《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)03 Individuals - energy and nutrient relations

IndivdualsEnergyandnatrientrelationsIndividualsENERGYANDNUTRIENTRELATIONS
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations ENERGY AND NUTRIENT RELATIONS Individuals

IndiidualsEnergy andnutrientrelationsxOrganismsone ofthreeusemain sourcesofenergy : lightorganic molecules, or inorganicmolecules.TFEECEOr
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations ❖ Organisms use one of three main sources of energy : light, organic molecules, or inorganic molecules
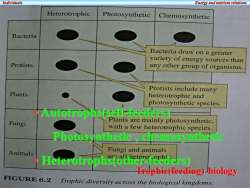
IndividualsEnergyandnutrientrelationsHeterotrophiePhotosyntheticChemosyntheticBacteriaBacteria draw on a greatervariety of energy sources thanProtistsany other group of organisms.Protists include manyPlantsheterotrophic andphotosyntheticspecies·Autotrophs(self-feeders)Plants are mainly photosynthetic,Fungiwith a fewheterotrophic speciesPhotosynthetic,chemosyntheticFungi and animalsAnimalsHeterotrophs(other-feeders)Trophic(feeding)biologyFIGURE6.2Trophic diversity across the biological kingdoms
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations • Autotrophs(self-feeders) Photosynthetic , chemosynthetic • Heterotrophs(other-feeders) Trophic(feeding) biology

IndivdualsEnergyandnutrientrelationsUsing Light and CO2
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations ➢ Using Light and CO2

IndividualsEnergyandnutrientrelations.Wave, photon.infraredvisiblelight(<400nm),light(400-700nm), ultraviolet light·Photosyntheticlly active radiationPAR.·(solar energy:53% infrared light, 45% visible light, 2%ultraviolet light)Photon flux density(number of photos μumol /m?.s)
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations •Wave, photon •infrared light(<400nm), visible light(400-700nm), ultraviolet light. •Photosyntheticlly active radiation, PAR. •(solar energy: 53% infrared light, 45% visible light, 2% ultraviolet light) •Photon flux density(number of photos mol /m2 .s)
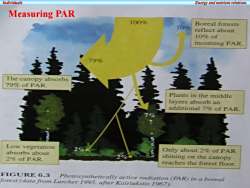
IndividualsEnergyandnatrientrelationsMeasuring PAR100%Boreal forests10%reflect about10%0fincomingPAR79%發福The canopy absorbs79%OfPARPlants in the middlelayersabsorb anadditional 7ofPARLow vegetationOnlyabout2%of PARabsorbs aboutshining on the canopy2%OfPARreaches the forest floorFIGURE6.3Photosyntheticallyactive radiationPARina borealforest(datafromLarcher1995.afterKairiukstis1967)
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations • Measuring PAR
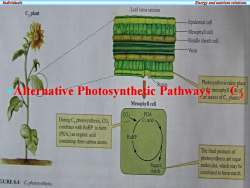
IndividualsEnergyandnutrientrelationsLeaf cross sectionC,plantEpidermal cellMesophyll cellBundle sheath cellVeinsPhotosynthesis takes placeISOAlternative Photosynthetic PathwaysmesophyllO1heleavesofCplants.Mesophyll cellPGACODuringpynthCacidcombineswithRuBPtoform(PGA.)an organic acidRuBPcontaining three carbon atoms.Thefinal products ofphotosynthesis are sugarSugars,molecules,which maybestarchcombinedtoformstarchGURE6.4C,photosynthesis
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations • Alternative Photosynthetic Pathways C3
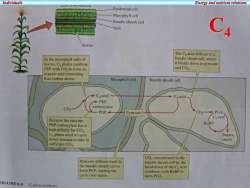
IndividualsEnergyandnutrientrelationsNCGuOnEpidermal cellMesophyll cellBundlesheathcellC4VeinStomaThe Caacid diffuses to abundle sheath cell.whereInthemesophyll cellsofitbreaks down to pyruvateleaves,Cplantscombineandco,PEPwithCO,toformanorganicacid containingfourcarbon atoms.Mesophyll cellBundle sheath cellChacidCyacidPEPcarboxylaseCOSPEPCOPGAPyruvateCacidBecausethe enzymeRuBPPEPcarboxylasehasahigh affinity for CO2Cplants needtoopenSugars,fewerstomata totakeinstarchsufficientCO,CO,concentrated in thePyruvate diffuses back tobundle sheath cell by thethe bundle sheath cell tobreakdown oftheCyacidformPEP,startingthecombineswithRuBptocyele over againform PGA.FIGURE6.5Caphotosvnthesis
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations C4
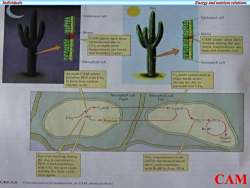
IndividualsEnergyandnatrientrelationsDayEpidermal cellEpidermalcellStomaStomaCAM plintsopen theirCAM plants olose thcirstomuta and take instomata during the day.CO,atnightwhenwhentemperatures aretemperatures are lowerhigh and humidity low.and humidity higherMesophyllcellMesophyll cellArnighr CAMplantsCaacids synthesized atcombine PEPwith COnight break downto form four-curbonduring the day toorganic acidspyruvate and cO2Mesophyll cellMesophyll cellNightDayCracidCaacidAPEPCO.PyruvateCo,PGARuBPSugars,starchPyruvate builtup duringCOaconcentrated inthethe day is converted tocellbythebreakdownofPEP,whichcombinesthe C, ncid combineswith Co,thenextnight,withRuBptoformPGAstarting thedaly cyeleoveragain.CAMUREG.GCrasxulaceanacidmerabolism,orCAM.photosynthesix
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations CAM

IndivdualsEnergyandnatrientrelationsC3 plants: lose 380-900g of water for agram(dryweight) of tissue producedCf:250-350gCAM: 50+/-
Individuals Energy and nutrient relations C3 plants: lose 380-900g of water for a gram(dry weight) of tissue produced C4 : 250-350g CAM: 50+/-
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)04 population Distribution and abundance.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)生态环境建设与生态工程技术的应用(石河子大学:王绍明).ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)04 population Growth.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)05 interactions Competition.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)05 interactions Exploitation.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)06 Large-scale ecology Geographic ecology.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)05 interactions Mutualism.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 生态系统生态学 Ecosystem Ecology.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 景观生态学.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 保护生物学——生物多样性的价值.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 地球生命的起源与进化——进化的历程.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 保护生物学的定义.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第三章 物质环境).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第二章 能量环境 2/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)普通生态学 General Ecology - 绪言.ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第1章 生物与环境、第二章 能量环境 1/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第四章 种群及其基本特征2/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)有机体与环境(第三章 物质环境).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(生物入侵——新世纪的生态学挑战).ppt
- 《生态学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)种群生态学(第四章 种群及其基本特征1/2).ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)03 Individuals- 2/2 water.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)03 Individuals -1/2 Temperature.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)04 population Dynamics.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)02 Natural History - 2/2.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)01 what is ecology.ppt
- 《生态学》课程PPT教学课件(生态学原理与应用)02 Natural History - 1/2.ppt
- 《环境工程原理》课程教学大纲 Principles of Environmental Engineering.doc
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第09章 吸附.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第10章 其它分离过程.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第07章 过滤.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第08章 吸收.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第05章 质量传递.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第06章 沉降.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第03章 流体流动.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第04章 热量传递.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第01章 绪论.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程授课教案(讲稿)第02章 质量衡算与能量衡算.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程实验教学大纲 Principles of Environmental Engineering.doc
- 《环境工程原理》课程作业习题(含解答)第09章 吸附.pdf
- 《环境工程原理》课程作业习题(含解答)第10章 其他分离过程.pdf
