《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 7 Hedging with Spreads

Chapter 7 Hedging with Spreads
Chapter 7 Hedging with Spreads

What is hedging? When a businessperson uses the futures market to protect against adverse price movements,the process is called hedging. Hedging involves taking a position in the futures market that is opposite to the position held in the cash or spot market
What is hedging? ◼ When a businessperson uses the futures market to protect against adverse price movements, the process is called hedging. ◼ Hedging involves taking a position in the futures market that is opposite to the position held in the cash or spot market

Selling Hedge If a businessperson buys a commodity in the cash market,he or she would then hedge that position by selling an equivalent quantity in the futures market
If a businessperson buys a commodity in the cash market, he or she would then hedge that position by selling an equivalent quantity in the futures market. Selling Hedge

Buying Hedge The buying hedge is used by a businessperson who anticipates buying a commodity at a future date and wants protection from a possible price increase. This person is said to be short the cash market and so would take a long position in the futures market (be a buyer)
◼ The buying hedge is used by a businessperson who anticipates buying a commodity at a future date and wants protection from a possible price increase. ◼ This person is said to be short the cash market and so would take a long position in the futures market (be a buyer). Buying Hedge

Conclusion: Hedging not only protects against the possible losses from adverse price movement;it also takes away the possibility of windfall profits that can accrue as the result of favorable price moves
Hedging not only protects against the possible losses from adverse price movement; it also takes away the possibility of windfall profits that can accrue as the result of favorable price moves. Conclusion:

The Basis 基差 The difference between the futures price and the spot price is known as the basis
The Basis 基差 The difference between the futures price and the spot price is known as the basis
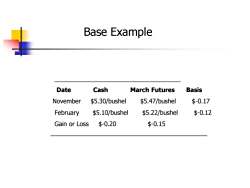
Base Example Date Cash March Futures Basis November $5.30/bushel $5.47/bushel $-0.17 February $5.10/bushel $5.22/bushel $-0.12 Gain or Loss $-0.20 $-0.15
_ Date Cash March Futures Basis November $5.30/bushel $5.47/bushel $-0.17 February $5.10/bushel $5.22/bushel $-0.12 Gain or Loss $-0.20 $-0.15 ————————————————————————— Base Example

SPREADS AND STRADDLES (套利和对冲) A spread is simply the simultaneous buying of one contract and selling of another. The price difference between two related markets or commodities. The purchase of one futures delivery month against the sale of another futures delivery month of the same commodity;
SPREADS AND STRADDLES (套利和对冲) ◼ A spread is simply the simultaneous buying of one contract and selling of another. ◼ The price difference between two related markets or commodities. ◼ The purchase of one futures delivery month against the sale of another futures delivery month of the same commodity;

SPREADS AND STRADDLES 套利和对冲 A spread can also apply to options.It involves buying one futures contract and selling another futures contract. The purpose is to profit from an unexpected change in the relationship between the purchase price of one and the selling price of the other
A spread can also apply to options. It involves buying one futures contract and selling another futures contract. The purpose is to profit from an unexpected change in the relationship between the purchase price of one and the selling price of the other. SPREADS AND STRADDLES 套利和对冲

SPREADS AND STRADDLES 套利和对冲 Because gains and losses occur only as the result of a change in the price difference- rather than as a result of a change in the overall level of futures prices spreads are often considered more conservative and less risky than having an outright long or short futures position
Because gains and losses occur only as the result of a change in the price difference – rather than as a result of a change in the overall level of futures prices - spreads are often considered more conservative and less risky than having an outright long or short futures position . SPREADS AND STRADDLES 套利和对冲
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 3 The Modern Futures Exchange.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 2 Beginning with the Basics.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 0 International Futures Markets Operation.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 1 The Journey Ahead.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程授课教案(讲义,英文版).doc
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学大纲 International Futures Market Operation.doc
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)12 时间序列计量经济模型.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)07 自相关(Autocorrelation).ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)10 滞后变量模型.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)11 联立方程模型的识别和估计.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)09 K元线性回归模型的扩展.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)08 随机解释变量.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)06 广义最小二乘法(GLS)与异方差(Heteroskedasticity).ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)02 简单线性回归模型.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)05 多重共线性(Multicollinearity).ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)01 计量经济学基本问题.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)04 K元线性回归模型.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)03 矩阵代数复习.ppt
- 《计量经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第十章 随机时间序列(含答案).doc
- 《计量经济学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第八章 线性回归模型扩展(含答案).doc
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 6 Getting Started in Trading Futures.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 5 The Variety of Futures Markets.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 4 Life on the Trading Floor.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 10 Technical Analysis Chart Patterns.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 11 Timing Indicators.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 8 How to Trade the Futures Options.ppt
- 《国际期货市场运作》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Chapter 9 Fundamental Analysis.ppt
- 《审计学》课程教学大纲 Auditing(64学时).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学大纲 Audit of financial(财务审计,64学时).doc
- 《审计学》课程授课教案(64学时,石河子大学:池玉莲).doc
- 《审计学》课程授课教案(2011-2012,上,石河子大学:池玉莲).doc
- 《审计学》课程授课教案(2015-2016,下,48学时,石河子大学:池玉莲).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)审计习题集(答案,非注册班).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)审计习题集(题目,非注册班).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)审计学习题集(答案108).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)审计学习题集(题目108).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)审计学各章习题集(答案2103).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第八章 审计报告和管理建议书(题目2103).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第六章 内部控制及其评价(题目2103).doc
- 《审计学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)第五章 审计程序(题目2103).doc
