《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-a-Computer History+ Di Devices

Computer History Manual calculators Abacus: Before Computers there was a Manual calculator called an abacus. Appeared around 1200 in China. Slide Rule: Other Manual calculator called a Slide Rule In 1621 an English mathematician used logarithms to construct the slide rule These Devices require the operator to apply algorithms(Step-by-step procedure)to perform calculations
Computer History Abacus: Before Computers there was a Manual calculator called an abacus. Appeared around 1200 in China. Slide Rule: Other Manual calculator called a Slide Rule In 1621 an English mathematician used logarithms to construct the slide rule. These Devices require the operator to apply algorithms (Step-by-step procedure) to perform calculations. Manual calculators

Mechanical calculators As early as 1623 appeared Schickard's Calculator. Mechanical calculator Implements algorithms autonomously. In 1642 appeared Pascaline To perform(addition,subtraction,multiplication,division)
• As early as 1623 appeared Schickard’s Calculator. • In 1642 appeared Pascaline • To perform (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) Mechanical calculators Mechanical calculator Implements algorithms autonomously

Calculators operate without Human power In 1822 appeared the Difference Engine These device intended to quikly and accurately calculate large tables of numbers used for astronomical and eng.applications. In 1834 appeared Analytical Engine These embodied many characteristics that define modern computers.He proposed storing programs and data for calculation on punced card. In 1890 Was a competition to find way to tabulate the censeus. Herman Hollerith design for an electronic punced card tabulating device. In 1924(international Business Machines(IBM)founded
Calculators operate without Human power In 1822 appeared the Difference Engine In 1834 appeared Analytical Engine In 1890 Was a competition to find way to tabulate the censeus. Herman Hollerith design for an electronic punced card tabulating device. In 1924 (international Business Machines (IBM)founded. These device intended to quikly and accurately calculate large tables of numbers used for astronomical and eng.applications. These embodied many characteristics that define modern computers. He proposed storing programs and data for calculation on punced card

Generations of Computers First-Generation: From 1943 until 1951 there were many prototypes(Expermental devices) such as: 。 Atanasoff-Berry Computer COLOSSUS ENIAC UNIVAC These devices use an electronic devices called a vacuum tube(Store individual bits of data) (RAM capacity of 12KB,magnetic tape for data storage and retrieval) Second-generation: In 1947 demonstrated by AT &T's Bell Laboratories These devices used Transistors(Small,cheaper and less power
First- Generation: From 1943 until 1951 there were many prototypes (Expermental devices) such as: • Atanasoff-Berry Computer • COLOSSUS • ENIAC • UNIVAC (RAM capacity of 12KB, magnetic tape for data storage and retrieval) Second- generation: In 1947 demonstrated by AT &T’s Bell Laboratories Generations of Computers These devices use an electronic devices called a vacuum tube (Store individual bits of data) These devices used Transistors(Small, cheaper and less power )

Generations of Computers Third-generation In 1958 Jack Kilby developed integrated circuits These was the key development for a small computers. In 1965 advent of third-generation IBM 360s. Fourth-generation In 1971 appeared the first microprocessor called the Intel Intel series: 4004,8008,8085,8086,80286,80386,80486,Pentium,Itanium microprocessors. In 1974,Motorola released 6800>>68000 used in MAC In 1976 released Appel I with 4KB In 1981 IBM began marketing called PC based on 8088 processor. The IBM used operating system called PC-Dos Later MS-DOS.Then windows 3.1 with graphical user interface
Third- generation In 1958 Jack Kilby developed integrated circuits. These was the key development for a small computers. In 1965 advent of third-generation IBM 360s. Fourth- generation In 1971 appeared the first microprocessor called the Intel Intel series: 4004,8008,8085,8086,80286,80386,80486,Pentium, Itanium microprocessors. In 1974, Motorola released 6800>>68000 used in MAC In 1976 released Appel I with 4KB In 1981 IBM began marketing called PC based on 8088 processor. The IBM used operating system called PC-Dos Later MS-DOS. Then windows 3.1 with graphical user interface. Generations of Computers
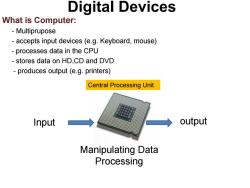
Digital Devices What is Computer: Multiprupose accepts input devices(e.g.Keyboard,mouse) processes data in the CPU stores data on HD,CD and DVD produces output(e.g.printers) Central Processing Unit Input output Manipulating Data Processing
What is Computer: - Multiprupose - accepts input devices (e.g. Keyboard, mouse) - processes data in the CPU - stores data on HD,CD and DVD - produces output (e.g. printers) Digital Devices Input output Manipulating Data Processing Central Processing Unit

Computers store data How do Computers store data: Temporarily store data. Permanently store data Data is typically stored in files on storage meduim like Hard disk
How do Computers store data: - Temporarily store data. - Permanently store data - Data is typically stored in files on storage meduim like Hard disk. Computers store data

Computers ability to store instructions Computer program (Software): Is a series of instructions that tells a computer how to carry out processing tasks Software:Adobe,MS-Office.etc Computers are Multipurpose machines: The series of instructions that loaded in the computer's memory for computing the tasks can easly replaced by a different set of instructions when it is time for computer to perfom another task. Computers run two type of Sotware: 1-Application software 2-System software(OS)
Computers ability to store instructions Computer program (Software): Is a series of instructions that tells a computer how to carry out processing tasks Software: Adobe, MS-Office.etc Computers are Multipurpose machines: The series of instructions that loaded in the computer’s memory for computing the tasks can easly replaced by a different set of instructions when it is time for computer to perfom another task. Computers run two type of Sotware: 1- Application software 2- System software (OS)

Types of Computers 1-A personal computer 2-Workstations: a-PC conncted to a network b-A powerful desktop computers used for high-performance tasks. 3-Server:Serve the computers on a network. 4-Client:any computer that request data from a server. 5-mainframe:A large and expensive computer,procecessed data for thousands of users,used generally by businesses or goverment 6-Supercomputrs(BlueGene/L.IBM)Compute-intensive problem. 7-Handheld Computers:PDA(personal digital assistant) iPods,Blackberries and smart phone
1- A personal computer 2- Workstations: a- PC conncted to a network b- A powerful desktop computers used for high- performance tasks. 3- Server: Serve the computers on a network. 4- Client: any computer that request data from a server. 5- mainframe: A large and expensive computer, procecessed data for thousands of users, used generally by businesses or goverment 6- Supercomputrs (BlueGene/L . IBM) Compute-intensive problem. 7- Handheld Computers: PDA( personal digital assistant) iPods, Blackberries and smart phone. Types of Computers
Devices Microcontrollers: mounted on a circuit board embeded in all sorts of devices microcontrollers is sometime called comupter-on-a chip because it includes many of the elements common to computers. also defined as multipurpose device that accepts input, produces output,stores data,and procecces according to a stored program. e.g.Smart phone and portable media Players. MicroController atat
Microcontrollers: mounted on a circuit board embeded in all sorts of devices microcontrollers is sometime called comupter –on-a chip because it includes many of the elements common to computers. also defined as multipurpose device that accepts input, produces output , stores data , and procecces according to a stored program. e.g. Smart phone and portable media Players. Devices
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《计算机导论》课程教学大纲 Computer Concepts.pdf
- 《微型计算机技术及应用》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,共十五章,完整版).pptx
- 《微机技术及应用》课程教学大纲 Microcmputer Technology and aplications.doc
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Polymorphism and Virtual Functions.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Inheritance.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Strings.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Streams and File IO.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Separate Compilation and Namespaces.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Constructors and Other Tools.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Structures and Classes.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Flow of Control.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 3 Function Basics.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 1 C++ Basics.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Parameters and Overloading.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 信源与信息熵.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论(主讲:王军选).ppt
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-b-Digital Data Representation.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-a-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-b-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)3-a-b-Computer Software.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4- operating system.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4-a- File mangement.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-a- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-b- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-a- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-b- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)7-a- Web.pdf
- 《数字图像处理技术》课程教学资源(实例)实验 - C语言附录实例.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言中详解指针.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C指针详解(经典详细).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言指针用法详解.pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)C语言指针详解.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)c语言指针完整教程.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(函数,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 指针.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(数组,带答案).pdf
