《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-a- The Internet

Internet Technology History: One of the resulting intiatives of U.S.government was Advanced Research Projects Agency(ARPA). The ARPANET created in 1969 to conncet computers between: The Initial ARPANET-1969 UCLA 50kBit/s UCSB National Science Foundation (NSF)in 1985 created larger (mainframe computers entire LANs at each site. The NSF network was internet,grew this network to Internet
History: One of the resulting intiatives of U.S. government was Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). The ARPANET created in 1969 to conncet computers between: National Science Foundation (NSF) in 1985 created larger (mainframe computers + entire LANs at each site. The NSF network was internet, grew this network to Internet. Internet Technology

Internet Infrastructure Internet backbone: Is a network of high-capacity commuincation links that provides the main routes for data traffic across the Internet Consists of: nterne high-speed fiber-optic links high-capacity routers The above Links Routers are maintained by Network services providers(Asps).These tid together by Network access points(NAPs). Inetrnet service provider(ISP): Is a company that offer Internet access to individuals,businesses,and small ISPs. ISPs operates routers,e-mail srver,web server and DNS server
Internet backbone: Is a network of high-capacity commuincation links that provides the main routes for data traffic across the Internet. Consists of: - high-speed fiber-optic links. - high-capacity routers The above Links + Routers are maintained by Network services providers(Asps). These tid together by Network access points(NAPs). Inetrnet service provider(ISP): Is a company that offer Internet access to individuals, businesses, and small ISPs. ISPs operates routers, e-mail srver, web server and DNS server One of the resulting intiatives of U.S. government was Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). The ARPANET created in 1969 to conncet computers between: National Science Foundation (NSF) in 1985 created larger (mainframe computers + entire LANs at each site. The NSF network was internet, grew this network to Internet. Internet Infrastructure
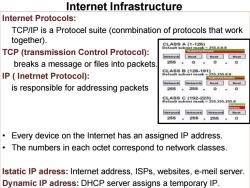
Internet Infrastructure Internet Protocols: TCP/IP is a Protocel suite (conmbination of protocols that work together). CLASS A(1-126)】 Default subnet mask-255.0.0.0 TCP(transmission Control Protocol): breaks a message or files into packets 255 0 0 IP Inetrnet Protocol): S0AsB128-191y -2552550.0 is responsible for addressing packets 255 .255 0 0asS19a3232 mmk255.255.255.0 letwork letworH 265 .256265 Every device on the Internet has an assigned IP address. The numbers in each octet correspond to network classes. Istatic IP adress:Internet address,ISPs,websites,e-meil server. Dynamic IP adress:DHCP server assigns a temporary IP
Internet Protocols: TCP/IP is a Protocel suite (conmbination of protocols that work together). TCP (transmission Control Protocol): breaks a message or files into packets. IP ( Inetrnet Protocol): is responsible for addressing packets • Every device on the Internet has an assigned IP address. • The numbers in each octet correspond to network classes. Istatic IP adress: Internet address, ISPs, websites, e-meil server. Dynamic IP adress: DHCP server assigns a temporary IP. Internet Infrastructure

Internet Infrastructure Domain names: http://www.google.com FTP Port 20 21 Domain name google.com E-mail Port 110 http://www Portocol port http://www Port 80 Utilities to measure the speed of Internet: Ping (Packet Internet Groper) Ipconfig(display current TCP/IP,DHCP,DNS configuration) Traceroute:records a packet's path in addition to its round-trip speed. Upstream speed:is the rate of data that is transmitted from your computer to the Internet. Downstream speed:is the rate of data arriving at your computer
Domain names: http://www.google.com Domain name = google.com http://www = Portocol & port Utilities to measure the speed of Internet: Ping (Packet Internet Groper) Ipconfig ( display current TCP/IP, DHCP,DNS configuration) Traceroute: records a packet’s path in addition to its round- trip speed. Upstream speed: is the rate of data that is transmitted from your computer to the Internet. Downstream speed: is the rate of data arriving at your computer. Internet Infrastructure FTP Port 20 & 21 E-mail Port 110 http://www Port 80
Fixed Ineternet Access Dial-up connection: Modem Telephone line RJ11 connector and Port ISDN: Voice call transmit data at te same time. DSL (Digital subscriber line): High-speed,digital,always-on.The voice singals are separated from the data signal. SES Americom ANC-6 ADSL: Downstream faster than upstream. Cable Internet: on broadband Internet access over the same infrastructure that offer cable television service. 胜tworked Satellite internet service: interne Backbon
Dial-up connection: Modem + Telephone line + RJ11 connector and Port ISDN: Voice call + transmit data at te same time. DSL (Digital subscriber line): High-speed, digital, always-on. The voice singals are separated from the data signal. ADSL: Downstream faster than upstream. Cable Internet: on broadband Internet access over the same infrastructure that offer cable television service. Satellite internet service: Fixed Ineternet Access
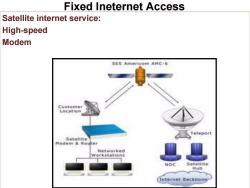
Fixed Ineternet Access Satellite internet service: High-speed Modem SES Americom AMC-6 Customer Teleport Satellite Networked Workstations Satellite Hub Internet Backbone
Satellite internet service: High-speed Modem Fixed Ineternet Access

Fixed Ineternet Access Fixed wireless services: WiMAX: Can be deployed rural areas where cable sevice is not available where the customers are too far away from a telephone switching station for DSL services WMAX WiMAX Woddwide Interoperablity ol Microwarve Access
Fixed wireless services: WiMAX: Can be deployed rural areas where cable sevice is not available where the customers are too far away from a telephone switching station for DSL services. Fixed Ineternet Access
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-b- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-a- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4-a- File mangement.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4- operating system.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)3-a-b-Computer Software.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-b-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-a-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-b-Digital Data Representation.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-a-Computer History+ Di Devices.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学大纲 Computer Concepts.pdf
- 《微型计算机技术及应用》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,共十五章,完整版).pptx
- 《微机技术及应用》课程教学大纲 Microcmputer Technology and aplications.doc
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Polymorphism and Virtual Functions.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Inheritance.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Strings.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Streams and File IO.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Separate Compilation and Namespaces.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References.ppt
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-b- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)7-a- Web.pdf
- 《数字图像处理技术》课程教学资源(实例)实验 - C语言附录实例.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言中详解指针.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C指针详解(经典详细).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言指针用法详解.pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)C语言指针详解.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)c语言指针完整教程.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(函数,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 指针.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(数组,带答案).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(分支与循环以前知识点,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)C程序设计讲义与习题(含参考答案).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)考试知识点复习(C语言程序设计复习样题及部分解析).doc
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第09章 文件.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第08章 结构体.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第07章 预处理命令.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第05章 函数.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第04章 数组.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第03章 三种基本控制结构(下).ppt
