广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(batch和动量Momentum NAG)

When gradient is small .. Hung-yi Lee李宏毅
When gradient is small … Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅
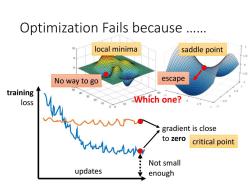
Optimization Fails because ..... local minima saddle point No way to go escape training 40 50 loss 00 0 Which one?。 1/2 gradient is close to zero critical point Not small updates enough
local minima Optimization Fails because …… updates training loss Not small enough gradient is close to zero saddle point critical point Which one? No way to go escape

Warning of Math
Warning of Math
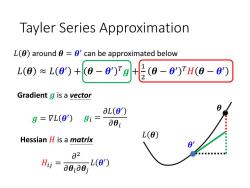
Tayler Series Approximation L(g)aroundθ=θ'can be approximated below L(0)≈L(a)+0-8)rg+E(0-g)H(g-g) Gradient g is a vector aL(0) g=7L(0) gi=001 L(0) Hessian H is a matrix 02 Hi=0010 、L(0')
Tayler Series Approximation 𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝒈 + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ Gradient 𝒈 is a vector Hessian 𝐻 is a matrix 𝒈𝑖 = 𝜕𝐿 𝜽 ′ 𝜕𝜽𝑖 𝐻𝑖𝑗 = 𝜕 2 𝜕𝜽𝑖𝜕𝜽𝑗 𝐿 𝜽 ′ 𝒈 = 𝛻𝐿 𝜽 ′ 𝐿 𝜽 around 𝜽 = 𝜽 ′ can be approximated below 𝜽 ′ 𝜽 𝐿 𝜽

Source of image:http://www.offconvex.org/2016/03/22/saddlepoints/ Hessian L()around =0'can be approximated below L(0)*1(9)+00☑叶60-9H6-0y At critical point telling the properties of critical points local min local max saddle point 4 2 0 0 0 -2-2 -2-2 -2
Hessian Source of image:http://www.offconvex.org/2016/03/22/saddlepoints/ telling the properties of critical points 𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝒈 + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝐿 𝜽 around 𝜽 = 𝜽 ′ can be approximated below At critical point
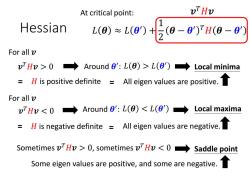
At critical point: vTHv Hessian 1 L(8)≈L(8)t(8-8)H(8-8) For all v vTHv>0→ Around 0':L(O)>L(θ')→Local minima H is positive definite All eigen values are positive. For all v vTHv0,sometimes vHv<0 Saddle point Some eigen values are positive,and some are negative
Hessian At critical point: 𝐻 is positive definite 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 > 0 Around 𝜽 Local minima ′ : 𝐿 𝜽 > 𝐿 𝜽 ′ All eigen values are positive. 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 0, sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 < 0 Saddle point 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ Around 𝜽 ′ : 𝐿 𝜽 < 𝐿 𝜽 ′ = = = 𝐻 is negative definite = All eigen values are negative. Some eigen values are positive, and some are negative. For all 𝒗 For all 𝒗
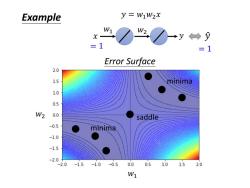
Example y=W1W2X W1 W2 →y←→ =1 =1 Error Surface 2.0 15 minima 10 W2 0.0 saddle -0.5 minima -1.0 -1.5 -2.0 2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 10 15 20 W1
𝑤1 𝑤2 𝑥 𝑦 𝑦 ො = 1 = 1 𝑦 = 𝑤1𝑤2𝑥 Example 𝑤1 𝑤2 Error Surface saddle minima minima

20 15 W1 W2 y →夕 106 =1 0.5 o L=(⊙-w1w2x)2=(1-w1w2)2 15 2.0 .0 -15 -10 -0.5 0.0 05 10 15 0W1 2(1-w1w2)(-w2) Critical point: W1=0,W2=0 =0 aL H=[9201a=22=-2 0W2 2(1-w1w2)(-w1) Saddle point =0 021 2(-w2)(-w2) 02L 0w1 -2+4W1W2 H =0 0w1∂w, =-2 02L -2+4W1W2 0w20W1 2(-w1)(-w1) =-2 =0
𝐿 = 𝑦 ො − 𝑤1𝑤2𝑥 2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤1 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤2 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤1 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤1 2 = 2 −𝑤2 −𝑤2 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤2 2 = 2 −𝑤1 −𝑤1 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤1𝜕𝑤2 = −2 + 4𝑤1𝑤2 𝜕 2𝐿 𝜕𝑤2𝜕𝑤1 = −2 + 4𝑤1𝑤2 𝑤1 𝑤2 𝑥 𝑦 𝑦 ො = 1 = 1 = 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 2 Critical point: 𝑤1 = 0, 𝑤2 = 0 𝐻 = 0 −2 −2 0 𝜆1 = 2, 𝜆2 = −2 Saddle point = 0 = 0 = 0 = −2 = 0 = −2 𝒈 𝐻

Don't afraid of saddle point? vTHv At critical point:L()L(+-)TH(-0' Sometimes vTHv>0,sometimes vTHv<0 Saddle point H may tell us parameter update direction! u is an eigen vector of H →uTHu=u(2u)=lul2 λis the eigen value of u λ<0 <0 <0 1 u L(0)≈L(0)+2(0-8)TH(0-6)→L(0)<L(8) 0-0'=2u 0=0'+u Decrease L
𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ Sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 > 0, sometimes 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 < 0 Saddle point 𝒖 is an eigen vector of 𝐻 𝒖 𝑇𝐻𝒖 = 𝒖 𝑇 𝜆𝒖 = 𝜆 𝒖 2 𝜆 is the eigen value of 𝒖 𝐻 may tell us parameter update direction! 𝜆 < 0 < 0 < 0 At critical point: 𝒗 𝑇𝐻𝒗 Don’t afraid of saddle point? 𝒖 𝒖 𝐿 𝜽 < 𝐿 𝜽 ′ 𝜽 = 𝜽 ′ + 𝒖 Decrease 𝐿 𝐿 𝜽 ≈ 𝐿 𝜽 ′ + 1 2 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝑇𝐻 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ 𝜽 − 𝜽 ′ = 𝒖
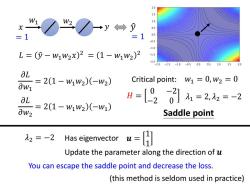
20 15 W2 +y←→ 09 1.0 L=(⊙-w1w2x)2=(1-w1w2)2 -15 2.0 2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 05 =21-w1w2)-w) Critical point: W1=0,W2=0 0W1 0L=2(1-ww2)(-w1) H=[920]=2,=-2 0W2 Saddle point =-2 Has sigenvector Update the parameter along the direction of u You can escape the saddle point and decrease the loss. (this method is seldom used in practice)
𝐿 = 𝑦 ො − 𝑤1𝑤2𝑥 2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤1 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤2 𝜕𝐿 𝜕𝑤2 = 2 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 −𝑤1 𝑤1 𝑤2 𝑥 𝑦 𝑦 ො = 1 = 1 = 1 − 𝑤1𝑤2 2 Critical point: 𝑤1 = 0, 𝑤2 = 0 𝐻 = 0 −2 −2 0 𝜆1 = 2, 𝜆2 = −2 Saddle point Has eigenvector 𝒖 = 1 1 𝜆2 = −2 You can escape the saddle point and decrease the loss. Update the parameter along the direction of 𝒖 (this method is seldom used in practice)
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第9讲 神经网络的优化(梯度下降、学习率adagrad adam、随机梯度下降、特征缩放).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第9讲 神经网络的优化(损失函数).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第8讲 集成学习(决策树的演化).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第7讲 集成学习(决策树).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第6讲 线性回归模型及其求解方法 Linear Regression Model and Its Solution.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第5讲 分类问题(4.4 朴素?叶斯分类器).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第5讲 分类问题(4.3 ?持向量机 SVM).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第4讲 分类问题(4.1 分类与回归问题概述 4.2 分类性能度量?法).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第3讲 特征工程 Feature Engineering.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第2讲 模型评估与选择.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第1讲 机器学习概述.pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《大语言模型》参考书籍PDF电子版 THE CHINESE BOOK FOR LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS(共十三章).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《Python数据科学手册》参考书籍PDF电子版(2016)Python Data Science Handbook,Essential Tools for Working with Data,Jake VanderPlas.pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《统计学习方法》参考书籍PDF电子版(清华大学出版社,第2版,共22章,作者:李航).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《神经网络与深度学习》参考书籍PDF电子版 Neural Networks and Deep Learning(共十五章).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《机器学习》参考书籍PDF电子版(清华大学出版社,著:周志华).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《动手学深度学习》参考书籍PDF电子版 Release 2.0.0-beta0(共十六章).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第07章 数据文件.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第06章 模块化程序设计.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第05章 编程思维与方法训练.ppt
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(自适应学习率 AdaGrad RMSProp).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(梯度消失和梯度爆炸BN).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(激活函数 dropout).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第11讲 感知机模型与多层感知机(前馈神经网络,DNN BP).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第12讲 卷积神经网络(卷积和池化层).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第12讲 卷积神经网络(LeNet, AlexNet, VGG和NiN).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第13讲 卷积神经网络计算机视觉应用(Inception, 批量归一化和残差网络ResNet).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第13讲 卷积神经网络计算机视觉应用(目标检测,计算机视觉训练技巧).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第14讲 循环神经网络(RNN).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第15讲 无监督学习——降维深度学习可视化(PCA Kmeans).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第15讲 无监督学习——降维深度学习可视化(Neighbor Embedding,LLE T-SNE).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第16讲 现代循环神经网络(高级循环神经网络).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第16讲 现代循环神经网络(编码器解码器,Seq2seq模型,束搜索).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第16讲 现代循环神经网络(嵌入向量, 词嵌入, 子词嵌入, 全局向量的词嵌入).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第17讲 注意力机制(概述).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第17讲 注意力机制(自注意力).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第18讲 变换器模型 Transformer.pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第18讲 变换器模型 Transformer.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第19讲 ViT及注意力机制改进(Vision Transformers ,ViTs).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第19讲 ViT及注意力机制改进(各式各样的Attention).pdf
