香港大学:Seminar on Applications of Mathematics - Voting

Outline Examples of voting system -What should be an ideal voting system Arrow's Impossibility Theorem Main idea of the proof of Arrow's Impossibility Theorem Yes-no voting systems and the dimension of these systems. How to quantify political power -Examples of power indices and their applications to the LEGCO voting system
Outline Examples of voting system What should be an ideal voting system ? Arrow's Impossibility Theorem Main idea of the proof of Arrow's Impossibility Theorem Yes-no voting systems and the dimension of these systems. How to quantify political power ? Examples of power indices and their applications to the LEGCO voting system

Simple majority vote for two candidates When there are only two candidates or alternatives,we can simply use the simple majority vote. The situation is much more complicated if we have at least three candidates or alternatives
Simple majority vote for two candidates When there are only two candidates or alternatives, we can simply use the simple majority vote. The situation is much more complicated if we have at least three candidates or alternatives

Voting Paradox Suppose we have three candidates,A,B and C,and that there are three voters with preferences as follows: Voter 1:A>B>C Voter 2:B >C>A Voter 3:C >A>B For A vs B,A wins(2 to 1) For B vs C,B wins(2 to 1) For C vs A,C wins(2 to 1) ■ Therefore,the requirement of majority rule then provides no clear winner. This is paradoxical,because it means that majority wishes can be in conflict with each other
Voting Paradox Suppose we have three candidates, A, B and C, and that there are three voters with preferences as follows: Voter 1: A> B> C Voter 2: B >C> A Voter 3: C >A> B For A vs B, A wins (2 to 1) For B vs C, B wins (2 to 1) For C vs A, C wins (2 to 1) Therefore, the requirement of majority rule then provides no clear winner. This is paradoxical, because it means that majority wishes can be in conflict with each other
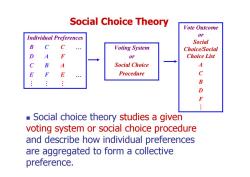
Social Choice Theory Vote Outcome Individual Preferences or Social B C C Voting System Choice/Social D A or Choice List C B A Social Choice A E F E Procedure C B D F Social choice theory studies a given voting system or social choice procedure and describe how individual preferences are aggregated to form a collective preference
M M M E F E … C B A D A F B C C … Individual Preferences Voting System or Social Choice Procedure Vote Outcome or Social Choice/Social Choice List A C B D F M Social Choice Theory Social choice theory studies a given voting system or social choice procedure and describe how individual preferences are aggregated to form a collective preference

Who is your favorite hero A C SUPERMAN B E D
Who is your favorite hero ? A B C E D

What is your preference My preference list is B>D>C>A>E How to determine who is the most popular hero?
What is your preference ? My preference list is B > D > C > A > E How to determine who is the most popular hero?
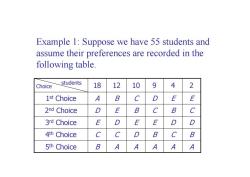
Example 1:Suppose we have 55 students and assume their preferences are recorded in the following table. Choice students 18 12 10 9 4 2 1st Choice A B C D E E 2nd Choice D E B C B 3rd Choice E D E E D 4th Choice C C D B B 5th Choice B A A A A A
A D E B C 10 A B E C D 9 A C D E B 12 2nd Choice D B C 3rd Choice E D D 4th Choice C C B 5th Choice B A A 1 A E E st Choice 18 4 2 students Choice Example 1: Suppose we have 55 students and assume their preferences are recorded in the following table
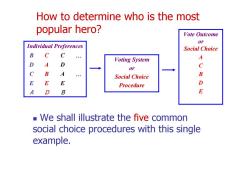
How to determine who is the most popular hero? Vote Outcome or Individual Preferences Social Choice B C C Voting System A D A C or C B A Social Choice B E E E Procedure D A D B E We shall illustrate the five common social choice procedures with this single example
A D B E E E C B A … D A D B C C … Individual Preferences Voting System or Social Choice Procedure Vote Outcome or Social Choice A C B D E We shall illustrate the five common social choice procedures with this single example. How to determine who is the most popular hero?

Social Choice Procedure 1: Plurality Voting Plurality voting is the social choice procedure that most directly generalizes the idea of simple majority vote from the easy case of two candidates to the complicated case of three or more candidates. The idea is simply to declare as the social choice(s) the candidate with the largest number of first-place rankings in the individual preference lists
Social Choice Procedure 1: Plurality Voting Plurality voting is the social choice procedure that most directly generalizes the idea of simple majority vote from the easy case of two candidates to the complicated case of three or more candidates. The idea is simply to declare as the social choice(s) the candidate with the largest number of first-place rankings in the individual preference lists
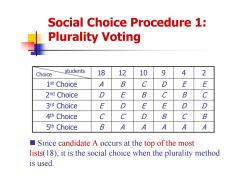
Social Choice Procedure 1: Plurality Voting students Choice 18 12 10 9 4 2 1st Choice A B C D E E 2nd Choice D E B C B 3rd Choice E D E E 4th Choice C C D B B 5th Choice B A A A A A Since candidate A occurs at the top of the most lists(18),it is the social choice when the plurality method is used
Social Choice Procedure 1: Plurality Voting Since candidate A occurs at the top of the most lists(18), it is the social choice when the plurality method is used. A D E B C 10 A B E C D 9 A C D E B 12 2nd Choice D B C 3rd Choice E D D 4th Choice C C B 5th Choice B A A 1 A E E st Choice Choice 18 4 2 students
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 香港大学:From Nash to Nash’s Game Theory.pdf
- 香港大学:博弈高手——浅论约翰·纳殊的诺具尔得理论.pdf
- 香港大学:谈情说数——跟爱情有关的数学.pdf
- 香港大学:《数趣漫话》谈情说数——跟爱情有关的数学.pdf
- 香港大学:拍卖中寻对策(PPT讲稿).pdf
- 佛山大学(佛山科学技术学院):2017版数学与应用数学(师范)专业理论课教学大纲汇编(合集).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:几何建模与处理基础(PPT讲稿)细分曲线(主讲:刘利刚).pdf
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第八章 向量代数与空间解析几何 第四节 空间直线及其方程.ppsx
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第八章 向量代数与空间解析几何 第六节 空间曲线及其方程.ppsx
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第八章 向量代数与空间解析几何 第五节 曲面及其方程.ppsx
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第八章 向量代数与空间解析几何 第二节 数量积、向量积、混合积.ppsx
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第八章 向量代数与空间解析几何 第三节 平面及其方程.ppsx
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第八章 向量代数与空间解析几何 第一节 向量及其线性运算.ppsx
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用 第四节 函数的单调性与曲线的凹凸性.pps
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用 第五节 函数的极值与最大最小值.pps
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用 第七节 曲率.pps
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用 第三节 泰勒公式.pps
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用 第二节 洛必达法则.pps
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第三章 微分中值定理与导数的应用 第一节 中值定理.pps
- 同济大学:《高等数学》课程教学资源(预习PPT讲稿)第二章 导数与微分 第四节 隐函数参数函数导数.pps
- 香港大学:Games and the Mathematical Mind.pdf
- 香港大学:Solving Polynomial Equations.pdf
- 香港大学:Solving Polynomial Equations(2006.12.5).pdf
- ON-LINE LIST COLOURING OF RANDOM GRAPHS.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《线性代数》课程教学资源(PPT课件)线性代数机算与应用.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《线性代数》课程教学资源(讲义)线性代数讲义(共六章,主讲:李仁先).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一部分 数理逻辑 第一章 命题逻辑(主讲:肖明军).ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第一部分 数理逻辑 第二章 谓词逻辑.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二部分 集合论 第三章 集合代数.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二部分 集合论 第四章 二元关系.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二部分 集合论 第五章 函数.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第二部分 集合论 第六章 集合的基数.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 代数结构 第七章 代数系统.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 代数结构 第八章 群论.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 代数结构 第九章 环与域.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 代数结构 第十章 格与布尔代数.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 图论 第十一章 图的基本概念.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 图论 第十二章 树.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《离散数学》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第三部分 图论 第十三章 几种特殊的图.ppt
- 《力学》课程教学资源(数学工具)力学数学预备知识——微积分初步.pdf
