《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 2 Flow of Control

Chapter 2 ABSOLUTE C++ Flow of Control WALTER SAVITCH SECOND EDITION PEARSON Copyright2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley All rights reserved
Chapter 2 Flow of Control

Learning Objectives Boolean Expressions Building,Evaluating Precedence Rules Branching Mechanisms ◆if-else ◆switch ◆Nesting if-.else ◆Loops ◆Vhile,do-while,for ◆Nesting loops Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-2
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-2 Learning Objectives ¨ Boolean Expressions ¨ Building, Evaluating & Precedence Rules ¨ Branching Mechanisms ¨ if-else ¨ switch ¨ Nesting if-else ¨ Loops ¨ While, do-while, for ¨ Nesting loops
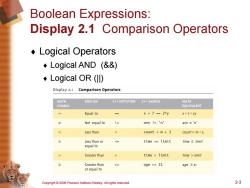
Boolean Expressions: Display 2.1 Comparison Operators ◆Logical Operators ·Logical AND(&&) ·Logical OR(Il) Display 2.1 Comparison Operators MATH ENGLISH C++NOTATION C++SAMPLE MATH SYMBOL EQUIVALENT Equal to X+7==2*y ×+7=2y Not equal to I= ans !='n' ans≠'nl Less than age>=21 age≥2l or equal to Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 23
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-3 Boolean Expressions: Display 2.1 Comparison Operators ¨ Logical Operators ¨ Logical AND (&&) ¨ Logical OR (||)

Evaluating Boolean Expressions ◆Data type bool ◆Returns true or false true,false are predefined library consts ◆Truth tables Display 2.2 next slide Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-4
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-4 Evaluating Boolean Expressions ¨ Data type bool ¨Returns true or false ¨true, false are predefined library consts ¨ Truth tables ¨Display 2.2 next slide
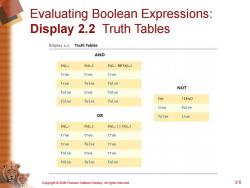
Evaluating Boolean Expressions: Display 2.2 Truth Tables Display 2.2 Truth Tables AND Exp_1 Exp_2 Exp_1 &Exp_2 true true true true false false NOT false true false false false false Exp !(Exp) true false OR false true Exp_1 Exp_2 Exp_Exp_2 true true true true false true false true true false false false Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-5
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-5 Evaluating Boolean Expressions: Display 2.2 Truth Tables

Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators(1 of 4) Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators Highest precedence Scope resolution operator (done first) Dot operator Member selection Array indexing Function call Postfix increment operator(placed after the variable) Postfix decrement operator(placed after the variable) + Prefix increment operator (placed before the variable) ! Prefix decrement operator(placed before the variable) Not +★ Unary minus Unary plus Dereference & Address of new Create (allocate memory) delete Destroy (deallocate) delete[] Destroy array (deallocate) sizeof Size of object () Type cast Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-6
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-6 Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators (1 of 4)
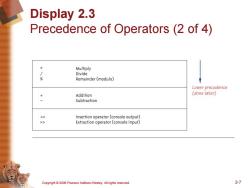
Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators(2 of 4) Multiply Divide % Remainder (modulo) Lower precedence Addition (done later) Subtraction Extraction operator(console input) Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-7
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-7 Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators (2 of 4)

Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators(3 of 4) Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators All operators in part 2 are of lower precedence than those in part 1. = Greater than or equal to Equal = Not equal & And Or Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-8
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-8 Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators (3 of 4)
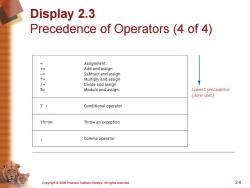
Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators(4 of 4) = Assignment += Add and assign Subtract and assign * Multiply and assign Divide and assign % Modulo and assign Lowest precedence (done last) ?: Conditional operator throw Throw an exception Comma operator Copyright006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-9
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-9 Display 2.3 Precedence of Operators (4 of 4)
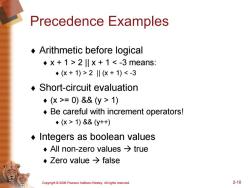
Precedence Examples Arithmetic before logical ◆x+1>2lx+12‖(仪+1)=0)&&(y>1) ◆Be careful with increment operators! ◆(X>1)&&(y++) Integers as boolean values ◆All non-zero values→true ◆Zero value→false Copyright 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley.All rights reserved. 2-10
Copyright © 2006 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 2-10 Precedence Examples ¨ Arithmetic before logical ¨ x + 1 > 2 || x + 1 2 || (x + 1) = 0) && (y > 1) ¨ Be careful with increment operators! ¨ (x > 1) && (y++) ¨ Integers as boolean values ¨ All non-zero values true ¨ Zero value false
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 3 Function Basics.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 1 C++ Basics.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 4 Parameters and Overloading.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第三章.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第二章 信源与信息熵.ppt
- 西安邮电大学:《信息论与编码》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第一章 绪论(主讲:王军选).ppt
- 《信息论与编码》课程教学资源(作业习题)第三章 信道与信道容量(含解答).pdf
- 《信息论与编码》课程教学资源(作业习题)自测题无答案.pdf
- 《信息论与编码》课程教学实验指导书.pdf
- 《信息论与编码》课程教学大纲 Element of Information Theory and Coding B.pdf
- 《信息论与编码》课程教学大纲 Element of Information Theory and Coding A.pdf
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第9章 信息安全标准与法律法规.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第2章 信息保密技术.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第7章 网络安全技术.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第8章 信息安全管理.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第6章 访问控制技术.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第5章 操作系统与数据库安全.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第1章 绪论.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第3章 信息认证技术.ppt
- 《信息安全概论》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第4章 信息隐藏技术.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Structures and Classes.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Constructors and Other Tools.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Separate Compilation and Namespaces.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Streams and File IO.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Strings.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Inheritance.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Polymorphism and Virtual Functions.ppt
- 《微机技术及应用》课程教学大纲 Microcmputer Technology and aplications.doc
- 《微型计算机技术及应用》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,共十五章,完整版).pptx
- 《计算机导论》课程教学大纲 Computer Concepts.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-a-Computer History+ Di Devices.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-b-Digital Data Representation.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-a-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-b-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)3-a-b-Computer Software.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4- operating system.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4-a- File mangement.pdf
