《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity

Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity z Temperature z pH z Water activity z Ionic Strength z Chemicals – Chelating agents – Reducing agents
Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity z Temperature z pH z Water activity z Ionic Strength z Chemicals – Chelating agents – Reducing agents
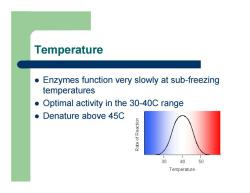
Temperature z Enzymes function very slowly at sub-freezing temperatures z Optimal activity in the 30-40C range z Denature above 45C
Temperature z Enzymes function very slowly at sub-freezing temperatures z Optimal activity in the 30-40C range z Denature above 45C

Temperature z Freezing – Activity depends on the enzyme (0 to –10C) – Below –10C almost always decrease activity z Factors involved in inconsistent behavior – Composition of medium – Rate and extent of freezing – Concentration effects – Viscosity – Changes in phase (crystallization of water, solidification of triacylglycerides)
Temperature z Freezing – Activity depends on the enzyme (0 to –10C) – Below –10C almost always decrease activity z Factors involved in inconsistent behavior – Composition of medium – Rate and extent of freezing – Concentration effects – Viscosity – Changes in phase (crystallization of water, solidification of triacylglycerides)
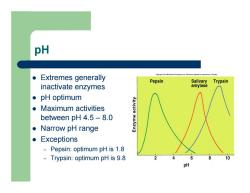
pH z Extremes generally inactivate enzymes z pH optimum z Maximum activities between pH 4.5 – 8.0 z Narrow pH range z Exceptions – Pepsin: optimum pH is 1.8 – Trypsin: optimum pH is 9.8
pH z Extremes generally inactivate enzymes z pH optimum z Maximum activities between pH 4.5 – 8.0 z Narrow pH range z Exceptions – Pepsin: optimum pH is 1.8 – Trypsin: optimum pH is 9.8

Water activity z Dried foods – Restricted water activity – Susceptible to enzymatic spoilage z The rate of enzymatic reactions in dried products is limited by the rate at which the substrate diffuses to the enzyme z Heat stability
Water activity z Dried foods – Restricted water activity – Susceptible to enzymatic spoilage z The rate of enzymatic reactions in dried products is limited by the rate at which the substrate diffuses to the enzyme z Heat stability

Electrolytes and Ionic Strength z Ions may be required components in the active site z Cation requirements of enzymes is sometimes specific z Salting in z Salting out
Electrolytes and Ionic Strength z Ions may be required components in the active site z Cation requirements of enzymes is sometimes specific z Salting in z Salting out

Chemicals z Chelating agents z Reducing agents z Alterations of substrates
Chemicals z Chelating agents z Reducing agents z Alterations of substrates

Enzymes in Food Processing z Polyphenoloxidase z Pectic enzymes z Amylases z Lipolytic enzymes z Lipoxygenase z Peroxidase z Ascorbic acid oxidase z Antioxidant enzymes
Enzymes in Food Processing z Polyphenoloxidase z Pectic enzymes z Amylases z Lipolytic enzymes z Lipoxygenase z Peroxidase z Ascorbic acid oxidase z Antioxidant enzymes

Polyphenoloxidase z Enzymatic browning z Cut surfaces of fruits and vegetables z Catalyze 2 types of reactions z Active between pH 5-7 z Cu cofactor z Inhibition
Polyphenoloxidase z Enzymatic browning z Cut surfaces of fruits and vegetables z Catalyze 2 types of reactions z Active between pH 5-7 z Cu cofactor z Inhibition

Pectic Enzymes z Pectic lyases: high-methoxyl pectins – Split glycosidic bonds adjacent to methyl ester z Structural elements – Changes in texture – Processing aids
Pectic Enzymes z Pectic lyases: high-methoxyl pectins – Split glycosidic bonds adjacent to methyl ester z Structural elements – Changes in texture – Processing aids
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品添加剂概论.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 风味化学.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 色素.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 维生素和矿物质.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 脂类 Lipids.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 蛋白质 Proteins.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 碳水化合物 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 水(主讲教师:迟玉杰).ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 功能食品简介 functional food.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第九章 食品中营养成分的代谢.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 酶.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第七章 矿物质.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第六章 维生素.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第五章 蛋白质.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第四章 脂类.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章 碳水化合物.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(试卷习题)食品化学试题库(答案).doc
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 水.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(试卷习题)食品化学试题库(试题).doc
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论 Food chemistry.ppt
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Browning Reactions.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Food Lipids.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Effects of Lipid Oxidation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Carbohydrates.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzymes.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Introduction.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water activity and toxins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Chemical Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Functionality.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Modifications of Food Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Denaturation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Primary sequence.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzyme Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Vitamin.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
