《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Eggs

Chapter 7 Eggs
Chapter 7 Eggs
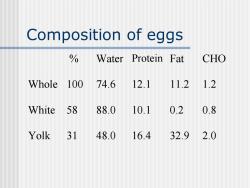
Composition of eggs % Water Protein Fat CHO Whole 100 74.6 12.1 11.2 1.2 White 58 88.0 10.1 0.2 0.8 Yolk 31 48.0 16.4 32.9 2.0
Composition of eggs % Water Protein Fat CHO Whole 100 74.6 12.1 11.2 1.2 White 58 88.0 10.1 0.2 0.8 Yolk 31 48.0 16.4 32.9 2.0

Composition of Eggs - egg white (albumen) • Water (~88%) • CHO (~1%) −mainly glucose, may cause brown discoloration in dried eggs and hard cooked eggs (Millard reaction) • Fat (trace)
Composition of Eggs - egg white (albumen) • Water (~88%) • CHO (~1%) −mainly glucose, may cause brown discoloration in dried eggs and hard cooked eggs (Millard reaction) • Fat (trace)

Composition of Eggs - egg white (albumen) • Proteins (~11%), most are glycoproteins −Three primary proteins: − ovalbumin (54%) Structure of Baked Products ovotransferrin (12%), Binds metal, Discoloration ovomucoid (11%) Protease Inhibitor − ovomucin (1.5%): A Fibrous Protein, contributes to the thickness of the white (4 x more abundant than in yolk), contributes to the stability of egg white foam
Composition of Eggs - egg white (albumen) • Proteins (~11%), most are glycoproteins −Three primary proteins: − ovalbumin (54%) Structure of Baked Products ovotransferrin (12%), Binds metal, Discoloration ovomucoid (11%) Protease Inhibitor − ovomucin (1.5%): A Fibrous Protein, contributes to the thickness of the white (4 x more abundant than in yolk), contributes to the stability of egg white foam

Composition of Eggs - egg white (albumen) • Proteins (cont’n) •globulins (8%): including lysozyme, are important for foaming •lysozyme: ability to hydrolyze a polysaccharide in the cell wall of some bacteria to prevent bacterial spoilage • others: ovoinhibitor, ovoflavoprotein, ovomicroglobulin, avidin (binds biotin, but is heat sensitive)
Composition of Eggs - egg white (albumen) • Proteins (cont’n) •globulins (8%): including lysozyme, are important for foaming •lysozyme: ability to hydrolyze a polysaccharide in the cell wall of some bacteria to prevent bacterial spoilage • others: ovoinhibitor, ovoflavoprotein, ovomicroglobulin, avidin (binds biotin, but is heat sensitive)

Composition of Eggs - egg yolk • Proteins (16.4%): • plasma (78%): livetin & LDL (protein content ~ 10%) • granular fraction: phosvitin (16%, carrier of Fe), lipovitellins (70%) & LDL (12%) • Water (48%)
Composition of Eggs - egg yolk • Proteins (16.4%): • plasma (78%): livetin & LDL (protein content ~ 10%) • granular fraction: phosvitin (16%, carrier of Fe), lipovitellins (70%) & LDL (12%) • Water (48%)

Composition of Eggs - egg yolk •Lipids (32 to 34%) − triglycerol (66%) − phospholipid (28%) including lecithin − (has remarkable emulsifying ability) − cholesterol (3%, or 250 mg) •The color of yolk depends on the presence of carotenoids. • xanthophylls not carotene (Lutein and zeaxanthin)
Composition of Eggs - egg yolk •Lipids (32 to 34%) − triglycerol (66%) − phospholipid (28%) including lecithin − (has remarkable emulsifying ability) − cholesterol (3%, or 250 mg) •The color of yolk depends on the presence of carotenoids. • xanthophylls not carotene (Lutein and zeaxanthin)


Egg Quality • Commercial grading of eggs according to the USDA standards • External quality: shell characteristics, shape, soundness, cleanliness, & color • Interior quality: size of the air cell, firmness of the white, & the yolk (distinct or flattened during aging) • Evaluated by candling
Egg Quality • Commercial grading of eggs according to the USDA standards • External quality: shell characteristics, shape, soundness, cleanliness, & color • Interior quality: size of the air cell, firmness of the white, & the yolk (distinct or flattened during aging) • Evaluated by candling

Egg quality during storage • The size of the air cell increases − water evaporates from the egg through shell • The egg white becomes thinner − ovomucin undergoes degradation • pH of white increases (from ~ 8 to ~9) − due to the loss of CO2 through the pores
Egg quality during storage • The size of the air cell increases − water evaporates from the egg through shell • The egg white becomes thinner − ovomucin undergoes degradation • pH of white increases (from ~ 8 to ~9) − due to the loss of CO2 through the pores
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Milk and Milk Products.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Meat.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Food Preservation.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Carbohydrates:Starch and Sugars.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)General Food Safety.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Objective Evaluation of Food.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Top Ten Food Companies Public and Private Companies.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Experimental Foods.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Water.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lipids and Fats.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Minerals.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Carbohydrate.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Water.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Gas Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Flour.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Food Enzymes.ppt
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)绪论 Physical Chemistry.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)00 Chapter 0 Introduction.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)01 Chapter 1 The properties of gases.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)02 Chapter 2 The First Law the concepts.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)03 Chapter 3 The First Law the machinery.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)04 br Chapter 4 The Second Law the concepts.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)05 Chapter 5 The Second Law the machinery.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)06 Chapter 6 Physical transformation of pure substances.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)07 Chapter 7 Simple mixtures.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)08 Chapter 8 Phase diagrams.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)09 Chapter 9 Chemical equilibrium.pdf
- 华东理工大学:《物理化学》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)10 Chapter 10 Equilibrium electrochemistry.pdf
- 安徽农业大学:《茶叶生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论 Tea Biochemistry(主讲:李大祥).ppt
- 安徽农业大学:《茶叶生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 茶叶中的化学成分及其性质.ppt
- 安徽农业大学:《茶叶生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)茶叶生物化学试题库(无答案).doc
- 安徽农业大学:《茶叶生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 茶树次级代谢.ppt
- 安徽农业大学:《茶叶生物化学》课程教学资源(试卷习题)茶叶生物化学期末考试A卷(试题).doc
- 安徽农业大学:《茶叶生物化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 环境对茶树物质代谢的作用.ppt
