《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 8 visible spectrophotometry

山东置子大家 Analytical chemistry Chapter 8 visible spectrophotometry Learning objectives >To introduce the basic principles and the measurement methods of spectrophotometry >To understand the Beer's law,to deeply understand the relationship between absorbance,transmittance and absorptivity; >To understand the color-forming reactions,be familiar with the procedure of establishment of the working condition; >To present modern instrumentation for obtain spectra from solids,liquids and gases
Analytical chemistry Chapter 8 visible spectrophotometry Learning objectives ➢To introduce the basic principles and the measurement methods of spectrophotometry ➢To understand the Beer’s law, to deeply understand the relationship between absorbance, transmittance and absorptivity; ➢To understand the color-forming reactions, be familiar with the procedure of establishment of the working condition; ➢To present modern instrumentation for obtaining molecular spectra from solids, liquids and gases

归东理工大军 Analytical chemistry 8.1 Introduction Molecular systems can be identified by their characteristic energy term schemes consists of discrete electronic,vibrational and rotational states.At room temperature the substances are mainly in their ground states. After absorbing appropriate types of electromagnetic radiation,transitions from ground states to excited states will be induced in the molecules of the sample. These excited states usually decay to their original ground states within 108s,with by emitting the previously absorbed radiation in all directions with the same or a lower frequency,or by radiationless 2025/4/3 relaxation
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 2 8.1 Introduction Molecular systems can be identified by their characteristic energy term schemes consists of discrete electronic, vibrational and rotational states. At room temperature the substances are mainly in their ground states. After absorbing appropriate types of electromagnetic radiation, transitions from ground states to excited states will be induced in the molecules of the sample. These excited states usually decay to their original ground states within 10-8 s, with by emitting the previously absorbed radiation in all directions with the same or a lower frequency, or by radiationless relaxation

G归东2大子 Analytical chemistry Molecular spectra can be obtained in the absorption or emission mode from samples.They are images of the interactions mentioned above and contain analytical information about the sample. Molecular absorption spectroscopy is used primarily for quantitative analysis and is probably more extensively applied in chemical and clinical laboratories throughout the world than any other single method. 2025/4/3 3
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 3 Molecular spectra can be obtained in the absorption or emission mode from samples. They are images of the interactions mentioned above and contain analytical information about the sample. Molecular absorption spectroscopy is used primarily for quantitative analysis and is probably more extensively applied in chemical and clinical laboratories throughout the world than any other single method
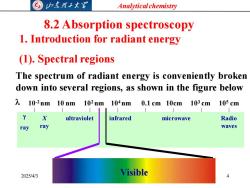
G归东理工大图 Analytical chemistry 8.2 Absorption spectroscopy 1.Introduction for radiant energy (1).Spectral regions The spectrum of radiant energy is conveniently broken down into several regions,as shown in the figure below 210-2nm10nm102nm104nm0.1cm10cm103cm105cm 2 X ultraviolet infrared microwave Radio ray ray waves 2025/4/3 Visible
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 4 8.2 Absorption spectroscopy 1. Introduction for radiant energy (1). Spectral regions The spectrum of radiant energy is conveniently broken down into several regions, as shown in the figure below ray X ray ultraviolet infrared microwave Radio waves 10-2 nm 10 nm 102 nm 104 nm 0.1 cm 10cm 103 cm 105 cm Visible

G山东理王大 Analytical chemistry The limits of these regions are determined by the practical limitations of appropriate experimental methods of production and detection of radiation. The differentiation of spectral regions has additional significance for the chemist in that the interactions of the radiations with chemical systems follow different mechanisms and provide different kinds of information. (2).Nature of light An investigation into the properties of electromagnetic energy reveals an essential duality in our understanding of the nature of light. 2025/4/3 5
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 5 The limits of these regions are determined by the practical limitations of appropriate experimental methods of production and detection of radiation. The differentiation of spectral regions has additional significance for the chemist in that the interactions of the radiations with chemical systems follow different mechanisms and provide different kinds of information. (2). Nature of light An investigation into the properties of electromagnetic energy reveals an essential duality in our understanding of the nature of light

G归东理工大图 Analytical chemistry In some respects its properties are those of wave while in others it appears to consist of a series of discrete particles of energy,called photons. Both wavelength and wave number are dependent on the refractive index of the medium through which the radiation is passing,whereas the frequency is independent of this property. V= -=VC 2025/4/3
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 6 In some respects its properties are those of wave ,while in others it appears to consist of a series of discrete particles of energy, called photons. Both wavelength and wave number are dependent on the refractive index of the medium through which the radiation is passing, whereas the frequency is independent of this property. c c v = =

©归东子大写 Analytical chemistry The energy content E of a photon is directly proportional to the frequency E=hy=h=hvc Thus there is an inverse relationship between energy content and wavelength,but a direct relation between energy and frequency or wave number. The intensity of abeam is proportional to the number of photons per second that are propagated in the beam. 2025/4/3 7
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 7 The energy content E of a photon is directly proportional to the frequency h c c hv h E = = = Thus there is an inverse relationship between energy content and wavelength, but a direct relation between energy and frequency or wave number. The intensity of abeam is proportional to the number of photons per second that are propagated in the beam

©山东理卫大 Analytical chemistry 2.Selective absorption of radiation and absorbance spectrum The term spectroscopy was originally used to describe a branch of science based upon the resolution of visible radiation into its component wavelengths. If a beam of white light passes through a glass container filled with liquid,the emergent radiation is always less powerful than that entering.The diminution of power is generally of different extent for different wavelengths. 2025/4/3
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 8 2. Selective absorption of radiation and absorbance spectrum The term spectroscopy was originally used to describe a branch of science based upon the resolution of visible radiation into its component wavelengths. If a beam of white light passes through a glass container filled with liquid, the emergent radiation is always less powerful than that entering. The diminution of power is generally of different extent for different wavelengths

©归东龙工大写 Analytical chemistry The loss is due in part to reflections at the surfaces and to scattering by any suspended particles present,but in the absence of such particles,it is primarily accounted for by the absorption of radiant energy by the liquid. If the energy absorbed is greater for some visible wavelengths than for others,the emergent beam will appear colored.The apparent color of the solution is always the complement of the color absorbed. A solution absorbing in the blue region will appear yellow,one that absorbs green will appear purple. 2025/4/3 9
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 9 The loss is due in part to reflections at the surfaces and to scattering by any suspended particles present, but in the absence of such particles, it is primarily accounted for by the absorption of radiant energy by the liquid. If the energy absorbed is greater for some visible wavelengths than for others, the emergent beam will appear colored. The apparent color of the solution is always the complement of the color absorbed. A solution absorbing in the blue region will appear yellow, one that absorbs green will appear purple

Analytical chemistry The general term for chemical analysis through the measurement of absorption of radiation is absorptiometry.The term colorimetry applies only in relation to the visible region.Spectrophotometry is a division of absorptiometry that refers specifically to the use of a spectrophotometer. When radiation passes through a layer of material, certain frequencies may be selectively removed by absorption,a process in which electromagnetic energy is transferred to the atoms,ions,or molecules constituting the sample. 2025/4/3 10
Analytical chemistry 2025/4/3 10 The general term for chemical analysis through the measurement of absorption of radiation is absorptiometry. The term colorimetry applies only in relation to the visible region. Spectrophotometry is a division of absorptiometry that refers specifically to the use of a spectrophotometer. When radiation passes through a layer of material, certain frequencies may be selectively removed by absorption, a process in which electromagnetic energy is transferred to the atoms, ions, or molecules constituting the sample
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)天平.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)滴定分析练习.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)有机酸摩尔质量.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)水硬度.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)胃舒平中铝镁含量的测定.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)COD的测定.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后教学资源(实验预习指导)分光光度法测铁.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第一章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第二章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第三章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第五章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第六章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第七章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第八章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后思考题(含答案)第十章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后习题(含答案)第三章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后习题(含答案)第五章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后习题(含答案)第六章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后习题(含答案)第七章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程课后习题(含答案)第八章.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 7 precipitation titration.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文)Chapter 6 Oxidation-reduction titration.pdf
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 5 Complexometric Titration.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文)Chapter 4.pdf
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 3 summarization of Titrimetric analysis.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 2 Errors and data treatment in quantitative analysis.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿,英文)Chapter 1 The classification of analytical chemistry.ppt
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题10.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题9.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题8.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题7.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题6.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题5.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题4.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题3.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题2.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(试题,含答案)分析化学试题1.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(知识拓展)自来水中余氯含量的测定.doc
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(文献资料)一种快速简便测定奶粉中蛋白质的方法.pdf
- 《分析化学》课程教学资源(知识拓展)禁止化学武器组织获诺贝尔和平奖.doc
