《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
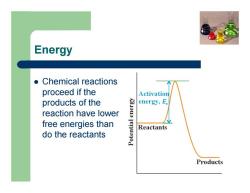
Energy z Chemical reactions proceed if the products of the reaction have lower free energies than do the reactants
Energy z Chemical reactions proceed if the products of the reaction have lower free energies than do the reactants

The fundamental equations of thermodynamics z The first law of thermodynamics Δ U = Δ Q + Δ w the total energy of a system is constant. z Enthalpy, H, is a function that describes energy changes at constant pressure. Δ Hp = cp (ΔT) p z For a biological system it defines the internal energy of a system – HEAT ΔH = +ve => heat is absorbed => ENDOTHERMIC ΔH = -ve => heat is evolved (given out) => EXOTHERMIC
The fundamental equations of thermodynamics z The first law of thermodynamics Δ U = Δ Q + Δ w the total energy of a system is constant. z Enthalpy, H, is a function that describes energy changes at constant pressure. Δ Hp = cp (ΔT) p z For a biological system it defines the internal energy of a system – HEAT ΔH = +ve => heat is absorbed => ENDOTHERMIC ΔH = -ve => heat is evolved (given out) => EXOTHERMIC
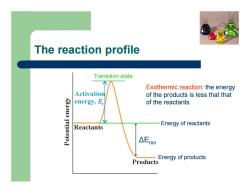
The reaction profile Δ Erxn Transition state Energy of reactants Energy of products Exothermic reaction: the energy of the products is less that that of the reactants
The reaction profile Δ Erxn Transition state Energy of reactants Energy of products Exothermic reaction: the energy of the products is less that that of the reactants


z The second law of thermodynamics Spontaneous processes are those which increase the entropy of the universe (i.e. system + surroundings). z Entropy is equal to a measurement of the randomness of a system. The fundamental equations of thermodynamics
z The second law of thermodynamics Spontaneous processes are those which increase the entropy of the universe (i.e. system + surroundings). z Entropy is equal to a measurement of the randomness of a system. The fundamental equations of thermodynamics

z The Gibbs Free Energy v1A + v2B ↔ v3C + v4D ΔrG0 = ∑viΔfG0(products) - ∑viΔfG0(reactants) dG = dH – TdS or ΔG = - RT ln Keq The fundamental equations of thermodynamics i) If ΔG0 0 (endergonic, signifying work-consuming) the reverse reaction is spontaneous. (iii) If ΔG0 = 0 the reaction is at equilibrium
z The Gibbs Free Energy v1A + v2B ↔ v3C + v4D ΔrG0 = ∑viΔfG0(products) - ∑viΔfG0(reactants) dG = dH – TdS or ΔG = - RT ln Keq The fundamental equations of thermodynamics i) If ΔG0 0 (endergonic, signifying work-consuming) the reverse reaction is spontaneous. (iii) If ΔG0 = 0 the reaction is at equilibrium

Chemical Kinetics z Study of the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence the rates. z Collision Theory – Collisions between reacting molecules are necessary before a reaction can occur – Only those collisions having sufficient energy are effective in bringing about a reaction activation energy – Colliding molecules must be properly oriented with respect to one another for the reaction to take place
Chemical Kinetics z Study of the rates of chemical reactions and the factors that influence the rates. z Collision Theory – Collisions between reacting molecules are necessary before a reaction can occur – Only those collisions having sufficient energy are effective in bringing about a reaction activation energy – Colliding molecules must be properly oriented with respect to one another for the reaction to take place

Chemical kinetics Factors affecting reaction rate: Concentrations of reactants Catalyst Temperature Surface area of solid reactants or catalyst
Chemical kinetics Factors affecting reaction rate: Concentrations of reactants Catalyst Temperature Surface area of solid reactants or catalyst
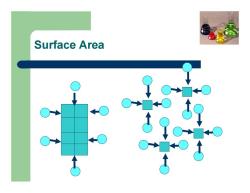
Surface Area
Surface Area
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water activity and toxins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Introduction.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzymes.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Carbohydrates.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Effects of Lipid Oxidation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Food Lipids.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Browning Reactions.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity.pdf
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品添加剂概论.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 风味化学.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 色素.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 维生素和矿物质.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 脂类 Lipids.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 蛋白质 Proteins.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 碳水化合物 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 水(主讲教师:迟玉杰).ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 功能食品简介 functional food.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第九章 食品中营养成分的代谢.ppt
- 江苏食品药品职业技术学院:《食品化学》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第八章 酶.ppt
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Functionality.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Modifications of Food Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Denaturation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Primary sequence.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzyme Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Vitamin.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Gas Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Water.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Carbohydrate.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Minerals.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lipids and Fats.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Water.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Experimental Foods.ppt
