《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-a- LANS_WANS
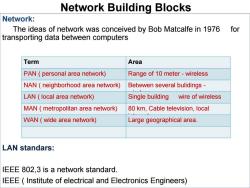
Network Building Blocks Network: The ideas of network was conceived by Bob Matcalfe in 1976 for transporting data between computers Term Area PAN(personal area network) Range of 10 meter-wireless NAN neighborhood area network) Betwwen several bulidings- LAN(local area network) Single building wire of wireless MAN(metropolitan area network) 80 km,Cable television,local WAN(wide area network) Large geographical area. LAN standars: IEEE 802,3 is a network standard. IEEE Institute of electrical and Electronics Engineers)
Network: The ideas of network was conceived by Bob Matcalfe in 1976 for transporting data between computers LAN standars: IEEE 802,3 is a network standard. IEEE ( Institute of electrical and Electronics Engineers) Network Building Blocks Term Area PAN ( personal area network) Range of 10 meter - wireless NAN ( neighborhood area network) Betwwen several bulidings - wireless LAN ( local area network) Single building wire of wireless MAN ( metropolitan area network) 80 km, Cable television, local internet. WAN ( wide area network) Large geographical area
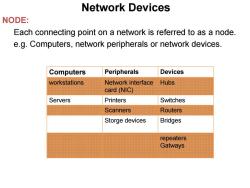
Network Devices NODE: Each connecting point on a network is referred to as a node. e.g.Computers,network peripherals or network devices. Computers Peripherals Devices workstations Network interface Hubs card(NIC) Servers Printers Switches Scanners Routers Storge devices Bridges repeaters Gatways
Network Devices NODE: Each connecting point on a network is referred to as a node. e.g. Computers, network peripherals or network devices. Computers Peripherals Devices workstations Network interface card (NIC) Hubs Servers Printers Switches Scanners Routers Storge devices Bridges repeaters Gatways

Clients,Servers and Peers Clients: Workstation Servers: File Server Application server Printer server Peer To Peer: There is no server in this network
Clients: Workstation Servers: File Server Application server Printer server Peer To Peer: There is no server in this network Clients, Servers and Peers
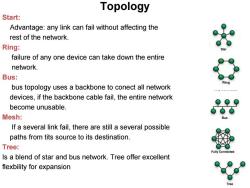
Topology Start: Advantage:any link can fail without affecting the rest of the network. Ring: failure of any one device can take down the entire network. Bus: bus topology uses a backbone to conect all network devices,if the backbone cable fail,the entire network become unusable. Mesh: If a several link fail,there are still a several possible paths from tits source to its destination. Tree: Is a blend of star and bus network.Tree offer excellent flexbility for expansion
Start: Advantage: any link can fail without affecting the rest of the network. Ring: failure of any one device can take down the entire network. Bus: bus topology uses a backbone to conect all network devices, if the backbone cable fail, the entire network become unusable. Mesh: If a several link fail, there are still a several possible paths from tits source to its destination. Tree: Is a blend of star and bus network. Tree offer excellent flexbility for expansion Topology
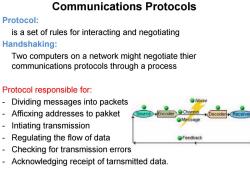
Communications Protocols Protocol: is a set of rules for interacting and negotiating Handshaking: Two computers on a network might negotiate thier communications protocols through a process Protocol responsible for: Dividing messages into packets Noise Afficxing addresses to pakket ource Channel Decode Intiating transmission Regulating the flow of data Feedback Checking for transmission errors Acknowledging receipt of tarnsmitted data
Communications Protocols Protocol: is a set of rules for interacting and negotiating Handshaking: Two computers on a network might negotiate thier communications protocols through a process Protocol responsible for: - Dividing messages into packets - Afficxing addresses to pakket - Intiating transmission - Regulating the flow of data - Checking for transmission errors - Acknowledging receipt of tarnsmitted data

Communications Protocols Sending E-mail: the file message wil be chopped up into a small pieces called packet. Every packet travels over the network includes the address of its destination devices.The adresses are IP address and MAC address. IP address: IP address assigned by ISPs or system managers or obtained through DHCP. IP address separated into FOUR sections,each sections is called an OCTET becuase in binary is represented by eight bits e.g.204.127.129.1 00000000.00000000.00000000.00000000
Sending E-mail: the file message wil be chopped up into a small pieces called packet. Every packet travels over the network includes the address of its destination devices. The adresses are IP address and MAC address. IP address: IP address assigned by ISPs or system managers or obtained through DHCP. IP address separated into FOUR sections, each sections is called an OCTET becuase in binary is represented by eight bits e.g. 204. 127.129.1 00000000.00000000.00000000.00000000 Communications Protocols

Wired Networks Wired network: Is one that uses cables to connect network devices. Advantages: Security,easy configure,Fast,large data transfer,Big PostScript jobs to a network printer. Ethernet: Is the most popular LAN technology.Ethernet defined by IEEE 802.3,the packet is accepted only by the device which it is addressed. An integral part of ethernet Technology relies on CSMA/CD protocol. CSMA/CD:is a protocol detects the collision(Collision occurs), deletes the colliding signals,reset the network,and prepares to retransmit tha data
Wired network: Is one that uses cables to connect network devices. Advantages: Security, easy configure, Fast, large data transfer, Big PostScript jobs to a network printer. Ethernet: Is the most popular LAN technology. Ethernet defined by IEEE 802.3, the packet is accepted only by the device which it is addressed. An integral part of ethernet Technology relies on CSMA/CD protocol. CSMA/CD: is a protocol detects the collision( Collision occurs), deletes the colliding signals, reset the network, and prepares to retransmit tha data. Wired Networks

Wired Networks Ethernet Equipment: Two or more Computers Ethernet router Surge strip or UPS Cable for each computer(STP Cable,Connectors RJ45) Internet access modem with cable for access internet. How fast is an Ethernet: From 10Mbps>>>>>>>>>>10Gbps Fast Ethernet:IEEE 802.3u 100Mbps Device managers >>Network adapters >>Network cards. Ethernet Port by checking a workstation for an Ethernet port
Ethernet Equipment: - Two or more Computers - Ethernet router - Surge strip or UPS - Cable for each computer ( STP Cable, Connectors RJ45) - Internet access modem with cable for access internet. How fast is an Ethernet: From 10Mbps>>>>>>>>>>10Gbps Fast Ethernet: IEEE 802.3u 100Mbps Device managers >>> Network adapters >>> Network cards. Ethernet Port : by checking a workstation for an Ethernet port Wired Networks
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4-a- File mangement.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)4- operating system.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)3-a-b-Computer Software.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-b-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)2-a-Computer Hardware.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-b-Digital Data Representation.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)1-a-Computer History+ Di Devices.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学大纲 Computer Concepts.pdf
- 《微型计算机技术及应用》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件,共十五章,完整版).pptx
- 《微机技术及应用》课程教学大纲 Microcmputer Technology and aplications.doc
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 14 Polymorphism and Virtual Functions.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 13 Inheritance.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 9 Strings.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 12 Streams and File IO.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 11 Separate Compilation and Namespaces.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 5 Arrays.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 8 Operator Overloading, Friends, and References.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 7 Constructors and Other Tools.ppt
- 《C++面向对象程序设计》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Chapter 6 Structures and Classes.ppt
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)5-b- LANS_WANS.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-a- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)6-b- The Internet.pdf
- 《计算机导论》课程教学课件(英文讲稿)7-a- Web.pdf
- 《数字图像处理技术》课程教学资源(实例)实验 - C语言附录实例.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言中详解指针.doc
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C指针详解(经典详细).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言指针用法详解.pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)C语言指针详解.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)c语言指针完整教程.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(函数,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第06章 指针.ppt
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(数组,带答案).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)C语言程序设计期中测试(分支与循环以前知识点,带答案).pdf
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(试卷习题)C程序设计讲义与习题(含参考答案).pdf
- 《C语言程序设计》课程教学资源(讲义资料)考试知识点复习(C语言程序设计复习样题及部分解析).doc
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第09章 文件.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第08章 结构体.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第07章 预处理命令.ppt
- 中国农业大学:《C语言程序设计》课程教学课件(PPT讲稿)第05章 函数.ppt
