重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性腮腺炎 MUMPS(英文)

MUMPS Epidemic Parotitis Associate Pr.Zhan xue DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND GASTROENTEROLOGY CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL.CQMU. 4Jun.2009 1 重庆医科大学儿童医院传染病教研室
1 DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASE AND GASTROENTEROLOGY CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL. CQMU. 4 Jun. 2009 Associate Pr. Zhan xue MUMPS Epidemic Parotitis

MUMPS A child with mumps often looks like a chipmunk with a full mouth due to the swelling of the parotids. 重庆 开室
2 MUMPS A child with mumps often looks like a chipmunk with a full mouth due to the swelling of the parotids

General view about Mumps Acute respiratory tract infection ■A systemic disease High affinity to nerve tissue and glands Nonsuppurative inflammation of salivary glands Meningocephalitis,pancreatitis,and orchitis Parotitis and orchitis described by Hippocrates in 5th century B.C. Viral etiology described by Johnson and Goodpasture in 1934 ■Notifiable disease 3 重庆医科大学儿童医院传染病教研室
3 ◼ Acute respiratory tract infection ◼ A systemic disease ◼ High affinity to nerve tissue and glands ◼ Nonsuppurative inflammation of salivary glands ◼ Meningocephalitis, pancreatitis, and orchitis ◼ Parotitis and orchitis described by Hippocrates in 5th century B.C. ◼ Viral etiology described by Johnson and Goodpasture in 1934 ◼ Notifiable disease General view about Mumps

Countries using mumps vaccine in their routine national immunization system,2005 Routine mumps implementation status Yes (110countries or 57%) 门1No82coar1esor43%) Source:WHOAIVB database,192 WHO Member States.Data as of September 2006 Date of slide:4 September 2006 WHO 重厌医科大学儿重医院传染病数研室
4 PREVENTION

MUMPS √ETIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY √PATHOPHYSIOLGY PATHOLOGY CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS √INVESTIGATONS DIAGNOSIS DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS √TREATMENT PROGNOSIS& PREVENTION 重庆医科大学儿童医综传染病教研室
5 ✓ ETIOLOGY ✓ EPIDEMIOLOGY ✓ PATHOPHYSIOLGY ✓ PATHOLOGY ✓ CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS ✓ INVESTIGATONS ✓ DIAGNOSIS ✓ DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS ✓ TREATMENT ✓ PROGNOSIS & PREVENTION MUMPS

ET OLOGY 6 重庆医科大学儿童医院传染病教研室
6 ETIOLOGY

Genus Paramyxovirus Human Parainfluenza Virus (1-4) Genus Rubulavirus Mumps Subfamily Genus Morbillivirus Paramyxovirinae 。Measles amily Genus Henipavirus Nipah virus and Hendra Virus aram o These viruses are animal paramyxoviruses capable of jumping species,and causing severe,often fatal disease in humans.This makes them a concerning emerging infection. o The natural reservoir of both is thought to be bats of the genus Pteropus.Humans become infected though close association with infected domestic animals.Neither is spread person-to-person o Hendra viruses cause respiratory illness with severe flu-like symptoms.Nipah virus causes encephalitis in Southeast Asia and in Australia. Genus Pneumovirus Subfamily ·RsV Pneumovirinae Genus Metapneumovirus Metapneumovirus 更大医科人字儿单医觉专华丙致至
7
ETIOLOGY-MUMIPORGRUSUS RV MaV Phylogenetic tree of MuV PIV4a SV5 SV41 Paramyxovirinae hPIV2 Subfamily Rubulavirus NDV Avulavirus SalV hPIV3 CDV Mev SeV Morbillivirus Respirovirus Henipavirus TPMV Copyright 2006 Nature Publishing Group 8 Nature Reviews Microbiology 重庆医科大学儿童医院传染病教研室
8 ETIOLOGY MUMPS VIRUS MUMPS VIRUS Phylogenetic tree of Paramyxovirinae Subfamily

ETIOLOGY-MUMIPRERUISUS ■ Classification:A RNA virus single-stranded negative Genus:Rubulavirus Family:paramyxoviridae ■ Serotype:Only one Location:Saliva,Cerebrospinal fluid Blood,Urine,infectious tissues cold-resistant Disinfections:Rapidly inactivate by chemical agents,heat and ultraviolet light Man are only host 9 重庆医科大学儿童医院传染病教研室
9 ETIOLOGY MUMPS VIRUS ◼ Classification: A RNA virus single-stranded negative Genus: Rubulavirus Family: paramyxoviridae ◼ Serotype: Only one ◼ Location: Saliva, Cerebrospinal fluid Blood, Urine, infectious tissues ◼ cold-resistant ◼ Disinfections: Rapidly inactivate by chemical agents, heat and ultraviolet light ◼ Man are only host MUMPS VIRUS
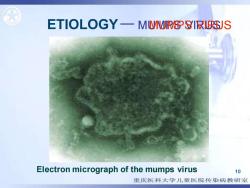
ETIOLOGY一MMRIRJS Electron micrograph of the mumps virus 10 重庆医科大学儿童医院传染病教研室
10 ETIOLOGY MUMPS VIRUS Electron micrograph of the mumps virus MUMPS VIRUS
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)小儿腹泻病和补液疗法(英文).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)婴儿肝炎综合征.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)麻疹.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)猩红热.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)狂犬病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性腮腺炎.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性乙型脑炎.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)小儿腹泻病和补液疗法.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)儿童爱滋病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)伤寒.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)中毒型细菌性痢疾.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)流行性脑脊髓膜炎.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)儿童结核病.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)传染性单核细胞增多症.ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)中毒型细菌性痢疾.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)猩红热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)液体疗法.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)婴儿肝炎综合症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)小儿原发性结核.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学资源(授课教案)麻疹.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)结核性脑膜炎 Tuberculous Meningitis(英文).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《小儿感染病学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)麻疹 MEASLES(英文).ppt
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)Mood Disorders.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)Stress-related disorders.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)器质性疾病所致精神障碍.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)应激相关障碍 Stress-Related Disorders.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)特殊人群的精神障碍.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)神经症(neuroses).pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)神经症性障碍 Neurotic Disorder.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神分裂症 schizophrenia.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神分裂症 schizophrenia.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神活性物质所致精神障碍.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神病学总论及相关法律问题.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神病学总论和症状学.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神障碍的护理与康复.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神科急诊与护理.pdf
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学大纲.docx
- 《运动解剖学》课程基本功大赛复习题及答案(共300题).docx
- 《运动解剖学》课程教学资源(授课教案)运动解剖学完整讲义.docx
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)总论.doc
