电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 Task Management

2 University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) Chapter 4 Task Management Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
2 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) Chapter 4 Task Management

3 1 Overview University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) Task management Scheduling Policy Synchronization,Communication,Mutex Coordinate mechanism Memory management Inventory management mechanism Interruption Time management Event dealing mechanisms: Event-triggered mechanism Time-triggered mechanism Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
3 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 1 Overview Task management Synchronization,Communication,Mutex Memory management Interruption & Time management Event dealing mechanisms: Event-triggered mechanism Time-triggered mechanism Coordinate mechanism Inventory management mechanism Scheduling Policy

4 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) _What does the kernel do Scheduling What does the kernel scheduling Tasks >What are tasks Real-Time Systems(RTS)? >Characteristics of tasks o Concurrence (Simultaneousness) Scheduler o Dynamic o Asynchrony Independence (Synchrony dependence) 0… Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
4 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management What does the kernel do ? Scheduling What does the kernel scheduling ? Tasks What are tasks & Real-Time Systems (RTS)? Characteristics of tasks o Concurrence (Simultaneousness) o Dynamic o Asynchrony & Independence (Synchrony & dependence) o …… Scheduler

5 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) >Classification of tasks o Periodic tasks o Sporadic tasks o Aperiodic tasks Critical tasks Non-critical tasks Hard real-time tasks √Soft real--time tasks Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
5 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management Classification of tasks o Periodic tasks o Sporadic tasks o Aperiodic tasks Critical tasks Non-critical tasks Hard real-time tasks Soft real-time tasks

6 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met >Tasks and their special requirements o Task: T(=1,2,n) o Task number: n o Period: P o Executing time: e; o Relative deadline: D o Absolute deadline: d What's the difference between task and process? o Release time: ri Time related parameters o Phasing: 工 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
6 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met ? Tasks and their special requirements ? o Task: Ti ( i=1,2,…,n ) o Task number: n o Period: Pi o Executing time: ei o Relative deadline: Di o Absolute deadline: di o Release time: ri o Phasing: Ii What's the difference between task and process? Time related parameters

7 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met Special measures for Guaranteeing task deadlines o Preemptive 0 Periodic task o Relative deadline (D)=Period (P) 0 Priority is inversely related to the period (P) 0 Other assumptions: 1)The cost of Preemption is negligible 2) Only processing requirements are significant 3)Tasks are independent,no precedence constraints Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
7 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met ? Special measures for Guaranteeing task deadlines o Preemptive o Periodic task o Relative deadline (Di ) o Priority o Other assumptions: 1) The cost of Preemption is negligible 2) Only processing requirements are significant 3) Tasks are independent, no precedence constraints is inversely related to the period (Pi ) = Period (Pi )

8 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met What does the scheduler do for Guaranteeing task deadlines 1)Which task should be executed by the processor? 2)When does a task begin to execute? 3)How long is a task executing Priority is inversely related to the period (P) Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
8 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met ? What does the scheduler do for Guaranteeing task deadlines ? 1) Which task should be executed by the processor? 2) When does a task begin to execute? 3) How long is a task executing ? Priority is inversely related to the period (Pi )

9 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met How to know a given scheduling policy can Guarantee task deadlines 1)Schedulability analysis on the policy (following) Priority is inversely related to the period (P) Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
9 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met ? How to know a given scheduling policy can Guarantee task deadlines ? 1) Schedulability analysis on the policy (following) Priority is inversely related to the period (Pi )

10 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met Necessary and sufficient conditions for schedulability If mine t ≤L,task7,isschedulable. yfs欧lmmg》s1,are化,网enne entire set T is schedulable. T={P,l=1,2,i;=1,2,…[P/P]} i={1,2,, Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
10 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met ? Necessary and sufficient conditions for schedulability If , task Ti min 1 is schedulable. i i t W t If , for i∈{1,…,n},then the entire set T is schedulable. max {min } 1 {1,..., } i i i n t W t τi={lPi | j=1,2,…,i ; l=1,2,…,[ Pi /Pj ]} i={1,2,…,n}
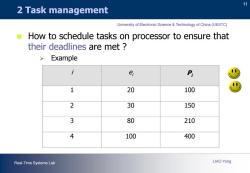
11 2 Task management University of Electronic Science Technology of China(UESTC) How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met >Example i e P 1 20 100 2 30 150 3 80 210 4 100 400 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong
11 Real-Time Systems Lab LIAO Yong University of Electronic Science & Technology of China (UESTC) 2 Task management How to schedule tasks on processor to ensure that their deadlines are met ? Example i ei Pi 1 20 100 2 30 150 3 80 210 4 100 400
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Software System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Hardware System.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 Overview(廖勇).pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Universal Hashing.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Random Rounding.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Moments.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Mixing.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Min-Cut.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Markov Chain.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lovász Local Lemma.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Identity Testing.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Finger printing.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Coupling.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Concentration.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chernoff.pdf
- 南京大学:《随机算法 Randomized Algorithms》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Balls and Bins.pdf
- 南京大学:《组合数学 Combinatorics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Ramsey Theory.pdf
- 南京大学:《组合数学 Combinatorics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)The Probabilistic Method.pdf
- 南京大学:《组合数学 Combinatorics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion(PIE).pdf
- 南京大学:《组合数学 Combinatorics》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Polya.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 ask Management.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Case Analysis - Use DARTS to Design a S/W System of Robot Controller.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Case 4.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《嵌入式系统设计 Embedded Systems Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Hot topics in ES.pdf
- 中国计算机学会学术著作丛书:《对等网络——结构、应用与设计 Peer-to-Peer Network Structure, Application and Design》PDF电子书(正文,共九章).pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Dynamic inference in probabilistic graphical models.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Dynamic Sampling from Graphical Models.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)On Local Distributed Sampling and Counting.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)What can be sampled locally?.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Convergence of MCMC and Loopy BP in the Tree Uniqueness Region for the Hard-Core Model.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Counting hypergraph matchings up to uniqueness threshold.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Simple average-case lower bounds for approximate near-neighbor from isoperimetric inequalities.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Spatial mixing and the connective constant - Optimal bounds.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Spatial Mixing of Coloring Random Graphs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Approximate Counting via Correlation Decay in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Approximate Counting via Correlation Decay on Planar Graphs.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Assigning Tasks for Efficiency in Hadoop.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Correlation Decay up to Uniqueness in Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Improved FPTAS for Multi-Spin Systems.pdf
- 《计算机科学》相关教学资源(参考文献)Cell-probe proofs and nondeterministic cell-probe complexity.pdf
