《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)04 population Growth

POPULATONGROWTH
POPULATION GROWTH
OOa

bLakeplankiomadiatomsand(b)copepodFIGURE9.1

ECOLOGYCONHPZSANDAPPLICATIOASPOPULATIONGROWIRIn the presence of abundantresources,populations cangrowatgeometric or exponential rates
❖ In the presence of abundant resources, populations can grow at geometric or exponential rates
ECOLOGYCONCEPZSANDAPPLICAZIONSPOPULATIONGROWIHGeometric Growth
➢ Geometric Growth

The geometric rateofincreaseX,is theratio of numbers ataNumberslatertime,Nttito numbers atat lateran earliertime.Nrime, t+1Geometric population growthPhlox drummondii(Leverich and Levin,1979Annual plant, insects......N,=Noat(N-No2, N,-N,a=Noaa......)Numbersatearliert+11Latertime,tEarlicrTimetimetimeFIGURE8.IOThegeometricrateofincrease
Geometric population growth Phlox drummondii(Leverich and Levin,1979) Annual plant, insects. Nt = N0 λ t (N1=N0 λ, N2=N1 λ= N0 λ λ. )

Numberatsomeinitialtimetimes2raisedto thepowertN,=NoatN,=NoatNumberof timeintervals,in hours.days, years, ete.AveragenumberofNumber atoffspring leftbyansome timetindividual during onetime intervalFIGURE 9.2 Anatomy of the equationfor geometric populationgrowth
Nt = N0λ t
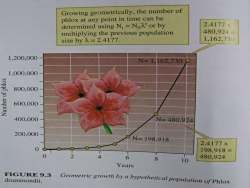
Growing geometrically,the number ofphlox at any point in time can be2.4177xdetermined using N, = No2' or by480.924=multiplying the previous population1.162.730sizeby2=2.4177.1,200.000N-1162.7301.000,000iooin800.000600.000400.000N=480.924200,0002N=198.9182.4177x0198.918=1024480.9246810YearsFICURE9.3Geometric growth by a hypothetical population of Phloxdrummondii
ECOLOGYCONCEPZSANDAPPLICAZIONSPOPULATIONGROWIRExponential Growth
➢ Exponential Growth

KONOPUSONGAOWTExponentialpopulationgrowthContinuous population growth in an unlimited environment can bemodeled as..dNN- No= rNr(%) = -dtNr>0:r<0:N, = No: ertr=0:
Exponential population growth Continuous population growth in an unlimited environment can be modeled as. = rN dN dt r(%) = Nt - N0 N0 Nt = N0 · ert r > 0 : r < 0 : r = 0 :
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)05 interactions Competition.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)05 interactions Exploitation.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)06 Large-scale ecology Geographic ecology.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)05 interactions Mutualism.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 生态系统生态学 Ecosystem Ecology.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 景观生态学.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 保护生物学——生物多样性的价值.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 地球生命的起源与进化——进化的历程.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 保护生物学的定义.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第三章 物质环境).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第二章 能量环境 2/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)普通生态学 General Ecology - 绪言.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第1章 生物与环境、第二章 能量环境 1/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第四章 种群及其基本特征2/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第三章 物质环境).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(生物入侵——新世纪的生态学挑战).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第四章 种群及其基本特征1/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第七章 种内与种间关系 2/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第五章 生物种及其变异与进化).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第六章 生活史对策).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)生态环境建设与生态工程技术的应用(石河子大学:王绍明).ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)04 population Distribution and abundance.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)03 Individuals - energy and nutrient relations.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)03 Individuals- 2/2 water.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)03 Individuals -1/2 Temperature.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)04 population Dynamics.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)02 Natural History - 2/2.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)01 what is ecology.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)02 Natural History - 1/2.ppt
- 《环境工程原理》课程教学大纲 Principles of Environmental Engineering.doc
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第09章 吸附.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第10章 其它分离过程.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第07章 过滤.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第08章 吸收.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第05章 质量传递.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第06章 沉降.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第03章 流体流动.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第04章 热量传递.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第01章 绪论.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第02章 质量衡算与能量衡算.pdf
