重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)结核性脑膜炎 Tuberculous Meningitis(英文)

Tuberculous Meningitis CHCUMS CHCUMS DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND GASTROENTEROLOGY
1 Tuberculous Meningitis CHCUMS DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND GASTROENTEROLOGY

EPIDEMIOLOGY TBM Tuberculous Meningitis (TBM) The younger the children,the more readily to develop TBM. 60%in Children aged 1-3 years ◆Death rate:15-30% 2
2 EPIDEMIOLOGY - TBM Tuberculous Meningitis (TBM) ◆ The younger the children, the more readily to develop TBM. ◆ 60% in Children aged 1-3 years ◆ Death rate: 15-30%

TBM (Tuberculous meningitis) TBM is the most serious complication of tuberculosis in children and is usually fatal without treatment. TBM always be a part of systemic disseminated tuberculosis. TBM often occurs within 1 year of initial infection,especially in the first 2 to 6 months of infection. 3
3 TBM (Tuberculous meningitis) ◆ TBM is the most serious complication of tuberculosis in children and is usually fatal without treatment. ◆ TBM always be a part of systemic disseminated tuberculosis. ◆ TBM often occurs within 1 year of initial infection, especially in the first 2 to 6 months of infection
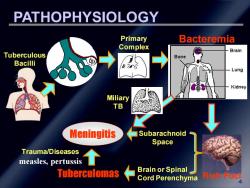
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Primary Bacteremia Complex Brain →® Tuberculous Bone Bacil Lung Kidney Miliary TB Meningitis Subarachnoid Space Trauma/Diseases measles,pertussis Tuberculomas Brain or Spinal Cord PerenchymaRo
4 Tuberculous Bacilli Primary Complex Bacteremia Rich Foci Subarachnoid Space Brain or Spinal Cord Perenchyma Tuberculomas Meningitis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Trauma/Diseases measles, pertussis Miliary TB

PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Meninges ◆ Diffuse Hyperemia ◆ Edema Inflammatory Exudates Conformation of Tubercles 5
5 PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Meninges ◆ Diffuse Hyperemia ◆ Edema ◆ Inflammatory Exudates ◆ Conformation of Tubercles

PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Subarachnoid Space A large amount of thick gelatinous exudates concentrate to the pavimentum cerebri,optic chiasma,bridge of varolius, bulbus rhachidicus and Sylvian fissure. Basal meningitis accounts for the frequent dysfunction of cranial nerves III, VL,andVⅡ. 6
6 PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Subarachnoid Space ◆A large amount of thick gelatinous exudates concentrate to the pavimentum cerebri, optic chiasma, bridge of varolius, bulbus rhachidicus and Sylvian fissure. ◆ Basal meningitis accounts for the frequent dysfunction of cranial nerves III, VI, and VII

PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Cerebral Parenchyma Tuberculous meningoencephalitis swelling and hyperemia of the parenchyma contribute to the intracranial hypertension,then ischemia of parenchyma occur,finally lead to the foci of encephalomalacia and necrosis. Hemiplegia may be present because of this change. Meninges,spinal,and spinal nerve root also involvement.The later always leads to paraplegina
7 PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Cerebral Parenchyma Tuberculous meningoencephalitis ◆ swelling and hyperemia of the parenchyma contribute to the intracranial hypertension, then ischemia of parenchyma occur, finally lead to the foci of encephalomalacia and necrosis. Hemiplegia may be present because of this change. ◆ Meninges, spinal, and spinal nerve root also involvement. The later always leads to paraplegina

PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Cerebral Vessels The bacteria invade the adventitia directly in the early stage and initiate the process of acute vasculitis. Progressive destruction of adventitia. disruption of elastic fibers,and finally intimal destruction (endoarteritis),lead to the obliterative vasculitis,which may facilitate the ischemia,encephalomalacia and necrosis of parenchyma
8 PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Cerebral Vessels ◆The bacteria invade the adventitia directly in the early stage and initiate the process of acute vasculitis. ◆Progressive destruction of adventitia, disruption of elastic fibers, and finally intimal destruction (endoarteritis), lead to the obliterative vasculitis, which may facilitate the ischemia, encephalomalacia and necrosis of parenchyma
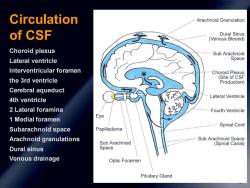
Circulation Arachnoid Granulation of CSF Dural Sinus (Venous Bloood) Choroid plexus Sub Arachnoid Lateral ventricle Space Interventricular foramen Choroid Plexus the 3rd ventricle (Site of CSF Production) Cerebral aqueduct Lateral Ventricle 4th ventricle 2 Lateral foramina Fourth Ventricle 1 Medial foramen Eye Spinal Cord Subarachnoid space Papilledema Arachnoid granulations Sub Arachnoid Space Sub Arachnoid (Spinal Canal) Dural sinus Space Venous drainage Optic Foramen Pituitary Gland
9 Circulation of CSF Choroid plexus Lateral ventricle Interventricular foramen the 3rd ventricle Cerebral aqueduct 4th ventricle 2 Lateral foramina 1 Medial foramen Subarachnoid space Arachnoid granulations Dural sinus Venous drainage

PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Hydrocephalus Hyperemia of choroids overproduction of CSF Inflammatory adherence of defective absorption Meninge of CSF CSF flow is obstructed on the route Communicating before the cerebral aqueduct and the hydrocephalus 4th ventricle Noncommunicating hydrocephalus 10
10 PATHOLOGICAL EFFECTS Hydrocephalus Hyperemia of choroids overproduction of CSF Inflammatory adherence of Meninge defective absorption of CSF Communicating hydrocephalus CSF flow is obstructed on the route before the cerebral aqueduct and the 4th ventricle Noncommunicating hydrocephalus
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性腮腺炎 MUMPS(英文).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)小儿腹泻病和补液疗法(英文).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)婴儿肝炎综合征.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)麻疹.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)猩红热.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)狂犬病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性腮腺炎.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性乙型脑炎.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)小儿腹泻病和补液疗法.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)儿童爱滋病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)伤寒.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)中毒型细菌性痢疾.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性脑脊髓膜炎.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)儿童结核病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)传染性单核细胞增多症.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)中毒型细菌性痢疾.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)猩红热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)液体疗法.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)婴儿肝炎综合症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)小儿原发性结核.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)麻疹 MEASLES(英文).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)Mood Disorders.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)Stress-related disorders.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)器质性疾病所致精神障碍.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)应激相关障碍 Stress-Related Disorders.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)特殊人群的精神障碍.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)神经症(neuroses).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)神经症性障碍 Neurotic Disorder.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神分裂症 schizophrenia.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神分裂症 schizophrenia.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神活性物质所致精神障碍.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神病学总论及相关法律问题.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神病学总论和症状学.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神障碍的护理与康复.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神科急诊与护理.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学大纲.docx
- 《运动解剖学》课程基本功大赛复习题及答案(共300题).docx
- 《运动解剖学》课程教学资源(授课教案)运动解剖学完整讲义.docx
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)总论.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)流脑.doc
