《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Methods of Analysis

Chapter 3Methods of AnalysisSJTU
SJTU 1 Chapter 3 Methods of Analysis

So far, we have analyzed relatively simple circuits byapplying Kirchhoff's laws in combination with Ohm's law.We can use this approach for all circuits, but as theybecome structurally more complicated and involve moreand more elements, this direct method soon becomescumbersome. In this chapter we introduce two powerfultechniques of circuit analysis: Nodal Analysis and MeshAnalysis.These techniques give us two systematic methods ofdescribing circuits with the minimum number ofsimultaneous equations. With them we can analyze almostany circuit by to obtain the required values of current orvoltage.2SJTU
SJTU 2 So far, we have analyzed relatively simple circuits by applying Kirchhoff’s laws in combination with Ohm’s law. We can use this approach for all circuits, but as they become structurally more complicated and involve more and more elements, this direct method soon becomes cumbersome. In this chapter we introduce two powerful techniques of circuit analysis: Nodal Analysis and Mesh Analysis. These techniques give us two systematic methods of describing circuits with the minimum number of simultaneous equations. With them we can analyze almost any circuit by to obtain the required values of current or voltage

Nodal AnalysisStepstoDetermineNodeVoltages1.Select a node as the reference node(ground), define the node voltages1,2,..n- to the remaining n- nodes. The voltages arereferenced with respectto the reference node.2.ApplyKCL to each of the n-1 independentnodes.Use Ohm's law toexpressthebranchcurrents intermsofnodevoltages.3.Solvethe resulting simultaneousequationsto obtaintheunknownnodevoltages3SJTU
SJTU 3 Nodal Analysis • Steps to Determine Node Voltages: 1. Select a node as the reference node(ground), define the node voltages 1 , 2 ,. n-1 to the remaining n-1nodes . The voltages are referenced with respect to the reference node. 2. Apply KCL to each of the n-1 independent nodes. Use Ohm’s law to express the branch currents in terms of node voltages. 3. Solve the resulting simultaneous equations to obtain the unknown node voltages
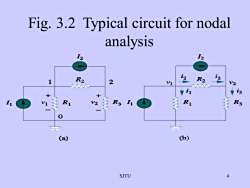
Fig. 3.2 Typical circuit for nodalanalysis15ini2R2R227V1V2订i3R1R3R1I1R3V2V1-0(b)(a)SJTU
SJTU 4 Fig. 3.2 Typical circuit for nodal analysis
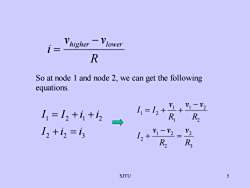
VlowerhigherRSo at node 1 and node 2, we can get the followingequationsV1V.-VI, = I2 +i +izRR2V2I2 +iz =is+V1-V2L.+R2R3SJTU5
SJTU 5 R v v i higher − lower = So at node 1 and node 2, we can get the following equations. 3 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 1 1 1 2 R v R v v I R v v R v I I = − + − = + + 2 2 3 1 2 1 2 I i i I I i i + = = + +

In terms of the conductance,equations becomeI, = I2 +GV +G,(Vi- V2)I2 +G2(Vi - V2)=G3V2Can also be cast in matrix form as[G +G22-G2[I-12-G2Gz+G,JLy2↓LI2Some examplesSJTU6
SJTU 6 In terms of the conductance, equations become 2 2 1 2 3 2 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 ( ) ( ) I G v v G v I I G v G v v + − = = + + − Can also be cast in matrix form as − = + − − + 2 1 2 2 1 2 3 2 2 1 2 I I I v v G G G G G G Some examples
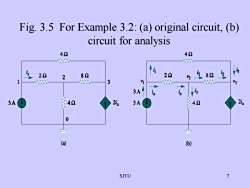
Fig. 3.5 For Example 3.2: (a) original circuit, (b)circuit for analysis4242i22诊2928222822V23V1V33设3AK2iy2ix3A403A400一(a)(b)7SJTU
SJTU 7 Fig. 3.5 For Example 3.2: (a) original circuit, (b) circuit for analysis
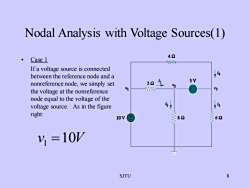
Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources(1)42CaselAAAIf a voltage source is connected1betweenthereferencenodeanda5V1122nonreferencenode, we simply setV2V1V3the voltage at the nonreferencenode equal to the voltage of thei2voltage source.As in the figureright:826210VV =10V8SJTU
SJTU 8 Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources(1) • Case 1 If a voltage source is connected between the reference node and a nonreference node, we simply set the voltage at the nonreference node equal to the voltage of the voltage source. As in the figure right: v1 =10V
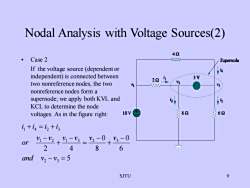
Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources(2)42Case2WAAASupernodeIf thevoltage source (dependentor4independent)isconnectedbetweeni15V2042twononreferencenodes,thetwoVV2nonreferencenodesformasupernode;we apply bothKVL and25KCL to determine thenode10V89262voltages. As in the figure righti+i=iz+iV2-0V3-0Vi-V2Vi-V3证or十2486andV2- V3 = 5门SJTU9
SJTU 9 Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources(2) • Case 2 If the voltage source (dependent or independent) is connected between two nonreference nodes, the two nonreference nodes form a supernode; we apply both KVL and KCL to determine the node voltages. As in the figure right: 5 6 0 8 0 2 4 2 3 1 2 1 3 2 3 1 4 2 3 − = − + − = − + − + = + and v v v v v v v v or i i i i
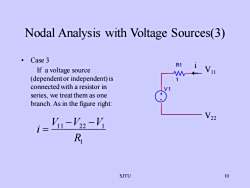
Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources(3)·Case3R1If avoltage source(dependentorindependent)isconnectedwitharesistorinV1Oseries,wetreatthemas onebranch. As in the figure right22Vi1 - V22 -ViRi10SJTU
SJTU 10 • Case 3 If a voltage source (dependent or independent) is connected with a resistor in series, we treat them as one branch. As in the figure right: Nodal Analysis with Voltage Sources(3) R1 1 V 1 i V11 V22 1 11 22 1 R V V V i − − =
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 Operational Amplifier.ppt
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Basic laws.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第1章 电路模型和电路定律例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第2章 电阻电路的等效变换例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第5章 含有运算放大器的电阻电路例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第4章 电路定理例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第3章 电阻电路的一般分析例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第7章 一阶电路和二阶电路时域分析例(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第9章 正弦稳态电路的分析例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第8章 相量法例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第6章 储能元件例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习3解答.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习2解答.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习1解答.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习3题目.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习2题目.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习1题目.doc
- 《电路》课程各章习题集(含典型题解)第二章 电阻电路的等效变换.doc
- 《电路》课程各章习题集(含典型题解)第一章 电路的基本概念和基本定律.doc
- 《电路》课程各章习题集(含典型题解)第五章 含有运算放大器的电阻电路.doc
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 Circuit Theorems.ppt
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Fundamental Knowledge.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)电路分析基础绪论 Fundamentals of Circuit Analysis(电路理论的回顾与展望).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 非线性电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 均匀传输线.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)附录A 磁路和铁心线圈.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 二端口网络.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 线性动态电路的复频域分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 电路方程的矩阵形式.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 三相电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 电路的频率响应.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 含有耦合电感的电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 相量法.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 正弦稳态电路的分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 一阶电路和二阶电路的时域分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 储能元件.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 含有运算放大器的电阻电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 电阻电路的一般分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电阻电路的等效变换.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 非正弦周期电流电路和信号的频谱.ppt
