广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第9讲 神经网络的优化(梯度下降、学习率adagrad adam、随机梯度下降、特征缩放)

Gradient descent
Gradient Descent

Review:Gradient Descent In step 3,we have to solve the following optimization problem: θ*=arg min L(0) L:loss functionθ:parameters Suppose that 0 has two variables {01,02} Randomly start at 00 09] 7L(0)= 0L(01)/a61 1aL(02)/a02 [aL(0)/a61 02 aL(0)/a62 01=00-nL(0) aL(0)/a61 aL(02)/a02 → 02=01-n7L(01)
Review: Gradient Descent • In step 3, we have to solve the following optimization problem: 𝜃 ∗ = arg min 𝜃 𝐿 𝜃 L: loss function 𝜃: parameters Suppose that θ has two variables {θ1 , θ2 } Randomly start at 𝜃 0 = 𝜃1 0 𝜃2 0 𝛻𝐿 𝜃 = 𝜕𝐿 𝜃1 Τ𝜕𝜃1 𝜕𝐿 𝜃2 Τ𝜕𝜃2 𝜃1 1 𝜃2 1 = 𝜃1 0 𝜃2 0 − 𝜂 𝜕𝐿 𝜃1 Τ 0 𝜕𝜃1 𝜕𝐿 𝜃2 Τ 0 𝜕𝜃2 𝜃 1 = 𝜃 0 − 𝜂𝛻𝐿 𝜃 0 𝜃1 2 𝜃2 2 = 𝜃1 1 𝜃2 1 − 𝜂 𝜕𝐿 𝜃1 Τ 1 𝜕𝜃1 𝜕𝐿 𝜃2 Τ 1 𝜕𝜃2 𝜃 2 = 𝜃 1 − 𝜂𝛻𝐿 𝜃 1
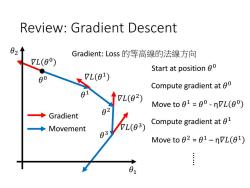
Review:Gradient Descent Gradient:Loss的等高線的法線方向 L(0) Start at position 00 80 7L(01) Compute gradient at 0 7L(02) Move to 01=00-nVL(00) ◆ Gradient 82 Movement L(03) Compute gradient at 01 83 Move to 02 =01-nVL(01) 01
Review: Gradient Descent Start at position 𝜃 0 Compute gradient at 𝜃 0 Move to 𝜃 1 = 𝜃 0 - η𝛻𝐿 𝜃 0 Compute gradient at 𝜃 1 Move to 𝜃 2 = 𝜃 1 – η𝛻𝐿 𝜃 1 Movement Gradient …… 𝜃 0 𝜃 1 𝜃 2 𝜃 3 𝛻𝐿 𝜃 0 𝛻𝐿 𝜃 1 𝛻𝐿 𝜃 2 𝛻𝐿 𝜃 3 𝜃1 𝜃2 Gradient: Loss 的等高線的法線方向

Gradient descent Tip 1:Tuning your learning rates
Gradient Descent Tip 1: Tuning your learning rates

0=0-1-VL0-1) Learning Rate Set the learning rate n carefully If there are more than three Loss parameters,you cannot visualize this. Very Large small Large Loss Just make No.of parameters updates But you can always visualize this
Learning Rate No. of parameters updates Loss Loss Very Large Large small Just make 1 1 i i i L Set the learning rate η carefully If there are more than three parameters, you cannot visualize this. But you can always visualize this

Adaptive Learning Rates Popular Simple Idea:Reduce the learning rate by some factor every few epochs. At the beginning,we are far from the destination,so we use larger learning rate After several epochs,we are close to the destination,so we reduce the learning rate E.g.1/t decay:n=n/vt+1 Learning rate cannot be one-size-fits-all Giving different parameters different learning rates
Adaptive Learning Rates • Popular & Simple Idea: Reduce the learning rate by some factor every few epochs. • At the beginning, we are far from the destination, so we use larger learning rate • After several epochs, we are close to the destination, so we reduce the learning rate • E.g. 1/t decay: 𝜂 𝑡 = 𝜂Τ 𝑡 + 1 • Learning rate cannot be one-size-fits-all • Giving different parameters different learning rates
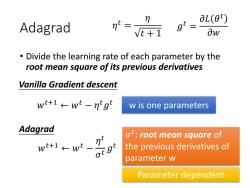
aL(0) Adagrad nt vt+1 gt 0w Divide the learning rate of each parameter by the root mean square of its previous derivatives Vanilla Gradient descent wt+1←wt-ng w is one parameters Adagrad ot:root mean square of w+1←wt_刀 the previous derivatives of parameter w Parameter dependent
Adagrad • Divide the learning rate of each parameter by the root mean square of its previous derivatives 𝜎 𝑡 : root mean square of the previous derivatives of parameter w w is one parameters 𝑔 𝑡 = 𝜕𝐿 𝜃 𝑡 𝜕𝑤 Vanilla Gradient descent Adagrad 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 𝑡𝑔 𝑡 𝜂 𝑡 = 𝜂 𝑡 + 1 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 𝑡 𝜎 𝑡 𝑔 𝑡 Parameter dependent
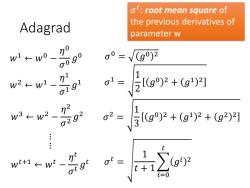
ot:root mean square of the previous derivatives of Adagrad parameter w w1←w0一 o090 0=V(g)2 w2←w1- 91 01=【g2+g鬥 w3←w22 0292 2-层g92+g+g1 w+1←wt-刀 1 t+ g)2 0
Adagrad 𝑤1 ← 𝑤0 − 𝜂 0 𝜎 0 𝑔 0 … … 𝑤2 ← 𝑤1 − 𝜂 1 𝜎 1 𝑔 1 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 𝑡 𝜎 𝑡 𝑔 𝑡 𝜎 0 = 𝑔0 2 𝜎 1 = 1 2 𝑔0 2 + 𝑔1 2 𝜎 𝑡 = 1 𝑡 + 1 𝑖=0 𝑡 𝑔𝑖 2 𝑤3 ← 𝑤2 − 𝜂 2 𝜎 2 𝑔 2 𝜎 2 = 1 3 𝑔0 2 + 𝑔1 2 + 𝑔2 2 𝜎 𝑡 : root mean square of the previous derivatives of parameter w

Adagrad Divide the learning rate of each parameter by the root mean square of its previous derivatives n-vt+i 1/t decay wt+1←wt wt+1←wt ∑=o(g)2
Adagrad • Divide the learning rate of each parameter by the root mean square of its previous derivatives 𝜂 𝑡 = 𝜂 𝑡 + 1 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 σ𝑖=0 𝑡 𝑔𝑖 2 𝑔 𝑡 1/t decay 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 𝜎 𝑡 𝑔 𝑡 𝜎 𝑡 = 1 𝑡 + 1 𝑖=0 𝑡 𝑔𝑖 2 𝜂 𝑡 𝜎 𝑡

Contradiction?-=vz gi= aL(0t) 0w Vanilla Gradient descent w+1←wt-ng Larger gradient, larger step Adagrad Larger gradient, w+1←wt、 larger step =9 (g2 Larger gradient, smaller step
Contradiction? 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 σ𝑖=0 𝑡 𝑔𝑖 2 𝑔 𝑡 Vanilla Gradient descent Adagrad Larger gradient, larger step Larger gradient, smaller step Larger gradient, larger step 𝑤𝑡+1 ← 𝑤𝑡 − 𝜂 𝑡𝑔 𝑡 𝑔 𝑡 = 𝜕𝐿 𝜃 𝑡 𝜕𝑤 𝜂 𝑡 = 𝜂 𝑡 + 1
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第9讲 神经网络的优化(损失函数).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第8讲 集成学习(决策树的演化).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第7讲 集成学习(决策树).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第6讲 线性回归模型及其求解方法 Linear Regression Model and Its Solution.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第5讲 分类问题(4.4 朴素?叶斯分类器).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第5讲 分类问题(4.3 ?持向量机 SVM).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第4讲 分类问题(4.1 分类与回归问题概述 4.2 分类性能度量?法).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第3讲 特征工程 Feature Engineering.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第2讲 模型评估与选择.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第1讲 机器学习概述.pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《大语言模型》参考书籍PDF电子版 THE CHINESE BOOK FOR LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS(共十三章).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《Python数据科学手册》参考书籍PDF电子版(2016)Python Data Science Handbook,Essential Tools for Working with Data,Jake VanderPlas.pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《统计学习方法》参考书籍PDF电子版(清华大学出版社,第2版,共22章,作者:李航).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《神经网络与深度学习》参考书籍PDF电子版 Neural Networks and Deep Learning(共十五章).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《机器学习》参考书籍PDF电子版(清华大学出版社,著:周志华).pdf
- 《机器学习》课程教学资源:《动手学深度学习》参考书籍PDF电子版 Release 2.0.0-beta0(共十六章).pdf
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第07章 数据文件.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第06章 模块化程序设计.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第05章 编程思维与方法训练.ppt
- 西北农林科技大学:《Visual Basic程序设计基础》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第04章 数组与自定义类型.ppt
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(batch和动量Momentum NAG).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(自适应学习率 AdaGrad RMSProp).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(梯度消失和梯度爆炸BN).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第10讲 神经网络的优化(激活函数 dropout).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第11讲 感知机模型与多层感知机(前馈神经网络,DNN BP).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第12讲 卷积神经网络(卷积和池化层).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第12讲 卷积神经网络(LeNet, AlexNet, VGG和NiN).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第13讲 卷积神经网络计算机视觉应用(Inception, 批量归一化和残差网络ResNet).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第13讲 卷积神经网络计算机视觉应用(目标检测,计算机视觉训练技巧).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第14讲 循环神经网络(RNN).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第15讲 无监督学习——降维深度学习可视化(PCA Kmeans).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第15讲 无监督学习——降维深度学习可视化(Neighbor Embedding,LLE T-SNE).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第16讲 现代循环神经网络(高级循环神经网络).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第16讲 现代循环神经网络(编码器解码器,Seq2seq模型,束搜索).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第16讲 现代循环神经网络(嵌入向量, 词嵌入, 子词嵌入, 全局向量的词嵌入).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第17讲 注意力机制(概述).pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第17讲 注意力机制(自注意力).pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(PPT讲稿)第18讲 变换器模型 Transformer.pptx
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第18讲 变换器模型 Transformer.pdf
- 广东工业大学:《机器学习》课程教学资源(课件讲义)第19讲 ViT及注意力机制改进(Vision Transformers ,ViTs).pdf
