《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzymes
Enzymes z Enzymes are proteins and certain class of RNA (ribozymes) which enhance the rate of a thermodynamically feasible reaction and are not permanently altered in the process
Enzymes z Enzymes are proteins and certain class of RNA (ribozymes) which enhance the rate of a thermodynamically feasible reaction and are not permanently altered in the process
Enzymes z Cofactors z Coenzymes z Holoenzyme z Apoenzyme
Enzymes z Cofactors z Coenzymes z Holoenzyme z Apoenzyme
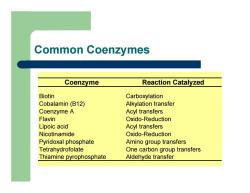
Common Coenzymes Coenzyme Reaction Catalyzed Biotin Carboxylation Cobalamin (B12) Alkylation transfer Coenzyme A Acyl transfers Flavin Oxido-Reduction Lipoic acid Acyl transfers Nicotinamide Oxido-Reduction Pyridoxal phosphate Amino group transfers Tetrahydrofolate One carbon group transfers Thiamine pyrophosphate Aldehyde transfer
Common Coenzymes Coenzyme Reaction Catalyzed Biotin Carboxylation Cobalamin (B12) Alkylation transfer Coenzyme A Acyl transfers Flavin Oxido-Reduction Lipoic acid Acyl transfers Nicotinamide Oxido-Reduction Pyridoxal phosphate Amino group transfers Tetrahydrofolate One carbon group transfers Thiamine pyrophosphate Aldehyde transfer

Why Enzymes? z Natures catalysts z Speed: 1016 over un-catalyzed rates! z Specificity: only the desired reaction occurs z Permit reactions under mild conditions
Why Enzymes? z Natures catalysts z Speed: 1016 over un-catalyzed rates! z Specificity: only the desired reaction occurs z Permit reactions under mild conditions

The Enzyme Reaction z Conventionally we say the enzyme acts on the substrate (S) to yield products (P) S P E Since E is a catalyst it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction
The Enzyme Reaction z Conventionally we say the enzyme acts on the substrate (S) to yield products (P) S P E Since E is a catalyst it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction
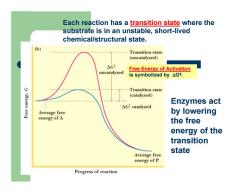
Each reaction has a transition state where the substrate is in an unstable, short-lived chemical/structural state. Free Energy of Activation is symbolized by ΔG‡. Enzymes act by lowering the free energy of the transition state
Each reaction has a transition state where the substrate is in an unstable, short-lived chemical/structural state. Free Energy of Activation is symbolized by ΔG‡. Enzymes act by lowering the free energy of the transition state

Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers z Enzyme speed reactions by lowering EA. – The transition state can be reached at moderate temperatures. z Enzymes do not change delta G. – It speed-up reactions that would occur eventually. z Because enzymes are so selective, they determine which chemical processes will occur at any time
Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers z Enzyme speed reactions by lowering EA. – The transition state can be reached at moderate temperatures. z Enzymes do not change delta G. – It speed-up reactions that would occur eventually. z Because enzymes are so selective, they determine which chemical processes will occur at any time

z Enzymes lower the free energy of activation by binding the transition state of the reaction better than the substrate z The enzyme must bind the substrate in the correct orientation otherwise there would be no reaction z Not a lock & key but induced fit – the enzyme and/or the substrate distort towards the transition state
z Enzymes lower the free energy of activation by binding the transition state of the reaction better than the substrate z The enzyme must bind the substrate in the correct orientation otherwise there would be no reaction z Not a lock & key but induced fit – the enzyme and/or the substrate distort towards the transition state
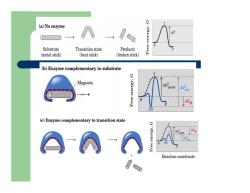
(a)No enzyme K8.oua △G Substrate Transition state Products (metal stick) (bent stick) (broken stick) (b)Enzyme complementary to substrate Magnets ES (c)Enzyme complementary to transition state Reaction coordinate

The active site z Typically a pocket or groove on the surface of the protein into which the substrate fits. z The specificity of an enzyme – fit between the active site and that of the substrate. z Enzyme changes shape – tighter induced fit, bringing chemical groups in position to catalyze the reaction
The active site z Typically a pocket or groove on the surface of the protein into which the substrate fits. z The specificity of an enzyme – fit between the active site and that of the substrate. z Enzyme changes shape – tighter induced fit, bringing chemical groups in position to catalyze the reaction
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Carbohydrates.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Effects of Lipid Oxidation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Food Lipids.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Browning Reactions.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity.pdf
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品添加剂概论.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 风味化学.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 色素.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 维生素和矿物质.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 脂类 Lipids.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 蛋白质 Proteins.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 碳水化合物 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 水(主讲教师:迟玉杰).ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 功能食品简介 functional food.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第九章 食品中营养成分的代谢.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 酶.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 矿物质.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 维生素.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 蛋白质.ppt
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Introduction.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water activity and toxins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Chemical Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Functionality.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Modifications of Food Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Denaturation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Primary sequence.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzyme Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Vitamin.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Gas Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Water.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Carbohydrate.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Minerals.ppt
