《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzyme Kinetics
Enzyme kinetics z Study of the rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions z Provides information on enzyme specificities and mechanisms
Enzyme kinetics z Study of the rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions z Provides information on enzyme specificities and mechanisms
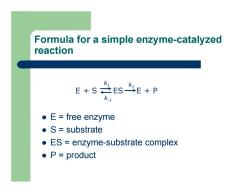
Formula for a simple enzyme-catalyzed reaction z E = free enzyme z S = substrate z ES = enzyme-substrate complex z P = product E + S ES E + P k 1 k-1 k2
Formula for a simple enzyme-catalyzed reaction z E = free enzyme z S = substrate z ES = enzyme-substrate complex z P = product E + S ES E + P k 1 k-1 k2
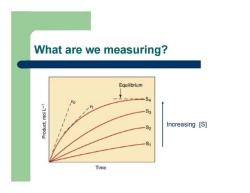
What are we measuring? Increasing [S]
What are we measuring? Increasing [S]
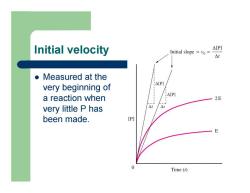
Initial velocity z Measured at the very beginning of a reaction when very little P has been made
Initial velocity z Measured at the very beginning of a reaction when very little P has been made
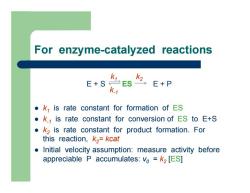
For enzyme-catalyzed reactions z k 1 is rate constant for formation of ES z k-1 is rate constant for conversion of ES to E+S z k2 is rate constant for product formation. For this reaction, k2= kcat z Initial velocity assumption: measure activity before appreciable P accumulates: v0 = k2 [ES ] E + S ES E + P k k 1 2 k-1
For enzyme-catalyzed reactions z k 1 is rate constant for formation of ES z k-1 is rate constant for conversion of ES to E+S z k2 is rate constant for product formation. For this reaction, k2= kcat z Initial velocity assumption: measure activity before appreciable P accumulates: v0 = k2 [ES ] E + S ES E + P k k 1 2 k-1
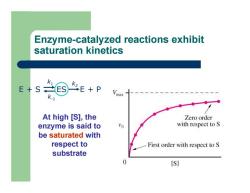
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions exhibit saturation kinetics E + S ES E + P k 1 k-1 k2 At high [S], the enzyme is said to be saturated with respect to substrate
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions exhibit saturation kinetics E + S ES E + P k 1 k-1 k2 At high [S], the enzyme is said to be saturated with respect to substrate

Steady State The more ES present, the faster ES will dissociate into E + P or E + S. Therefore, when the reaction is started by mixing enzymes and substrates, the [ES] builds up at first, but quickly reaches a STEADY STATE, in which [ES] remains constant. This steady state will persist until almost all of the substrate has been consumed
Steady State The more ES present, the faster ES will dissociate into E + P or E + S. Therefore, when the reaction is started by mixing enzymes and substrates, the [ES] builds up at first, but quickly reaches a STEADY STATE, in which [ES] remains constant. This steady state will persist until almost all of the substrate has been consumed
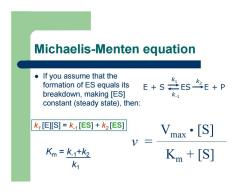
Michaelis-Menten equation z If you assume that the formation of ES equals its breakdown, making [ES] constant (steady state), then: Km = k-1 + k2 k 1 v = Vmax • [S] Km + [S] E + S ES E + P k 1 k-1 k2 k1 [E][S] = k-1 [ES] + k2 [ES ]
Michaelis-Menten equation z If you assume that the formation of ES equals its breakdown, making [ES] constant (steady state), then: Km = k-1 + k2 k 1 v = Vmax • [S] Km + [S] E + S ES E + P k 1 k-1 k2 k1 [E][S] = k-1 [ES] + k2 [ES ]
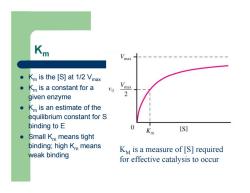
Km z Km is the [S] at 1/2 Vmax z Km is a constant for a given enzyme z Km is an estimate of the equilibrium constant for S binding to E z Small Km means tight binding; high Km means weak binding KM is a measure of [S] required for effective catalysis to occur
Km z Km is the [S] at 1/2 Vmax z Km is a constant for a given enzyme z Km is an estimate of the equilibrium constant for S binding to E z Small Km means tight binding; high Km means weak binding KM is a measure of [S] required for effective catalysis to occur

Understanding Vmax The theoretical maximal velocity z Vmax is a constant for a given enzyme z Vmax is the theoretical maximal rate of the reaction - but it is NEVER achieved z To reach Vmax would require that ALL enzyme molecules have tightly bound substrate
Understanding Vmax The theoretical maximal velocity z Vmax is a constant for a given enzyme z Vmax is the theoretical maximal rate of the reaction - but it is NEVER achieved z To reach Vmax would require that ALL enzyme molecules have tightly bound substrate
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Primary sequence.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Denaturation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Modifications of Food Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Functionality.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Chemical Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water activity and toxins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Introduction.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzymes.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Carbohydrates.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Effects of Lipid Oxidation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Food Lipids.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Browning Reactions.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity.pdf
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品添加剂概论.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 风味化学.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 色素.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 维生素和矿物质.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 脂类 Lipids.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Vitamin.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Gas Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Water.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Carbohydrate.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Minerals.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lipids and Fats.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Water.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Experimental Foods.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Top Ten Food Companies Public and Private Companies.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Objective Evaluation of Food.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)General Food Safety.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Carbohydrates:Starch and Sugars.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Food Preservation.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Meat.ppt
