《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems

PHYSICAL STATE OF INGREDIENTS IN FOOD SYSTEMS Food Dispersions 1. True solution 2. Colloidal dispersion 3. Emulsion 4. Foam 5. Gel Dispersions 1. Continuous phase 2. Dispersed phase May be solid, liquid, or gas
PHYSICAL STATE OF INGREDIENTS IN FOOD SYSTEMS Food Dispersions 1. True solution 2. Colloidal dispersion 3. Emulsion 4. Foam 5. Gel Dispersions 1. Continuous phase 2. Dispersed phase May be solid, liquid, or gas

True Solution The dispersion of particle < 1 nm in liquid. Examples: sugar, lactose, minerals, and vitamins. Colloidal Dispersion (SOL) Dispersion of particle sizes between 10-100 nm in liquid. Common colloids: dispersion of proteins, large molecular salts. Example: milk
True Solution The dispersion of particle < 1 nm in liquid. Examples: sugar, lactose, minerals, and vitamins. Colloidal Dispersion (SOL) Dispersion of particle sizes between 10-100 nm in liquid. Common colloids: dispersion of proteins, large molecular salts. Example: milk

Emulsions Liquid/liquid systems of 2 immiscible substances are called emulsion. Substances or particle size = 10-100 microns. Examples: butter (w/o), margarine (w/o), mayonnaise (o/w), salad dressing (o/w), milk (o/w), cream (o/w), and chip-dip (o/w). Water Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil H O H O H O H O Oil/Water Water/Oil 2 2 2 2 Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil
Emulsions Liquid/liquid systems of 2 immiscible substances are called emulsion. Substances or particle size = 10-100 microns. Examples: butter (w/o), margarine (w/o), mayonnaise (o/w), salad dressing (o/w), milk (o/w), cream (o/w), and chip-dip (o/w). Water Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil H O H O H O H O Oil/Water Water/Oil 2 2 2 2 Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil
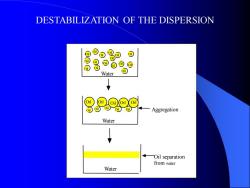
DESTABILIZATION OF THE DISPERSION Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Water Water Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Water Oil Aggregation Oil separation from water
DESTABILIZATION OF THE DISPERSION Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Water Water Oil Oil Oil Oil Oil Water Oil Aggregation Oil separation from water

EMULSIFIER Oil Water Mayonnaise Water Oil Margarine Emulsifier Hydrophobicgroup Hydrophilic group
EMULSIFIER Oil Water Mayonnaise Water Oil Margarine Emulsifier Hydrophobicgroup Hydrophilic group

CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF EMULSIFIERS CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 O C (CH2)16 CH3 O O N CH2 CH2 O P O CH2 O CH O C (CH2)14 CH3 O CH2 O C (CH2)16 CH3 HO CH HO CH2 O CH2 O C (CH2)16 CH3 CH O C (CH2)16 CH3 HO CH2 O O Phospholipids (Lecithin) Hydrophobic ( fat-soluble) Hydrophilic (water-soluble) Mono-Glycerides(mono-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Di-glycerides (di-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic - +
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF EMULSIFIERS CH3 CH3 CH3 CH2 O C (CH2)16 CH3 O O N CH2 CH2 O P O CH2 O CH O C (CH2)14 CH3 O CH2 O C (CH2)16 CH3 HO CH HO CH2 O CH2 O C (CH2)16 CH3 CH O C (CH2)16 CH3 HO CH2 O O Phospholipids (Lecithin) Hydrophobic ( fat-soluble) Hydrophilic (water-soluble) Mono-Glycerides(mono-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Di-glycerides (di-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic - +

O C CH CH 2 O C (CH 2)16 CH 3 C CH C H2 H O OH H OH HO O OH O H2 O C CH CH 2 O C (CH 2)16 CH 3 C CH C O CH 2 CH 2 O CH 2 CH 2OH CH2 CH2 O CH 2 CH 2OH Span 60 (sorbitan mono-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Tween 60 (polyoxyalkylene sorbitan mono-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic
O C CH CH 2 O C (CH 2)16 CH 3 C CH C H2 H O OH H OH HO O OH O H2 O C CH CH 2 O C (CH 2)16 CH 3 C CH C O CH 2 CH 2 O CH 2 CH 2OH CH2 CH2 O CH 2 CH 2OH Span 60 (sorbitan mono-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Tween 60 (polyoxyalkylene sorbitan mono-stearate) Hydrophobic Hydrophilic

SOME DESIRABLE CHARACTERISTICS OF FOOD EMULSIFIERS 1. Ability to reduce interfacial tension below 10 dynes/cm 2. Ability to be rapidly absorbed at the interface 3. Ability to function effectively at low concentrations 4. Resistance to chemical change 5. Lack of odor, color, and toxicity 6. Economical
SOME DESIRABLE CHARACTERISTICS OF FOOD EMULSIFIERS 1. Ability to reduce interfacial tension below 10 dynes/cm 2. Ability to be rapidly absorbed at the interface 3. Ability to function effectively at low concentrations 4. Resistance to chemical change 5. Lack of odor, color, and toxicity 6. Economical

FOAM Gas is dispersed in liquid or semi-liquid. Dispersed-phase: gas Continuous-phase: liquid It requires a 3rd component possessing protective or stabilizing properties to maintain the dispersion. Example: whipped topping
FOAM Gas is dispersed in liquid or semi-liquid. Dispersed-phase: gas Continuous-phase: liquid It requires a 3rd component possessing protective or stabilizing properties to maintain the dispersion. Example: whipped topping

The important foam stability factors are: 1. Surface tension 2. Concentration of separate phase 3. Presence of foaming agent to lower surface tension 4. Viscosity of liquid - the higher the viscosity, the more stable the foam. 5. Presence and thickness of adsorption layer (a 3rd stabilizing material)
The important foam stability factors are: 1. Surface tension 2. Concentration of separate phase 3. Presence of foaming agent to lower surface tension 4. Viscosity of liquid - the higher the viscosity, the more stable the foam. 5. Presence and thickness of adsorption layer (a 3rd stabilizing material)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Vitamin.ppt
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzyme Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Primary sequence.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Denaturation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Modifications of Food Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Functionality.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Chemical Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water activity and toxins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Introduction.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzymes.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Carbohydrates.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Effects of Lipid Oxidation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Food Lipids.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Browning Reactions.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity.pdf
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品添加剂概论.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Gas Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Water.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Carbohydrate.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Minerals.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lipids and Fats.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Water.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Experimental Foods.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Top Ten Food Companies Public and Private Companies.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Objective Evaluation of Food.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)General Food Safety.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Carbohydrates:Starch and Sugars.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Food Preservation.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Meat.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Milk and Milk Products.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Eggs.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Flour.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Food Enzymes.ppt
