《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Denaturation

Protein Denaturation z Any modification in conformation not accompanied by rupture of peptide bonds z Ultimate step might correspond to a totally unfolded polypeptide structure z Reversible or irreversible
Protein Denaturation z Any modification in conformation not accompanied by rupture of peptide bonds z Ultimate step might correspond to a totally unfolded polypeptide structure z Reversible or irreversible

Effects of Denaturation z Decreased solubility z Altered water binding capacity z Loss of biological activity z Destruction of toxins z Improved digestibility z Increased intrinsic viscosity z Inability to crystallize
Effects of Denaturation z Decreased solubility z Altered water binding capacity z Loss of biological activity z Destruction of toxins z Improved digestibility z Increased intrinsic viscosity z Inability to crystallize
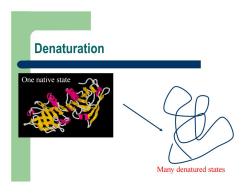
Denaturation One native state Many denatured states
Denaturation One native state Many denatured states

Physical Agents
Physical Agents

Thermal Denaturation z Rate of denaturation depends on the temperature z As T is increased – Affect interactions of tertiary structure – Increased flexibility → reversible – H-bonds begin to break → water interaction – Increased water binding – Increased viscosity of solution – Structures different from native protein
Thermal Denaturation z Rate of denaturation depends on the temperature z As T is increased – Affect interactions of tertiary structure – Increased flexibility → reversible – H-bonds begin to break → water interaction – Increased water binding – Increased viscosity of solution – Structures different from native protein

Thermal Denaturation z Upon cooling – Aggregation – Loss of solubility z Water content affects heat denaturation z Other consequences – Splitting of disulfide bonds – Chemical alterations of amino residues – Inter- or Intra- crosslinks
Thermal Denaturation z Upon cooling – Aggregation – Loss of solubility z Water content affects heat denaturation z Other consequences – Splitting of disulfide bonds – Chemical alterations of amino residues – Inter- or Intra- crosslinks

Effect of Cold Temperatures z Can result in denaturation – Gliadins, egg and milk proteins z Remain active – Some lipases and oxidases – Release from sub-cellular compartments z Proteins with high hydrophobic/polar amino residues and structures dependent on hydrophobic interactions
Effect of Cold Temperatures z Can result in denaturation – Gliadins, egg and milk proteins z Remain active – Some lipases and oxidases – Release from sub-cellular compartments z Proteins with high hydrophobic/polar amino residues and structures dependent on hydrophobic interactions

Interfaces z Liquid-air or Liquid-liquid interfaces z If allowed at interfaces – Unfold z Depends on – Rigidity of the 3-D structure – Number and location of hydrophobic groups – Accelerated if applied energy to cause shear z Reversible?
Interfaces z Liquid-air or Liquid-liquid interfaces z If allowed at interfaces – Unfold z Depends on – Rigidity of the 3-D structure – Number and location of hydrophobic groups – Accelerated if applied energy to cause shear z Reversible?

Others z Mechanical treatments z Hydrostatic Pressure z Irradiation
Others z Mechanical treatments z Hydrostatic Pressure z Irradiation
Chemical Agents
Chemical Agents
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Modifications of Food Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Protein Functionality.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Proteins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Chemical Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water activity and toxins.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Introduction.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzymes.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Carbohydrates.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Effects of Lipid Oxidation.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Food Lipids.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Water.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Browning Reactions.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Factors Influencing Enzyme Activity.pdf
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 食品添加剂概论.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 风味化学.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 色素.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 维生素和矿物质.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 脂类 Lipids.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 蛋白质 Proteins.ppt
- 湖北工业大学:《食品化学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 碳水化合物 Carbohydrates.ppt
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Primary sequence.pdf
- 《食品化学 Food Chemistry》课程教学课件(讲稿,英文版)Enzyme Kinetics.pdf
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Vitamin.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Lipid.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Introduction.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Physical State of Ingredients in Food Systems.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Protein.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Gas Liquid Chromatography.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Water.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Spectroscopy.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Carbohydrate.ppt
- 《食品化学与分析 Food Chemistry and Analysis》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)Minerals.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Lipids and Fats.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Water.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Experimental Foods.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Top Ten Food Companies Public and Private Companies.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Objective Evaluation of Food.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)General Food Safety.ppt
- 《Food Safety and Home Food Preservation》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)Carbohydrates:Starch and Sugars.ppt
