厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lab-2土壤细菌的分离与纯化

实验二 土壤细菌的分离与纯化 一 教学要求 通过从土壤中分离纯化细菌,初步掌握微 生物的分离纯化方法和无菌操作技术。 二 实验原理 - 常用的分离纯化方法 microorganisms exist in nature as mixed populations. However, to study microorganisms in the laboratory we must have them in the form of a pure culture, that is, one in which all organisms are descendants of the same organism
实验二 土壤细菌的分离与纯化 一 教学要求 通过从土壤中分离纯化细菌,初步掌握微 生物的分离纯化方法和无菌操作技术。 二 实验原理 - 常用的分离纯化方法 microorganisms exist in nature as mixed populations. However, to study microorganisms in the laboratory we must have them in the form of a pure culture, that is, one in which all organisms are descendants of the same organism

•单细胞挑取法 简易单细胞挑取法 micromanipulator
•单细胞挑取法 简易单细胞挑取法 micromanipulator

•平板分离法 streak plate method The most common way of separating bacterial cells on the agar surface to obtain isolated colonies is the streak plate method. It provides a simple and rapid method of diluting the sample by mechanical means. As the loop is streaked across the agar surface, more and more bacteria are rubbed off until individual separated organisms are deposited on the agar. After incubation, the area at the beginning of the streak pattern will show confluent growth, while the area near the end of the pattern should show discrete colonies
•平板分离法 streak plate method The most common way of separating bacterial cells on the agar surface to obtain isolated colonies is the streak plate method. It provides a simple and rapid method of diluting the sample by mechanical means. As the loop is streaked across the agar surface, more and more bacteria are rubbed off until individual separated organisms are deposited on the agar. After incubation, the area at the beginning of the streak pattern will show confluent growth, while the area near the end of the pattern should show discrete colonies

pour plate method Another method of separating bacteria is the pour plate method. With the pour plate method, the bacteria are mixed with melted agar until evenly distributed and separated throughout the liquid. The melted agar is then poured into an empty plate and allowed to solidify. After incubation, discrete bacterial colonies can then be found growing both on the agar and in the agar
pour plate method Another method of separating bacteria is the pour plate method. With the pour plate method, the bacteria are mixed with melted agar until evenly distributed and separated throughout the liquid. The melted agar is then poured into an empty plate and allowed to solidify. After incubation, discrete bacterial colonies can then be found growing both on the agar and in the agar

spread plate method The spin plate method involves diluting the bacterial sample in tubes of sterile water, saline, or broth. Small samples of the diluted bacteria are then pipetted onto the surface of agar plates. A sterile, bent-glass rod is then used to spread the bacteria evenly over the entire agar surface
spread plate method The spin plate method involves diluting the bacterial sample in tubes of sterile water, saline, or broth. Small samples of the diluted bacteria are then pipetted onto the surface of agar plates. A sterile, bent-glass rod is then used to spread the bacteria evenly over the entire agar surface

三 材料与器材 ⚫ 金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus)和普通 变形菌(Proteus vulgaris)斜面菌种。 ⚫ 已灭菌的牛肉膏、高氏1号、土豆蔗糖培 养各1瓶,49.5 mL 无菌水(带玻璃珠)1 瓶、4.5 mL无菌水6 管、80%乙酸、10% 酚酸、95% 乙醇。 ⚫ 无菌培养皿12套、1 mL无菌移液管10 支、 土壤样品、天平等
三 材料与器材 ⚫ 金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus)和普通 变形菌(Proteus vulgaris)斜面菌种。 ⚫ 已灭菌的牛肉膏、高氏1号、土豆蔗糖培 养各1瓶,49.5 mL 无菌水(带玻璃珠)1 瓶、4.5 mL无菌水6 管、80%乙酸、10% 酚酸、95% 乙醇。 ⚫ 无菌培养皿12套、1 mL无菌移液管10 支、 土壤样品、天平等

四 操作步骤 • 制备土壤稀释液
四 操作步骤 • 制备土壤稀释液
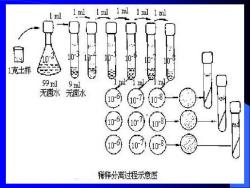
1 ml 1 ml 1 ral 1 xl 1 ml 1ml 10 th- 1克土样 99l 9ml 无满水 无茵水 10 10 稀释分离过程示意图

• 倾注平板
• 倾注平板

•培养
•培养
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lab-1培养基的配制与灭菌.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十八、印相和放大.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)模块四 显微摄影与暗房技术.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十五、石蜡切片法(四)染色、封藏(附:冰冻切片法).ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十四、石蜡切片法(三)切片、贴片.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十三、石蜡切片法(二)透明、透蜡、包埋.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十二石蜡切片法(一)取材、固定、洗涤、脱水.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)模块三 生物显微制片技术.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)蛋白质实验技术模块.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)绪论.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十一、Feulgen及PAS反应.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验十免疫细胞化学染色观察肿瘤细胞蛋白的表达与分布.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验九、免疫荧光染色观察肿瘤细胞骨架.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)模块二 细胞化学技术与免疫荧光染色.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验八、透射电子显微镜及扫描电子显微镜的使用.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验七、荧光显微镜及激光扫描共聚焦显微镜使用.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验六、活细胞观察及相差显微镜的使用.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验五、植物细胞液泡系观察与生物显微绘图.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验四、动物细胞线粒体的超活染色与油镜观察.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验三、细胞的形态多样性及细胞计数.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lab-3土壤中细菌总数的测定.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)实验一、淀粉的提取和水解.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)生物化学实验实验准备.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.10_植物制片技术及高等植物形态结构.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.11_组织培养实验.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.1_GUS基因检测.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.2_环境样品的采集、处理与分析.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.3_颈卵器植物的观察.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.4_切花保鲜及采后生理.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.5_显微绘图和低等植物的观察.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.6_叶绿体色素的提取分离及理化性质.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.7_遗传转化.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.8_植物生物学实验有关试剂配制.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)5.9_植物叶片光合速率的测定.doc
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)lab1-细菌的革兰氏染色.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)lab2-细菌的芽孢染色.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)LAB 3-7大分子物质的水解实验和IMVIC实验.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lab-8细菌的快速测定.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lab-9霉菌的形态观察与鉴定.ppt
- 厦门大学:《现代生物实验学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)lab-1中和剂的选择.ppt
