西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)01.Neuronal Dynamics——Activations and Signals(主讲:高新波)

NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS NEURONS AS FUNCTIONS Neurons behave as functions. Neurons transduce an unbounded input activation x(t)at time t into a bounded output signal S(x(t)). 2
2 NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS NEURONS AS FUNCTIONS Neurons behave as functions. Neurons transduce an unbounded input activation x(t) at time t into a bounded output signal S(x(t))
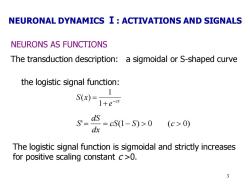
NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS NEURONS AS FUNCTIONS The transduction description:a sigmoidal or S-shaped curve the logistic signal function: S(x)= +e-a =eS(1-S)>0 (c>0) dx The logistic signal function is sigmoidal and strictly increases for positive scaling constant c>0. 3
3 NEURONS AS FUNCTIONS The transduction description: a sigmoidal or S-shaped curve the logistic signal function: cx e S x − + = 1 1 ( ) ' = = cS(1− S) 0 (c 0) dx dS S The logistic signal function is sigmoidal and strictly increases for positive scaling constant c >0. NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS
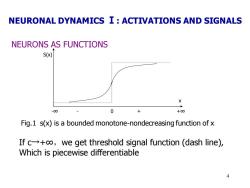
NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS NEURONS AS FUNCTIONS S(x) X -00 0 +00 Fig.1 s(x)is a bounded monotone-nondecreasing function of x If c+o,we get threshold signal function (dash line), Which is piecewise differentiable 4
4 NEURONS AS FUNCTIONS S(x) x -∞ - 0 + +∞ Fig.1 s(x) is a bounded monotone-nondecreasing function of x If c→+∞,we get threshold signal function (dash line), Which is piecewise differentiable NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS

NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS SIGNAL MONOTONICITY In general,signal functions are monotone nondecreasing S'>=0.This means signal functions have an upper bound or saturation value. The staircase signal function is a piecewise-differentiable Monotone-nondecreasing signal function. 5
5 SIGNAL MONOTONICITY In general, signal functions are monotone nondecreasing S’>=0. This means signal functions have an upper bound or saturation value. The staircase signal function is a piecewise-differentiable Monotone-nondecreasing signal function. NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS

NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS SIGNAL MONOTONICITY An important exception:bell-shaped signal function or Gaussian signal functions S(x)=e-cx c>0 S=-2cxe S S"o∝-x The sign of the signal-activation derivation s'is opposite the sign of the activation x.We shall assume signal functions are monotone nondecreasing unless stated otherwise. 6
6 SIGNAL MONOTONICITY An important exception: bell-shaped signal function or Gaussian signal functions 0 2 = − S x e c cx ( ) S cxe S x cx = − − − ' 2 , ' 2 The sign of the signal-activation derivation s’ is opposite the sign of the activation x. We shall assume signal functions are monotone nondecreasing unless stated otherwise. NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS

NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS SIGNAL MONOTONICITY Generalized Gaussian signal function define potential or radial basis function S (x): s=6p22x,-41 input activation vector:x=(xi,…,xn)∈R" variance:o, mean vector:=() we shall consider only scalar-input signal functions:S (x 7
7 SIGNAL MONOTONICITY Generalized Gaussian signal function define potential or radial basis function : ( ) ] 2 1 ( ) exp[ 2 = − 2 − n j i j j i i S x x n x = (x1 , , xn )R ( , , ) i n i i = 1 input activation vector: variance: mean vector: NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS 2 i S (x) i we shall consider only scalar-input signal functions: ( ) i i S x

NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS SIGNAL MONOTONICITY neurons are nonlinear but not too much so----a property as semilinearity Linear signal functions make computation and analysis comparatively easy - do not suppress noise linear network are not robust Nonlinear signal functions increases a network's computational richness increases a network's facilitates noise suppression risks computational and analytical intractability favors dynamical instability 8
8 SIGNAL MONOTONICITY neurons are nonlinear but not too much so ---- a property as semilinearity Linear signal functions - make computation and analysis comparatively easy - do not suppress noise - linear network are not robust Nonlinear signal functions - increases a network’s computational richness - increases a network’s facilitates noise suppression - risks computational and analytical intractability - favors dynamical instability NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS

NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS SIGNAL MONOTONICITY Signal and activation velocities the signal velocity:S =dS/dt 5= dS dx dx dt -Sx Signal velocities depend explicitly on action velocities 9
9 SIGNAL MONOTONICITY Signal and activation velocities the signal velocity: =dS/dt Signal velocities depend explicitly on action velocities S S x dt dx dx dS S = = ' NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS
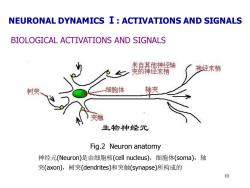
NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS 来自其他神经轴 突的神经末梢 神经末梢 树突 细胞体 轴突 突触 生物神经元 Fig.2 Neuron anatomy 神经元(Neuron)是由细胞核(cell nucleus),细胞体(soma),轴 突(axon),树突(dendrites)和突触(synapse)所构成的 10
10 BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS Fig.2 Neuron anatomy 神经元(Neuron)是由细胞核(cell nucleus),细胞体(soma),轴 突(axon),树突(dendrites)和突触(synapse)所构成的 NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS
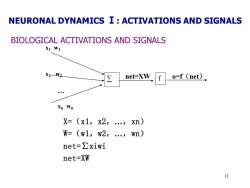
NEURONAL DYNAMICS I:ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS X1 W1 X2-W2 net=XW f o=f (net), Xn Wn X=(x1,x2,.,xn) W=(w1,w2,..,wn) net=∑xiwi net-XW 11
11 X=(x1,x2,…,xn) W=(w1,w2,…,wn) net=∑xiwi net=XW x2 w2 ∑ f o=f(net) xn wn … net=XW x1 w1 BIOLOGICAL ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS NEURONAL DYNAMICS Ⅰ: ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《神经网络与模糊系统》课程教学资源(主题演讲)选择性集成 Selective Ensemble(南京大学:周志华).ppt
- 《神经网络与模糊系统》课程教学资源(主题演讲)机器学习研究进展(南京大学:王珏).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)进化计算 SOFT COMPUTING Evolutionary Computing.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)模糊系统与模糊逻辑 Fuzzy Theory.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)模糊神经网络 Neuro-fuzzy Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)人工神经网络 Artificial Neural Networks.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)有关人工智能的故事.doc
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)人工智能 AI.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 用于机器人的Ubuntu linux.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 机器人的逆向运动学.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 机器人的动力学.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 速度和静态力.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 空间描述和变换.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 机器人的线性控制.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 机器人的顺向运动学.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第3章 机器人编程的Python基础知识.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第2章 机器人编程的C++基础知识.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 机器人概述(主讲:杨智勇).pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)绪论、第1章 极限与配合及检测.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人工程专业导论》理论课教学大纲 Introduction to robot engineering.doc
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)02. Neuronal Dynamics——Activation Models(1/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)02. Neuronal Dynamics——Activation Models(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)03. 突触动力学 - 非监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics I——Unsupervised Learning(1/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)03. 突触动力学 - 非监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics I——Unsupervised Learning(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)04. 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics II——Supervised Learning(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)05. 结构和平衡 Architectures and Equilibria.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)06. 模糊与概率 Fuzziness versus Probability.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)07. 模糊联想记忆 Fuzzy Associative Memories(FAM).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)08. 模糊与神经网络的比较——以倒车系统为例 Comparison of Fuzzy and Neural Truck Backer-Upper Control Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)09. 模糊图像变换编码 Fuzzy Image Transform Coding.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)10. 模糊与卡尔曼滤波目标跟踪控制系统的比较 Comparison of Fuzzy and Kalman-Filter Target-Tracking Control Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 02 ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 03 Neuronal Dynamics 2:Activation Models.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 04 SYNAPTIC DYNAMICS 1:UNSUPERVISED LEARNING.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 05-1 第五章 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督学习.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 05-2 Synaptic DynamicsII:Supervised Learning.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 06 Architecture and Equilibra 结构和平衡.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 07-1 Fuzziness vs. Probability.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 07-2 Fuzziness vs. Probability 模糊集合的模糊程度——模糊熵.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 08-1 Fuzzy Associative Memories.ppt
