《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-a-Computer Hardware

Computer Hardware Personal Computer Basics Personal computer: Computer system include peripheral devices(input,output and storage equipment) Components: 1-System unit is case that Top Cover Panel hold the components. Front f Frame Back Ot Frome 2-Keyboard Power Cord Exernel 5.25' P角ug Dnve Bays 3-Mouse Ports Extarnalmemel 4-Hard disk drive 35 Drive Bays Power Supply Power Supply LEDand 5-CD and DVD drives Fan Vent IO Template 6-Storage Expansion Siot inserts 7-Sound system Drive Power Vent Holes Connectors 8-Display System(LCD CRT) Feet Bottom Of Freme 9-Network and Internet access (Back Peir) 10-Printer
Computer Hardware Personal computer: Computer system include peripheral devices ( input, output and storage equipment) Components: 1-System unit is case that hold the components. 2- Keyboard 3- Mouse 4- Hard disk drive 5- CD and DVD drives 6- Storage 7- Sound system 8- Display System ( LCD & CRT) 9- Network and Internet access 10- Printer Personal Computer Basics

Types of Computers ·1-Tower ·2-Desktop ·3-mini Case 4-computer the circuitry is integrated into the back of flat-panel screen. 5-Portable computer Notebook and Netbook ·6-table computer 7-Ultra-mobile computer Home computers-Media Centre PC- Business systems-Game computers There are three personal computers platforms: 1-PC 2-Mac 3-Linux
• 1- Tower • 2- Desktop • 3- mini Case • 4- computer the circuitry is integrated into the back of flat-panel screen. • 5- Portable computer Notebook and Netbook • 6- table computer • 7- Ultra- mobile computer • Home computers - Media Centre PC - Business systems - Game computers There are three personal computers platforms: 1- PC 2- Mac 3- Linux Types of Computers
Microprocessors and Memory Microprocessor (Processor): Intel pentium 3.2 GHz(Million cycles per second): Microprocessor's clock operates at a speed of 3.2 billion per second) intel. The speed of the microprocessor clock-a entium4 timing 800M9SBromtSiae us): instructions Refers to the circuitry that transports data to and from the microprocessor. ·Vord size: A number of bits that the microprocessor can manipulate at one time.e.g.32-bits or 64-bits (32 bits registers or 64-bits) 2 MB Cache (Cash)measured in KB. 。Cash: is special high-speed memory that allows a microprocessor to access data more rapidly than memory
Microprocessor (Processor): • Intel pentium 3.2 GHz (Million cycles per second): • 800M Hz FSB (front side bus): Refers to the circuitry that transports data to and from the microprocessor. • Word size: A number of bits that the microprocessor can manipulate at one time. e.g. 32-bits or 64-bits (32 bits registers or 64-bits) • 2 MB Cache (Cash) measured in KB. • Cash: is special high-speed memory that allows a microprocessor to access data more rapidly than memory. Microprocessors and Memory The speed of the microprocessor clock- a timing device that sets the pace for excuting instructions Microprocessor’s clock operates at a speed of 3.2 billion per second)
Microprocessors and Memory CISC(Complex instruction set computer)technology. RISC (Reduced instructions set computer)technology. RISC processor performs instructions faster than CISC. Microprocessor excute more than one instructions at a time 1-Serial processing (one by one),one instruction at a time. 2-Pipelining processing(Starting with next before it completes the pervious) 3-Parallel processing (Multiple instructions are excuted at the same time)
• CISC (Complex instruction set computer) technology. • RISC (Reduced instructions set computer)technology. RISC processor performs instructions faster than CISC. Microprocessor excute more than one instructions at a time 1- Serial processing (one by one) , one instruction at a time. 2- Pipelining processing (Starting with next before it completes the pervious) 3- Parallel processing (Multiple instructions are excuted at the same time) Microprocessors and Memory
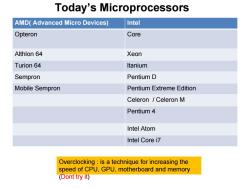
Today's Microprocessors AMD(Advanced Micro Devices) Intel Opteron Core Althlon 64 Xeon Turion 64 Itanium Sempron Pentium D Mobile Sempron Pentium Extreme Edition Celeron /Celeron M Pentium 4 Intel Atom Intel Core i7 Overclocking is a technique for increasing the speed of CPU,GPU,motherboard and memory (Dont try it)
AMD( Advanced Micro Devices) Intel Opteron Core Althlon 64 Xeon Turion 64 ltanium Sempron Pentium D Mobile Sempron Pentium Extreme Edition Celeron / Celeron M Pentium 4 Intel Atom Intel Core i7 Today’s Microprocessors Overclocking : is a technique for increasing the speed of CPU, GPU, motherboard and memory (Dont try it)
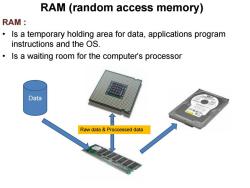
RAM (random access memory) RAM: Is a temporary holding area for data,applications program instructions and the OS. Is a waiting room for the computer's processor Data Raw data Proccessed data
RAM : • Is a temporary holding area for data, applications program instructions and the OS. • Is a waiting room for the computer’s processor RAM (random access memory) Data Raw data & Proccessed data
How does RAM work? In RAM microscopic electronic parts called Capacitors. The capacitors,that can only hold a charge,or not hold a charge,are arranged in banks of eight.If a capacitor has a charge,it is given a value of 1.If it doesn't hold a charge,it carries a value of 0. 。 RAM address on each bank helps the computer locate data. RAM is volatile,this means it requires power to hold data. If the computer run out memory,then the computer allocate data on HD(Virtual memory)
• In RAM microscopic electronic parts called Capacitors. • The capacitors, that can only hold a charge, or not hold a charge, are arranged in banks of eight. If a capacitor has a charge, it is given a value of “1”. If it doesn’t hold a charge, it carries a value of “0”. • RAM address on each bank helps the computer locate data. • RAM is volatile, this means it requires power to hold data. • If the computer run out memory, then the computer allocate data on HD( Virtual memory). How does RAM work?
ROM Read-only memory) ROM: Is type of memory circuitry that hold the computer's startup routline. ROM is permanent and non-volatile. ROM contains small set of instructions called the ROM BIOS ROM BIOS(Basic input/output system): Is a set of instructions tell the computer how to access the hard disk,find the operating system and load it into RAM. EEPROM(electrically erasable programmable read-only memory): Is a non-volatile chip that requires no power to hold data EEPROMs replace CMOS technology that required power from a small battery integrated into the system board
ROM: Is type of memory circuitry that hold the computer’s startup routline. - ROM is permanent and non-volatile. - ROM contains small set of instructions called the ROM BIOS ROM BIOS(Basic input/output system): Is a set of instructions tell the computer how to access the hard disk, find the operating system and load it into RAM. EEPROM( electrically erasable programmable read-only memory): Is a non-volatile chip that requires no power to hold data. EEPROMs replace CMOS technology that required power from a small battery integrated into the system board ROM ( Read-only memory)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-b-Digital Data Representation.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-a-Computer History+ Di Devices.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学大纲 Computer Concepts.pdf
- 《微型计算机技术及应用》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,共十五章,完整版).pptx
- 《微机技术及应用》课程教学大纲 Microcmputer Technology and aplications.doc
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Polymorphism and Virtual Functions.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Inheritance.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Strings.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Streams and File IO.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Separate Compilation and Namespaces.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Constructors and Other Tools.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Structures and Classes.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Flow of Control.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 3 Function Basics.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 1 C++ Basics.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Parameters and Overloading.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章.ppt
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-b-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)3-a-b-Computer Software.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4- operating system.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4-a- File mangement.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-a- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-b- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-a- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-b- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)7-a- Web.pdf
- 《数字图像处理技术》课程教学资源(实例)实验 - C语言附录实例.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言中详解指针.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C指针详解(经典详细).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言指针用法详解.pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)C语言指针详解.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)c语言指针完整教程.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(函数,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 指针.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(数组,带答案).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(分支与循环以前知识点,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)C程序设计讲义与习题(含参考答案).pdf
