西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)05. 结构和平衡 Architectures and Equilibria

神经网络与模糊系统 Chapter 6 Architecture and Equilibria 结构和平衡 学生:李琦 导师:高新波
Architecture and Equilibria 结构和平衡 Chapter 6 神经网络与模糊系统 学生: 李 琦 导师:高新波

6.1 Neutral Network As Stochastic Gradient system Classify Neutral network model By their synaptic connection topologies and by how learning modifies their connection topologies synaptic connection topologies 1.feedforward:if no closed synaptic loops 2.feedback:if closed synaptic loops or feedback pathways how learning modifies their connection topologies 1.Supervised learning:use class-membership information of training samples 2Unsupervised learning:use unlabelled training samplings 2003.11.19 2
2003.11.19 2 6.1 Neutral Network As Stochastic Gradient system Classify Neutral network model By their synaptic connection topologies and by how learning modifies their connection topologies 1. : 2. : feedforward if no closed synaptic loops feedback if closed synaptic loops or feedback pathways 1. : 2. : Supervised learning use class membership information of training samples Unsupervised learning use unlabelled training samplings − synaptic connection topologies how learning modifies their connection topologies
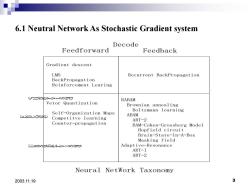
6.1 Neutral Network As Stochastic Gradient system Decode Feedforward Feedback Gradient descent LMS Recurrent BackPropagation BackPropagation Reinforcement Learing C∽=Qh>H∽aa RABAM Vetor Quantization Brownian annealing Boltzmann learning Self-Organization Maps rsooo ABAM Competitve learning ART-2 Counter-propagation BAM-Cohen-Grossberg Model Hopfield circuit Brain-State-In-A-Box Masking field ○二∽台QaDs>H∽qG Adaptive-Resonance ART-1 ART-2 Neural NetWork Taxonomy 2003.11.19 3
2003.11.19 3 6.1 Neutral Network As Stochastic Gradient system Gradient descent LMS BackPropagation Reinforcement Learing Recurrent BackPropagation Vetor Quantization Self-Organization Maps Competitve learning Counter-propagation RABAM Brownian annealing Boltzmann learning ABAM ART-2 BAM-Cohen-Grossberg Model Hopfield circuit Brain-State-In-A-Box Masking field Adaptive-Resonance ART-1 ART-2 Feedforward Feedback Decode S u p e r v i s e d U n s u p e r v i s e d E n c o d e Neural NetWork Taxonomy

6.2 Global Equilibria:convergence and stability Three dynamical systems in neural network: synaptic dynamical system N neuronal dynamical system joint neuronal-synaptic dynamical system (M) Historically,Neural engineers study the first or second neural network.They usually study learning in feedforward neural networks and neural stability in nonadaptive feedback neural networks.RABAM and ART network depend on joint equilibration of the synaptic and neuronal dynamical systems. 2003.11.19 4
2003.11.19 4 6.2 Global Equilibria: convergence and stability Three dynamical systems in neural network: synaptic dynamical system neuronal dynamical system joint neuronal-synaptic dynamical system Historically,Neural engineers study the first or second neural network.They usually study learning in feedforward neural networks and neural stability in nonadaptive feedback neural networks. RABAM and ART network depend on joint equilibration of the synaptic and neuronal dynamical systems. M x ( , ) x M

6.2 Global Equilibria:convergence and stability Equilibrium is steady state(for fixed-point attractors) Convergence is synaptic equilibrium.M=0 Stability is neuronal equilibrium.*=0 More generally neural signals reach steady state even though the activations still change.We denote steady state in the neuronal field F:F=0 Global stability:x=0,M=0 Stability-Equilibrium dilemma Neurons fluctuate faster than synapses fluctuate. Convergence undermines stability. 2003.11.19 5
2003.11.19 5 6.2 Global Equilibria: convergence and stability Equilibrium is steady state (for fixed-point attractors) Convergence is synaptic equilibrium. Stability is neuronal equilibrium. More generally neural signals reach steady state even though the activations still change. We denote steady state in the neuronal field : Global stability: Stability - Equilibrium dilemma : Neurons fluctuate faster than synapses fluctuate. Convergence undermines stability. Μ = 0 x = 0 F x Fx = 0 x = 0,M = 0

6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids:AVQ Algorithms Competitive learning adaptively quantizes the input pattern space R".Probability density function p(x)characterizes the continuous distributions of patterns in R. We shall prove that competitive AVQ synaptic vector m, converge exponentially quickly to pattern-class centroids and. more generally,at equilibrium they vibrate about the centroids in a Browmian motion 2003.11.19 6
2003.11.19 6 6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids: AVQ Algorithms We shall prove that competitive AVQ synaptic vector converge exponentially quickly to pattern-class centroids and, more generally, at equilibrium they vibrate about the centroids in a Browmian motion. m j Competitive learning adaptively quantizes the input pattern space . Probability density function characterizes the continuous distributions of patterns in . n R p(x) n R

6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids:AVQ Algorithms Competitive AVQ Stochastic Differential Equations: R”=DUD2UD3.UDk D:∩Dj=D,fi≠j The Random Indicator function ()xED 0fx廷D Supervised learning algorithms depend explicitly on the indicator functions.Unsupervised learning algorithms don't require this pattern-class information. Centriod of Di ∫D.p(x) X,= p(x)dx 2003.11.19 7
2003.11.19 7 6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids: AVQ Algorithms 1 2 3.... , k n R D D D D D D if i j i j = = The Random Indicator function Supervised learning algorithms depend explicitly on the indicator functions.Unsupervised learning algorithms don’t require this pattern-class information. Centriod of : 1 ( ) 0 j j D j if x D I x if x D = ( ) ( ) j j D j D xp x dx x p x dx = Competitive AVQ Stochastic Differential Equations: Dj

6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids:AVQ Algorithms The Stochastic unsupervised competitive learning law: m;=S,y儿x-m,]+nj We want to show that at equilibrium m=x or E(m)=x As discussed in Chapter 4:S (x) The linear stochastic competitive learning law: m,=1o,(xx-m,]+n) The linear supervised competitive learning law: ri,=r(x)Ip (x)[x-mjl+n ,(x)=1p,(x)-∑1(x) 2003.11.19 8
2003.11.19 8 6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids: AVQ Algorithms The Stochastic unsupervised competitive learning law: ( )[ ] m S y x m n j j j j j = − + We want to show that at equilibrium or E( ) m x m x j j j j = = ( ) j j D As discussed in Chapter 4: S I x The linear stochastic competitive learning law: ( )[ ] j j D j j m = − + I x x m n The linear supervised competitive learning law: ( )[ ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) j j i j j D j j j D D i j r I x x m n r I x I x m x x = − + = −

6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids:AVQ Algorithms The linear differential competitive learning law: m,=S,[x-mj1+nj In practice: in,=sgn[yx-mjl+nj 1 讨z>0 讨z=0 2003.11.19 9
2003.11.19 9 6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids: AVQ Algorithms The linear differential competitive learning law: In practice: [ ] m S x m n j j j j = − + sgn[ ][ ] 1 0 sgn[ ] 0 0 1 0 m y x m n j j j j if z z if z if z = − + = = −

6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids:AVQ Algorithms Competitive AVQ Algorithms 1.Initialize synaptic vectors:m(0)=x(i),i=1,......,m 2.For random sample x(t),find the closest (winning)synaptic vector m (t):m,(t)-x(t)=minlm,(t)-x(t where+gives the squared Euclidean norm of x 3.Update the wining synaptic vectors m()by the UCL,SCL,or DCL learning algorithm. 2003.11.19 10
2003.11.19 10 6.3 Synaptic convergence to centroids: AVQ Algorithms Competitive AVQ Algorithms 1. Initialize synaptic vectors: mi (0) = x(i) , i =1,......,m 2.For random sample , find the closest (“winning”) synaptic vector : x(t) m (t) j ( ) ( ) min ( ) ( ) j i i m t x t m t x t − = − 3.Update the wining synaptic vectors by the UCL ,SCL,or DCL learning algorithm. m (t) j 2 2 2 1 ....... where x x x = + + n gives the squared Euclidean norm of x
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)04. 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics II——Supervised Learning(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)03. 突触动力学 - 非监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics I——Unsupervised Learning(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)03. 突触动力学 - 非监督学习 Synaptic Dynamics I——Unsupervised Learning(1/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)02. Neuronal Dynamics——Activation Models(2/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)02. Neuronal Dynamics——Activation Models(1/2).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)01.Neuronal Dynamics——Activations and Signals(主讲:高新波).ppt
- 《神经网络与模糊系统》课程教学资源(主题演讲)选择性集成 Selective Ensemble(南京大学:周志华).ppt
- 《神经网络与模糊系统》课程教学资源(主题演讲)机器学习研究进展(南京大学:王珏).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)进化计算 SOFT COMPUTING Evolutionary Computing.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)模糊系统与模糊逻辑 Fuzzy Theory.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)模糊神经网络 Neuro-fuzzy Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)人工神经网络 Artificial Neural Networks.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)有关人工智能的故事.doc
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程教学资源(学科综述)人工智能 AI.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人操作系统》课程教学资源(PPT课件讲稿)第1章 用于机器人的Ubuntu linux.ppt
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 机器人的逆向运动学.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 机器人的动力学.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 速度和静态力.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 空间描述和变换.pdf
- 烟台理工学院:《机器人学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第九章 机器人的线性控制.pdf
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)06. 模糊与概率 Fuzziness versus Probability.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)07. 模糊联想记忆 Fuzzy Associative Memories(FAM).ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)08. 模糊与神经网络的比较——以倒车系统为例 Comparison of Fuzzy and Neural Truck Backer-Upper Control Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)09. 模糊图像变换编码 Fuzzy Image Transform Coding.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2003)10. 模糊与卡尔曼滤波目标跟踪控制系统的比较 Comparison of Fuzzy and Kalman-Filter Target-Tracking Control Systems.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 02 ACTIVATIONS AND SIGNALS.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 03 Neuronal Dynamics 2:Activation Models.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 04 SYNAPTIC DYNAMICS 1:UNSUPERVISED LEARNING.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 05-1 第五章 突触动力学Ⅱ:有监督学习.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 05-2 Synaptic DynamicsII:Supervised Learning.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 06 Architecture and Equilibra 结构和平衡.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 07-1 Fuzziness vs. Probability.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 07-2 Fuzziness vs. Probability 模糊集合的模糊程度——模糊熵.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 08-1 Fuzzy Associative Memories.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 10 模糊图像变换编码.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 08-2 Fuzzy Associative Memories 模糊联想记忆 FUZZY ASSOCIATIVE MEMMORIESⅡ.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 09-2 模糊倒车控制系统——拖斗拖车.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 11 模糊与卡尔曼滤波目标跟踪控制系统的比较 Comparison of Fuzzy and Kalman-Filter Target-Tracking control system.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2004)Chapter 09-1 模糊与神经网络倒车系统比较.ppt
- 西安电子科技大学:《神经网络与模糊系统 Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems》课程PPT课件讲稿(2006)Chapter 02 NEURAL DYNAMIC1:ACTIVATIONHS AND SIGNALS(主讲:高新波).ppt
