnosisClinical studyand treatment.教材TEXTBOOKUSEDShen Xiaoming, Wang Weipin, Chief Editor,《PEDIATRICS》7thEdition,People'sHealthPublication2008及参考资料REFERENCES1.胡亚美,江载芳:诸福棠实用儿科学.第7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,20022. Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook ofpediatrics.16th ed.Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B.Saunders, 2001PPT教具TEACHINGAIDSPPT教具教学程序Procedures详细见讲稿主要内容及安排(教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分Details see the contents and配)arrangement
重庆医科大学儿科学教案 感染性疾病-中毒型细菌性痢疾 教师:许红梅 授课题目TEACHING TOPIC Toxic Bacillary Dysentery 第几次课 TIMES 7 th 教学方法 METHODS Class teaching 教学对象 OBJECTIVE Seven years students in Grade 2007, 2006 , 2005, 2004,2003,2002,2001 学时: TIME 80 minutes 授课目的 PURPOSE Study the Toxic Bacillary Dysentery to.know how to diagnosis and treat this disease 本课重点 EMPHASIS Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of the Toxic Bacillary Dysentery 本课难点 DIFFICULTIES Pathogenesis, early diagnosis and treatment of the Toxic Bacillary Dysentery 深化与拓宽 The developments The treatment of septic shock 英语要求 English requirements All in English 践性教学安排 Clinical study Clinically, combined with the patients to learn the manifestations and treatment; To discuss the diagnosis and differential diagnosis and treatment. 教材 TEXT BOOK USED Shen Xiaoming, Wang Weipin, Chief Editor,《PEDIATRICS》7th Edition,People’s Health Publication,2008 及参考资料 REFERENCES 1. 胡亚美,江载芳. 诸福棠实用儿科学.第 7 版.北京:人民卫生出版 社,2002 2. Behrman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Nelson textbook of pediatrics.16th ed. Science Press, Harcourt Asia, W.B. Saunders, 2001 教具 TEACHING AIDS PPT 教具 PPT 教学程序 Procedures (教学内容详细安排、教学方法的运用、师生活动设计、及时间分 配) 详细见讲稿主要内容及安排 Details see the contents and arrangement
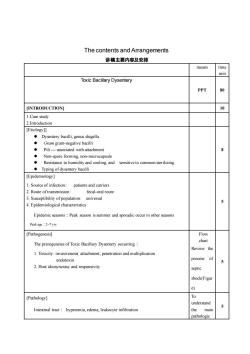
The contents and Arrangements讲稿主要内容及安排timemeansminToxic Bailary DysenteryPPT80INTRODUCTION!101.Case study2.Introduction[Etiology]Dysentery bacilli,genus shigellaGram gram-negative bacillipiliassociated with attachmenNon-spore forming, non-microcapsuleResistance to humidity and cooling, andsensitiveto common sterilizing. Typing of dysentery bacilli[Epidemiology]1. Source of infection::patients and carriers2. Route of transmissiorfecal-oral route3. Susceptibility of population:universal54.Epidemiological characteristicsEpidemic seasons:Peakason is summer and sporadicoccurinotherseasonPeak age : 2-7 yrs[Pathogenesis]FlowchartThe prerequisites of Toxic Bacillary Dysentery occurring :Review the.Toxicity:iand multiplicationveness(attaonetraticprocessofendotoxin2.Host idiosyncrasy and responsiviysepticshock(Figur/e)O[Pathology]understand 0Intestinal tract : hyperemia, edema, leukocyte infiltrationthemainpathologic
The contents and Arrangements 讲稿主要内容及安排 means time min Toxic Bacillary Dysentery PPT 80 [INTRODUCTION] 10 1.Case study 2.Introduction [Etiology]] ⚫ Dysentery bacilli, genus shigella ⚫ Gram gram-negative bacilli ⚫ Pili - associated with attachment ⚫ Non-spore forming, non-microcapsule ⚫ Resistance to humidity and cooling, and sensitive to common sterilizing ⚫ Typing of dysentery bacilli 8 [Epidemiology] 1. Source of infection:: patients and carriers 2. Route of transmission: fecal-oral route 3. Susceptibility of population: universal 4. Epidemiological characteristics Epidemic seasons:Peak season issummer and sporadic occur in other seasons Peak age:2~7 yrs 5 [Pathogenesis] The prerequisites of Toxic Bacillary Dysentery occurring: 1. Toxicity: invasiveness( attachment, penetration and multiplication endotoxin 2. Host idiosyncrasy and responsivity Flow chart Review the process of septic shock(Figur e) 5 [Pathology] Intestinal tract: hyperemia, edema, leukocyte infiltration To understand the main pathologic 5
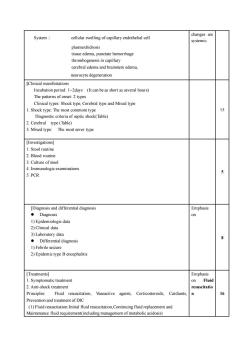
changes areSystem :cellular swelling of capillary endothelial cellsystemic.plasmexhidrosisissueedema,punctatehemorrhagethrombogenesis in capillarycerebral edema andbrainstem edemaneurocyte degeneration[Clinical manifestationsIncubation period: 1~2days(It can be as short as several hours)The patterns of onset: 2 typesClinical typepeshypCbralyadMix51. Shock type: The most commom typeDiagnostic criteria of septic shock(Table)2. Cerebral type(Table)3. Mixed type:The most sever type[Investigations]1. Stool routine2. Blood routine3. Culture of stool4. Immunologic examinations5.PCR[Diagnosis and differential diagnosisEmphasis.Diagnosiso1) Epidemiologic data2) Clinical data 3) Laboratory data8.Differential diagnosis1) Febrile seizur2)Epidemic type Bencephalitis[Treatments]Emphasis1.Symptomatic treatmentonFluid2. Anti-shock treatmentresuscitatioPrinciples:Fluid resuscitation,Vasoactiveagents,Corticosteroids,Cardiants,6Prevention and treatment of DIC(1) Fluid resuscitation:Initial fluid resuscitation,Continuing fluid replacement andMaintenance fluid requirement(including management of metabolic acidosis)
System: cellular swelling of capillary endothelial cell plasmexhidrosis tissue edema, punctate hemorrhage thrombogenesis in capillary cerebral edema and brainstem edema, neurocyte degeneration changes are systemic. [Clinical manifestations Incubation period: 1~2days (It can be as short as several hours) The patterns of onset: 2 types Clinical types: Shock type, Cerebral type and Mixed type 1. Shock type: The most commom type Diagnostic criteria of septic shock(Table) 2. Cerebral type (Table) 3. Mixed type: The most sever type 15 [Investigations] 1. Stool routine 2. Blood routine 3. Culture of stool 4. Immunologic examinations 5. PCR 5 [Diagnosis and differential diagnosis ⚫ Diagnosis 1) Epidemiologic data 2) Clinical data 3) Laboratory data ⚫ Differential diagnosis 1) Febrile seizure 2) Epidemic type B encephalitis Emphasis on 8 [Treatments] 1. Symptomatic treatment 2. Anti-shock treatment Principles: Fluid resuscitation, Vasoactive agents, Corticosteroids, Cardiants, Prevention and treatment of DIC (1) Fluid resuscitation:Initial fluid resuscitation,Continuing fluid replacement and Maintenance fluid requirement(including management of metabolic acidosis) Emphasis on Fluid resuscitatio n 16
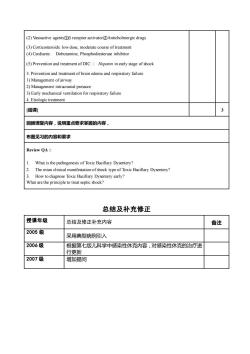
(2) Vaso:agentsβ receptor activatorAnticholinergic drugs(3) Corticosteroids: low dose, moderate course oftreatment(4) Cardiants:Dobutamine, Phosphodiesterase inhibitor(5)Prevention and treatment ofDIC: :Heparin inearly stage ofshock3.Preventofnedemdrespiratoryfailure1)Managementofairway2) Management intracranial pressure3)Early mechanical ventilation for respiratory failure4. Etiologic treatment[结课]3回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容,布置见习的内容和要求Review QA :What is the pathogenesis of Toxic BacillaryDysentery?The mian clinical manifestation of shock type of Toxic Bacillary Dysentery?3 How to diagnose Toxic Baillary Dysentery early?What aretheprincipletotreat septic shock?总结及补充修正授课年级总结及修正补充内容备注2005级采用典型病例引入2006级根据第七版儿科学中感染性休克内容,对感染性休克的治疗进行更新2007级增加提问
(2) Vasoactive agents① receptor activator②Anticholinergic drugs (3) Corticosteroids: low dose, moderate course of treatment (4) Cardiants: Dobutamine, Phosphodiesterase inhibitor (5) Prevention and treatment of DIC:: Heparin in early stage of shock 3. Prevention and treatment of brain edema and respiratory failure 1) Management of airway 2) Management intracranial pressure 3) Early mechanical ventilation for respiratory failure 4. Etiologic treatment [结课] 3 回顾课堂内容,说明重点要求掌握的内容, 布置见习的内容和要求 Review QA: 1. What is the pathogenesis of Toxic Bacillary Dysentery? 2. The mian clinical manifestation of shock type of Toxic Bacillary Dysentery? 3. How to diagnose Toxic Bacillary Dysentery early? What are the principle to treat septic shock? 总结及补充修正 授课年级 总结及修正补充内容 备注 2005 级 采用典型病例引入 2006 级 根据第七版儿科学中感染性休克内容,对感染性休克的治疗进 行更新 2007 级 增加提问
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)21 Chronic Gastritis in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)18 Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)24 Mumps.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)22 Infantale Diarrhea and Fluid Therapy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)23 Infantile Hepatitis Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)25 Scarlet Fever.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)01 Introduction of Pediatrics.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)04 Neonatal Jaundice.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)05 Neonatal Septicemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)02 Growth and Development.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)03 Nutrition During Childhood.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)09 Haematopoiesis and Blood Cell Counts.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)08 Congenital Heart Disease.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)06 Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)07 Bronchopneumonia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学大纲 Teaching Outline for Pediatrics Course(英文).pdf
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十九章 自动临床生物化学分析仪的应用及评价.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 治疗药物浓度监测.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 妊娠的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《临床生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 肿瘤标志物的生物化学检验.ppt
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)19 Tuberculosis Meningitis.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)16 Measles.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)17 Varicella.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)14 Congenital Hypothyroidism.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)15 Growth Hormone Deficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)10 Nutritional Iron Deficiency Anemia.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)13 Immunodeficiency.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)11 Acute Convulsion in Children.doc
- 《儿科学》课程教学资源(授课教案)12 Acute Glomerulonephritis,Nephrotic Syndrome.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)08 questions of immune system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)07 questions of urinological system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)09 questions of endocrine disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)10 questions of infectious diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)06 questions of nervous system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)03 questions of respiratory diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)04 questions of circulatory system.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)05 questions of blood disorders.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)02 questions of neonatal diseases.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(复习题)01 questions of children healthcare.doc
- 《儿科学》课程作业习题(典型病例)06 nephrotic syndrome-2.doc
