《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 Circuit Theorems

Chapter 4Circuit TheoremsSJTU
SJTU 1 Chapter 4 Circuit Theorems

Linearity Property: Linearity is the property of an elementdescribing a linear relationship betweencause and effect: A linear circuit is one whose output islinearly ( or directly proportional) to itsinput.2SJTU
SJTU 2 Linearity Property • Linearity is the property of an element describing a linear relationship between cause and effect. • A linear circuit is one whose output is linearly ( or directly proportional) to its input
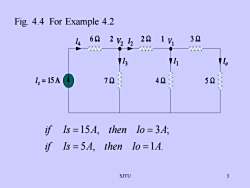
Fig. 4.4 For Example 4.23262222 V2/21VI14A1111.172421,=15A52ifIs =15A, then Io = 3A;if Is =5A, then lo=1A.3SJTU
SJTU 3 Fig. 4.4 For Example 4.2 5 , 1 . 15 , 3 ; if Is A then Io A if Is A then Io A = = = =

Superposition(1): The superposition principle states thatvoltage across (or current through) anelement in a linear circuit is the algebraicsum of the voltages across (or currentsthrough) that element due to eachindependent source acting aloneSJTU
SJTU 4 Superposition(1) • The superposition principle states that voltage across (or current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone

Superposition(2)Steps to Apply Superposition Principle:1.Turn off all independent source except one source. Findthe output(voltage or current) due to that active sourceusing nodal or mesh analysis.2.Repeat step 1 for each of the other independent sources3.Find the total contribution by adding algebraically all thecontributions due to the independent sources5SJTU
SJTU 5 • Steps to Apply Superposition Principle: 1. Turn off all independent source except one source. Find the output(voltage or current) due to that active source using nodal or mesh analysis. 2. Repeat step 1 for each of the other independent sources. 3. Find the total contribution by adding algebraically all the contributions due to the independent sources. Superposition(2)
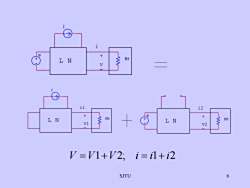
i十R1LNVi1i2X+R1R1LNLNV1V2V=V1+V2: i=il+i2SJTU6
SJTU 6 j R1 V e + - L N i j + - V1 R1 i1 L N i2 - L N + V2 e R1 V =V1+V 2; i = i1+ i2
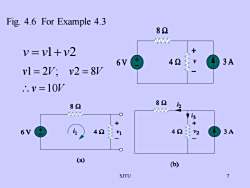
Fig. 4.6 For Example 4.382V=vl+v2十3A426Vvl= 2V: v2 =8V.. v = 10V821282M3+十V2i42423A6VV1(a)(b)7SJTU
SJTU 7 Fig. 4.6 For Example 4.3 v = v1+v2 v V v V v V 10 1 2 ; 2 8 = = =
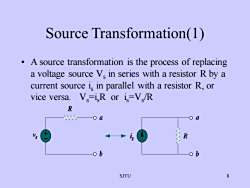
Source Transformation(1): A source transformation is the process of replacinga voltage source V. in series with a resistor R by acurrent source i, in parallel with a resistor R, orV,=i,R or i=Vs/Rvice versa.Roa0RVob68SJTU
SJTU 8 Source Transformation(1) • A source transformation is the process of replacing a voltage source Vs in series with a resistor R by a current source is in parallel with a resistor R, or vice versa. Vs=isR or is=Vs /R
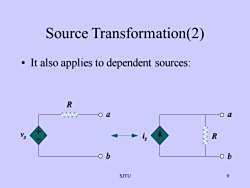
Source Transformation(2): It also applies to dependent sources:RWaa2SS66O9SJTU
SJTU 9 Source Transformation(2) • It also applies to dependent sources:
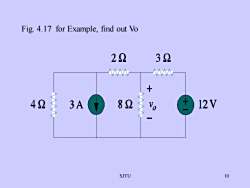
Fig. 4.17 for Example, find out Vo2232+428212V3A2O10SJTU
SJTU 10 Fig. 4.17 for Example, find out Vo
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 Methods of Analysis.ppt
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 Operational Amplifier.ppt
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Basic laws.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第1章 电路模型和电路定律例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第2章 电阻电路的等效变换例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第5章 含有运算放大器的电阻电路例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第4章 电路定理例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第3章 电阻电路的一般分析例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第7章 一阶电路和二阶电路时域分析例(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第9章 正弦稳态电路的分析例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第8章 相量法例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学课件(例题讲解)第6章 储能元件例题(PPT).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习3解答.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习2解答.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习1解答.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习3题目.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习2题目.doc
- 《电路》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测与练习1题目.doc
- 《电路》课程各章习题集(含典型题解)第二章 电阻电路的等效变换.doc
- 《电路》课程各章习题集(含典型题解)第一章 电路的基本概念和基本定律.doc
- 《电路》课程英文课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 Fundamental Knowledge.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)电路分析基础绪论 Fundamentals of Circuit Analysis(电路理论的回顾与展望).ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十七章 非线性电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十八章 均匀传输线.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)附录A 磁路和铁心线圈.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十六章 二端口网络.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十四章 线性动态电路的复频域分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十五章 电路方程的矩阵形式.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 三相电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 电路的频率响应.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 含有耦合电感的电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 相量法.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 正弦稳态电路的分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 一阶电路和二阶电路的时域分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 储能元件.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 含有运算放大器的电阻电路.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 电阻电路的一般分析.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 电阻电路的等效变换.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十三章 非正弦周期电流电路和信号的频谱.ppt
- 《电路》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 电路模型和电路定律.ppt
