电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 14 冗余运算 Redundant Arithmetic

电子种越女学 University of Electroale Science and Technelery of China 986 Chapter 14 Redundant Arithmetic Xiang LING National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communications
Chapter 14 Redundant Arithmetic Xiang LING National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communications

数值表征系统 /96 ■数值表征是一个古老的数学问题 ■源于先祖的”结绳计事” ■革命性的突破在于印度人发明的“阿拉伯数字” ■数值表征的基本问题 ■表示 ·计算 ■数值表征的研究方法 ■经典代数 ■近世代数 2
2 数值表征系统 数值表征是一个古老的数学问题 源于先祖的”结绳计事” 革命性的突破在于印度人发明的“阿拉伯数字” 数值表征的基本问题 表示 计算 数值表征的研究方法 经典代数 近世代数
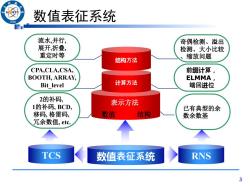
43 数值表征系统 /966 流水,并行, 奇偶检测、溢出 展开,折叠, 检测、大小比较 重定时等 结构方法 、缩放问题 CPA,CLA,CSA, 前缀计算 BOOTH,ARRAY, ELMMA, Bit level 计算方法 端回进位 2的补码, 1的补码,BCD, 表示方法 已有典型的余 移码,格雷码, 数值 结构 数余数基 冗余数值,etc. TCS 数值表征系统 RNS 3
3 数值表征系统 表示方法 数值 结构 计算方法 结构方法 数值表征系统 流水,并行, 展开,折叠, 重定时等 CPA,CLA,CSA, BOOTH, ARRAY, Bit_level 2的补码, 1的补码, BCD, 移码, 格雷码, 冗余数值, etc. 前缀计算, ELMMA, 端回进位 TCS RNS 已有典型的余 数余数基 奇偶检测、溢出 检测、大小比较 、缩放问题

14.1 Redundant and non redundant /96 A non-redundant radix-r number has digits from the seto,1,...r-1}and all numbers can be represented in a unique way. A radix-r redundant signed-digit number system is based on digit set S={β,(β-1).1,0,1,2,.,a, where the notation x denotes-x,1≤β,a≤(r-l) The digit set s contains more than r values multiple representations for any number in signed digit format.Hence,the name redundant. ■A symmetric signed digit has a=β. 4
4 14.1 Redundant and non redundant A non-redundant radix-r number has digits from the set{0, 1, … , r-1} and all numbers can be represented in a unique way. A radix-r redundant signed-digit number system is based on digit set S={β,(β-1),…1,0,1,2,…,α}, where the notation x denotes –x, 1≤ β, α≤(r-1). The digit set S contains more than r values → multiple representations for any number in signed digit format. Hence, the name redundant. A symmetric signed digit has α=β

14.1 Redundant and non redundant /986 Carry-free addition is an attractive property of redundant signed-digit numbers. This allows most significant digit (msd)first redundant arithmetic,also called on-line arithmetic. 5
5 Carry-free addition is an attractive property of redundant signed-digit numbers. This allows most significant digit (msd) first redundant arithmetic, also called on-line arithmetic. 14.1 Redundant and non redundant

14.2 Redundant number representations 96 A symmetric signed-digit representation uses the digit set Dr.=a1,0,1,..a}where r is the radix and a is the largest digit in the set. A number in this representation is written as W- Xe=xr-1xw-3Xw-3…xn=∑xw-广 i=0 The sign of the number is given by the sign of the most significant non-zero digit. ·Digit set D={1,0,1, ■3=00110r0101 6
6 14.2 Redundant number representations A symmetric signed-digit representation uses the digit set D={α, …, 1, 0, 1, …, α }, where r is the radix and α is the largest digit in the set. A number in this representation is written as : The sign of the number is given by the sign of the most significant non-zero digit. Digit set D={1,0,1}, 3=0011 or 0101 1 0 , 1 2 3 0 1 . .... W i i r W W W W i X x x x x x r

14.2 Redundant number representations /966 Minimally redundant and maximally redundant Digit Set D.r.d 0 Redundancy Factor p r-1 Incomplete 是 Minimally redundant =「r/2 and r-1 >1 The greater the redundancy factor,the greater the redundancy of the representation. D2.1>is also referred to as signed binary digit (SBD), redundant signed digit(RSD),and borrow save(BS) representations. 7
7 Minimally redundant and maximally redundant The greater the redundancy factor, the greater the redundancy of the representation. D is also referred to as signed binary digit (SBD), redundant signed digit (RSD), and borrow save (BS) representations. r 1 14.2 Redundant number representations

14.3 Carry-free Radix-2 Addition and /96 subtraction Redundant number representations limit the carry propagation to a few bit-positions,which is usually independent of the word length W. The algorithm to carry out signed binary digit addition is not unique,and therefore its logic implementation can be diverse. A radix-2 signed digit number is coded using 2 unsigned binary numbers,1 positive and 1 negative,as X=X+-X-. 8
8 14.3 Carry-free Radix-2 Addition and subtraction Redundant number representations limit the carry propagation to a few bit-positions, which is usually independent of the word length W. The algorithm to carry out signed binary digit addition is not unique, and therefore its logic implementation can be diverse. A radix-2 signed digit number is coded using 2 unsigned binary numbers, 1 positive and 1 negative, as X=X+-X -

14.3 Carry-free Radix-2 Addition and /96 subtraction In a hybrid operation,1st input operand and the output operand are in redundant signed digit representation,and the 2nd input operand is conventional unsigned number. A signed digit addition can be viewed as a concatenation of one hybrid addition and one hybrid subtraction. 9
9 In a hybrid operation, 1st input operand and the output operand are in redundant signed digit representation, and the 2nd input operand is conventional unsigned number. A signed digit addition can be viewed as a concatenation of one hybrid addition and one hybrid subtraction. 14.3 Carry-free Radix-2 Addition and subtraction

/966 Appendix:PPM operator In b b d=anbvancvbac PPM c=a⊕b⊕c d Symbol cquations schematic 10
10 In Appendix: PPM operator
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 位级运算 Bit-Level Arithmetic Architectures.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 缩放噪声 Scaling and Roundoff Noise.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 算法强度缩减 Algorithmic strength reduction in filters and transforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 快速卷积 Fast Convolution.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 递归滤波器 Pipelined and Parallel Recursive and Adaptive Filters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 脉动阵列 Systolic Architecture.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 折叠 Folding.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 展开 Unfolding.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 重定时 Retiming.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 流水与并行 Pipelining and Parallel Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 迭代界 Iteration Bound.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 导论 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 00 简介 Introduction to VLSI(凌翔).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(教学大纲,凌翔).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电子无源元件工艺实验》课程实验课件讲稿 Electronic Passive Components Process Experiment Course(主讲:戴丽萍).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《半导体封装测试与可靠性 Packaging,Testing and Reliability of Semiconductor》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,思政版).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《半导体封装测试与可靠性 Packaging,Testing and Reliability of Semiconductor》课程教学资源(教学大纲,思政版).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 4 VLSI for DSP.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 3 Verification and Test.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 2.2 FPGA Design with Verilog(Supplementary).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 15 数字强度缩减 Numerical Strength Reduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述——研究意义(王忆文).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述——测试的基本知识.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 电路测试基础.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 验证、模拟和仿真.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 自动测试生成.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 电流测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第11章 存储器测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12章 Soc测试(1/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 专用可测性设计.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 扫描设计.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 边界扫描.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8、9章 内建自测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12章 Soc测试(2/2)IEEE P1500 嵌入式核可测性标准.pdf
- 《现代编码理论与技术》课程教学资源(学习资料)Turbo码启示录——从默默无闻到广泛应用.doc
- 华南理工大学:《现代编码理论与技术》课程教学资源(讲义)第三章 线性分码组.doc
- 华南理工大学:《现代编码理论与技术》课程教学资源(讲义)第五章 循环码(陆以勤).doc
- 华南理工大学:《现代编码理论与技术》课程教学资源(讲义)第四章 多项式环与有限域.doc
- 华南理工大学:《现代编码理论与技术》课程教学资源(讲义)第六章 循环码的译码.doc
- 华南理工大学:《现代编码理论与技术》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一章 纠错码的基本概念.ppt
