西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 05-2 Synaptic DynamicsII:Supervised Learning

Synaptic DynamicsII:Supervised Learning The Backpropagation Algorithm and Spport Vector Machines JingLIU 2004.11.3
Synaptic DynamicsII : Supervised Learning The Backpropagation Algorithm and Spport Vector Machines JingLIU 2004.11.3

History of BP Algorithm Rumelhart [1986]popularized the BP algorithm in the Paralle/Distributed Processing edited volume in the late 1980's. ■ BP algorithm overcame the limitations of the perceptron algorithm,limitations that Minsky and Papert[1969]had carefully enumerated. BP's popularity begot waves of criticism.BP algorithm often failed to converge,and at best converged to local error minima. The wave of criticism challenged BP's historical priority. The wave of criticism challenge whether the BP learning was new.The algorithm not offer a new kind of learning
History of BP Algorithm ◼ Rumelhart [1986]popularized the BP algorithm in the Parallel Distributed Processing edited volume in the late 1980’s. ◼ BP algorithm overcame the limitations of the perceptron algorithm, limitations that Minsky and Papert[1969] had carefully enumerated. ◼ BP’s popularity begot waves of criticism. BP algorithm often failed to converge, and at best converged to local error minima. ◼ The wave of criticism challenged BP’s historical priority. ◼ The wave of criticism challenge whether the BP learning was new. The algorithm not offer a new kind of learning

Multilayer feedforward NNs Output layer Hidden layer Input layer ■■■■■■■■■■■■■
Multilayer feedforward NNs

Feedforward Sigmoidal Representation Theorems Feedforward sigmoidal architectures can in principle represent any Borel-measurable function to any desired accuracy-if the network contains enough hidden"neurons between the input and output neuronal fields. So the MLP can solve the problems of nonlinear separable problems and function approximate
Feedforward Sigmoidal Representation Theorems ◼ Feedforward sigmoidal architectures can in principle represent any Borel-measurable function to any desired accuracy—if the network contains enough “hidden” neurons between the input and output neuronal fields. ◼ So the MLP can solve the problems of nonlinear separable problems and function approximate

Feedforward Sigmoidal Representation Theorems We can explain the theorem in the following two aspects: To improve the NNs'classification ability,we must use multilayer networks,at least one hidden layers. One the other hand,when feedforward-sigmoidal neural networks finely approximate complicated functions,the networks may suffer a like "explosion"of hidden neurons and interconnecting synapses
Feedforward Sigmoidal Representation Theorems ◼ We can explain the theorem in the following two aspects: ◼ To improve the NNs’ classification ability, we must use multilayer networks, at least one hidden layers. ◼ One the other hand, when feedforward –sigmoidal neural networks finely approximate complicated functions, the networks may suffer a like “explosion” of hidden neurons and interconnecting synapses
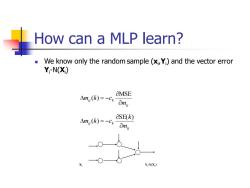
How can a MLP learn? We know only the random sample (xi,Y)and the vector error Y-N(X) OMSE △m,k)=-c4am, aSE(k) Am(k)=-Cx my Y-N(X
How can a MLP learn? ◼ We know only the random sample (xi ,Yi ) and the vector error Yi -N(Xi ) ij ij k m m k c = − MSE ( ) ij ij k m k m k c = − SE( ) ( ) Xi Yi-N(Xi)
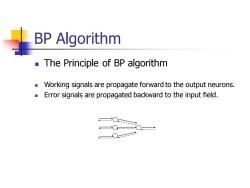
BP Algorithm The Principle of BP algorithm Working signals are propagate forward to the output neurons. Error signals are propagated backward to the input field
BP Algorithm ◼ The Principle of BP algorithm ◼ Working signals are propagate forward to the output neurons. ◼ Error signals are propagated backward to the input field
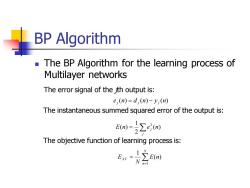
BP Algorithm The BP Algorithm for the learning process of Multilayer networks The error signal of the th output is: e,(n)=d,(n)-y,(n) The instantaneous summed squared error of the output is: m=∑em The objective function of learning process is: Hn()
BP Algorithm ◼ The BP Algorithm for the learning process of Multilayer networks The error signal of the jth output is: The instantaneous summed squared error of the output is: The objective function of learning process is: e (n) d (n) y (n) j = j − j = j E n e j (n) 2 1 ( ) 2 = = N n AV E n N E 1 ( ) 1

BP Algorithm In the case of learning sample by sample: 0,(n) d,(n) y,m)y,(n) e,(n) y(n)○ ○ p,(n) The gradient of at nth iteration is: E(n) 50=e,mp心m@
BP Algorithm ◼ In the case of learning sample by sample: ◼ The gradient of E(n) at nth iteration is: v (n) j y (n) i (n) j y (n) j d (n) j e (n) j w (n) ji ( ) ( ( )) ( ) ( ) ( ) e n v n y n w n E n j j j i ji = − (n) j

BP Algorithm The modification quantity of weight w is: E(n)--n,(n)y.(n) △w,m=-naNm where δ,(n)=e,(n)p(v,(n) (1) For j is an output neuron:5,(n)=(d,(n)-y (n)((m)) (2) For j is a hidden neuron: 6,0m= aEmo'v,n》 ay,(n))' d,(m)=py,(n∑d(m)wg(m) [△wu]=[n][δ,(n][y,(n)]
BP Algorithm ◼ The modification quantity of weight wji is: where (1) For j is an output neuron: (2) For j is a hidden neuron: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) n y n w n E n w n j i ji ji = − = − (n) e (n) (v (n)) j j j j = = k j (n) j (v j (n)) k (n)wkj (n) (n) (d (n) y (n)) (v (n)) j j j j j = − ( ( )) ( ) ( ) ( ) v n y n E n n j j j = − [ w ] [ ] [ (n)] [ y (n)] ij j i = • •
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 05-1 第五章 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督学习.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 04 SYNAPTIC DYNAMICS 1:UNSUPERVISED LEARNING.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 03 Neuronal Dynamics 2:Activation Models.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 02 ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)10. 模糊与卡尔曼滤波目标跟踪控制系统的比较 Comparison of Fuzzy and Kalman-Filter Target-Tracking Control Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)09. 模糊图像变换编码 Fuzzy Image Transform Coding.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)08. 模糊与神经网络的比较——以倒车系统为例 Comparison of Fuzzy and Neural Truck Backer-Upper Control Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)07. 模糊联想记忆 Fuzzy Associative Memories(FAM).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)06. 模糊与概率 Fuzziness versus Probability.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)05. 结构和平衡 Architectures and Equilibria.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)04. 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics II——Supervised Learning(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)03. 突触动力学 - 非监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics I——Unsupervised Learning(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)03. 突触动力学 - 非监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics I——Unsupervised Learning(1/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)02. Neuronal Dynamics——Activation Models(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)02. Neuronal Dynamics——Activation Models(1/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)01.Neuronal Dynamics——Activations and Signals(主讲:高新波).ppt
- 《神经网络与模糊系统》课程教学资源(主题演讲)选择性集成 Selective Ensemble(南京大学:周志华).ppt
- 《神经网络与模糊系统》课程教学资源(主题演讲)机器学习研究进展(南京大学:王珏).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)进化计算 SOFT COMPUTING Evolutionary Computing.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)模糊系统与模糊逻辑 Fuzzy Theory.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 06 Architecture and Equilibra 结构和平衡.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 07-1 Fuzziness vs. Probability.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 07-2 Fuzziness vs. Probability 模糊集合的模糊程度——模糊熵.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 08-1 Fuzzy Associative Memories.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 10 模糊图像变换编码.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 08-2 Fuzzy Associative Memories 模糊联想记忆 FUZZY ASSOCIATIVE MEMMORIESⅡ.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 09-2 模糊倒车控制系统——拖斗拖车.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 11 模糊与卡尔曼滤波目标跟踪控制系统的比较 Comparison of Fuzzy and Kalman-Filter Target-Tracking control system.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 09-1 模糊与神经网络倒车系统比较.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 02 NEURAL DYNAMIC1:ACTIVATIONHS AND SIGNALS(主讲:高新波).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 03-1 NEURONAL DYNAMICS 2:ACTIVATION MODELS.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 03-2 NEURONAL DYNAMICS 2:ACTIVATION MODELS.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 04-1 Synaptic Dynamics:Unsupervised Learning Part Ⅰ.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 04-2 Synaptic Dynamics:Unsupervised Learning Part Ⅱ.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 04-3 Part3 Differential Heb learning & Differential Competitive learning.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 05-1 突触动力学Ⅱ——有监督学习.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 05-2 Backpropagation Algorithm.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 10 模糊图像变换编码.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 05-3 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督的学习.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 06 Architecture and Equilibria 结构和平衡.ppt
