电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 04 重定时 Retiming

电子种越女学 University of Electroale Science and Technelery of China 986 Chapter 4 Retiming Dr.Ling National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communication
Chapter 4 Retiming Dr. Ling National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communication
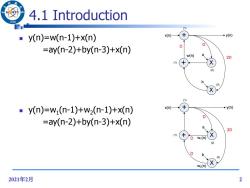
43 4.1 Introduction 96 () y(n)=w(n-1)+x(n) x(n) →yn) D D =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) w(n) a 2D (1) (2) b (2) (1) ay(n)=w(n-1)+w2(n-1)+x(n) x(n) →yn) D =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) a 2D (1) w(n) (2) (2) w2(n) 2021年2月 2
2021年2月 2 4.1 Introduction y(n)=w(n-1)+x(n) =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) y(n)=w1 (n-1)+w2 (n-1)+x(n) =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) + X + X D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) x(n) y(n) a b w(n) + X + X D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) x(n) y(n) a b w1(n) D w2(n)

Retiming? /96 Retiming is a transformation technique used to change the locations of delay elements in a circuit without affection the input/output characteristics of the circuit. Retiming has many applications in synchronous circuit design,including reducing the clock period of the circuit, reducing the number of registers in the circuit, -reducing the power consumption of the circuit, logic synthesis. 2021年2月 3
2021年2月 3 Retiming? Retiming is a transformation technique used to change the locations of delay elements in a circuit without affection the input/output characteristics of the circuit. Retiming has many applications in synchronous circuit design, including reducing the clock period of the circuit, reducing the number of registers in the circuit, reducing the power consumption of the circuit, logic synthesis
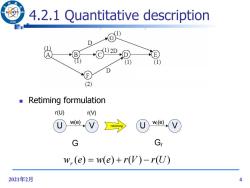
4.2.1 Quantitative description 966 1)2D 1) (1) D (2) Retiming formulation r(U) r U w(e) V U w(e) retiming V G Gr w,(e)=w(e)+r(V)-r(U) 2021年2月 4
2021年2月 4 4.2.1 Quantitative description Retiming formulation w (e) w(e) r(V) r(U) r U V w(e) r(U) r(V) retiming U V wr(e) G Gr
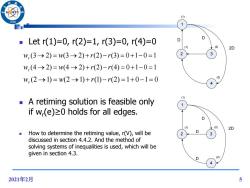
(1) /96 ■Letr(1)=0,r(2)=1,r(3)=0,r(4)=0 D (1) (2) 2D w,(3→2)=1w(3→2)+r(2)-r(3)=0+1-0=1 2 3 w,(4→2)=w(4→2)+r(2)-r(4)=0+1-0=1 w,(2→1)=w(2→1)+r(1)-r(2)=1+0-1=0 (2) (1) A retiming solution is feasible only if w-(e)>0 holds for all edges. (1) (2) 2D How to determine the retiming value,r(V),will be 2 3 discussed in section 4.4.2.And the method of solving systems of inequalities is used,which will be given in section 4.3. D (2) 2021年2月 5
2021年2月 5 Let r(1)=0, r(2)=1, r(3)=0, r(4)=0 A retiming solution is feasible only if wr (e)≥0 holds for all edges. How to determine the retiming value, r(V), will be discussed in section 4.4.2. And the method of solving systems of inequalities is used, which will be given in section 4.3. 1 4 2 3 D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) D w (3 2) w(3 2) r(2) r(3) 0 1 0 1 r wr (4 2) w(4 2) r(2) r(4) 0 1 0 1 1 4 2 3 D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) wr (2 1) w(2 1) r(1) r(2) 1 0 1 0

4.2.2 Properties of retiming /96 The weight of the retimed route p=Vo>V1>...Vk is given by w(p)=w(p)+r(Vk)- r(Vo) Retiming does not change the number of delays in a cycle. ■ Retiming does not alter the iteration bound in a DFG. As the number of delays in a cycle does not change. -W-(p)=w(p)+r(Vo)-r(Vo)=w(p) Adding the constant value j to the retiming value of each node does not change the mapping from G to G.. 2021年2月 6
2021年2月 6 4.2.2 Properties of retiming The weight of the retimed route p=V0V1…Vk is given by wr (p)=w(p)+r(Vk )- r(V0 ) Retiming does not change the number of delays in a cycle. Retiming does not alter the iteration bound in a DFG. As the number of delays in a cycle does not change. wr (p)=w(p)+r(V0 )-r(V0 )=w(p) Adding the constant value j to the retiming value of each node does not change the mapping from G to Gr

4.3 Solving systems inequalities Given a set of M inequalities,where each inequality has the form r-rsk for integer values of k. Draw a constrain graph. Draw the node i for N variables ri,i=1,..N; ■Draw the node N+l; For each inequality ri-ri with length k; ■For each node i,.draw edge N+l→i with length0. ■ Solve using a shortest path algorithm. Bellman-Ford algorithm(single-point shortest path algorithm) Floyd-Warshall algorithm(all-point shortest path algorithm) ■ If a solution exists(if no negative cycle in constraint graph), the retiming value r is obtained (r is the minimum-length from node N+1 to node i). 2021年2月 7
2021年2月 7 4.3 Solving systems inequalities Given a set of M inequalities, where each inequality has the form ri -rj≤k for integer values of k. Draw a constrain graph. Draw the node i for N variables ri , i=1,..N; Draw the node N+1; For each inequality ri -rj≤k, draw edge ji with length k; For each node i, draw edge N+1i with length 0. Solve using a shortest path algorithm. Bellman-Ford algorithm (single-point shortest path algorithm) Floyd-Warshall algorithm (all-point shortest path algorithm) If a solution exists (if no negative cycle in constraint graph), the retiming value r is obtained (ri is the minimum-length from node N+1 to node i). J i w
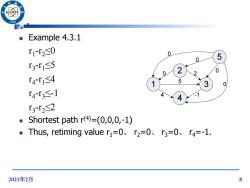
966 Example 4.3.1 r1-r2≤0 0 0 5 r3-r15 ● 0 r4r1≤4 5 0 r4r3≤-1 4 r3-r2≤2 ■ Shortest path r(4)=(0,0,0,-1) ■Thus,retiming value r1=0、r2=0、r3=0、r4=-1. 2021年2月 8
2021年2月 8 Example 4.3.1 r1 -r2≤0 r3 -r1≤5 r4 -r1≤4 r4 -r3≤-1 r3 -r2≤2 Shortest path r(4)=(0,0,0,-1) Thus, retiming value r1=0、 r2=0、 r3=0、 r4=-1. 2 1 4 3 0 5 4 -1 5 0 2 0 0 0

4.4 Retiming techniques 96 Two special cases of retiming Cutset retiming ·pipelining ■Two algorithms To minimize the clock period To minimize the number of registers 2021年2月 9
2021年2月 9 4.4 Retiming techniques Two special cases of retiming Cutset retiming pipelining Two algorithms To minimize the clock period To minimize the number of registers

4.4.1 Cutset retiming and pipelining Cutset retiming only affects the weights of the edges in the cutset. If the two disconnected subgraphs are labeled G1 and G2,then cutset retiming consists of adding k delays to each edge from Gi to G2, then removing k delays from each edge from G2 to G1. 2021年2月 10
2021年2月 10 4.4.1 Cutset retiming and pipelining Cutset retiming only affects the weights of the edges in the cutset. If the two disconnected subgraphs are labeled G1 and G2 , then cutset retiming consists of adding k delays to each edge from G1 to G2 , then removing k delays from each edge from G2 to G1
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 03 流水与并行 Pipelining and Parallel Processing.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 02 迭代界 Iteration Bound.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 01 导论 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Systems.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 00 简介 Introduction to VLSI(凌翔).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(教学大纲,凌翔).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《电子无源元件工艺实验》课程实验课件讲稿 Electronic Passive Components Process Experiment Course(主讲:戴丽萍).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《半导体封装测试与可靠性 Packaging,Testing and Reliability of Semiconductor》课程教学资源(课件讲稿,思政版).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《半导体封装测试与可靠性 Packaging,Testing and Reliability of Semiconductor》课程教学资源(教学大纲,思政版).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 4 VLSI for DSP.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 3 Verification and Test.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 2.2 FPGA Design with Verilog(Supplementary).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 2.1 FPGA Design with Verilog(FPGA Design Method、Design Examples).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1.3 Introduction-Our Course.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1.2 Introduction-ASIC Design.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《ASIC设计 Application Specific Integrated Circuit Design》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Topic 1.1 Introduction-IC technology.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第20讲 高阶有源滤波器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第19讲 有源滤波器.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第9讲 信号流图分析法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6讲 网络函数拓扑法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代网络理论与综合 Theory and Synthesize of Electric Network》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5讲 不定导纳函数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 05 展开 Unfolding.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 06 折叠 Folding.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 07 脉动阵列 Systolic Architecture.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 10 递归滤波器 Pipelined and Parallel Recursive and Adaptive Filters.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 08 快速卷积 Fast Convolution.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 09 算法强度缩减 Algorithmic strength reduction in filters and transforms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 缩放噪声 Scaling and Roundoff Noise.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 13 位级运算 Bit-Level Arithmetic Architectures.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 14 冗余运算 Redundant Arithmetic.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《DSP算法实现技术与架构 VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems Design and Implementation》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 15 数字强度缩减 Numerical Strength Reduction.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述——研究意义(王忆文).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述——测试的基本知识.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 电路测试基础.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 验证、模拟和仿真.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 自动测试生成.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第10章 电流测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第11章 存储器测试.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第12章 Soc测试(1/2).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 专用可测性设计.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《集成电路可测性设计 VLSIDesign》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 扫描设计.pdf
