重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)疟疾(英文)
置庆医科大学脑床学院裁来讲满 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称传染病学年级2004级授课专业 留学生 教师袁喆职称 副牧授授课方式 大课示教学时4 题目章节Part3 Chapter3 Malaria 教材名称Lemology 作者 Chief Editor:Liu Zhengwen 出版社Xi'an Jiaotong University 版次 2004.1 教学目的要求 3 Features of】 alaria 6.Preventl of Malaria 教学难 1.Epidemic Process and The effect Factors. of Malaria 1.Definition Etiology 教学重点 4.Pathogenesis erential Diagnosis 外语 要求 English Language 教学 Classroom lectures and multimedia 1,15th Edition Mandell Douglas and Bennett's Principales and Practice of Infectious Diseasea Vol-2. 参考 2001 edited by Gerald LMandell,Jone E.Bennett,Raphael Dolin,publishing by Harcourt Ansia and 资料 Churchill Livingstone 2.4th Edition Kelley's Textbook of Internal Medicine 2004 edited by H.David Humes,publishing by Lippincott Williams&Wilkins Ine. 教学组长: 教研室主任: 年 日 制表时间:2004年8月 1
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 1 重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 传染病学 年级 2004 级 授课专业 留学生 教 师 袁 喆 职称 副教授 授课方式 √大课 示教 学时 4 题目章节 Part 3 Chapter3 Malaria 教材名称 Lemology 作者 Chief Editor :Liu Zhengwen 出 版 社 Xi’an Jiaotong University 版次 2004 .11 教 学 目 的 要 求 1.Etiology 2.Epidemiology 3.Features of Malaria 4.Diagnosis of Malaria 5.Treatment of Malaria 6.Preventl of Malaria 教 学 难 点 1.Epidemic Process and The effect Factors。 2.Pathogenesis of Malaria。 教 学 重 点 1. Definition 2. Etiology 3.Epidemiology 4. Pathogenesis 5. Clinical manifestation of Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis 6. Complications 7. Laboratory Findings 8. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis 9.Treatment of Epidemic cerebrospinal meningitis 外语 要求 English Language 教学 方法 手段 Classroom lectures and multimedia 参考 资料 1、15th Edition Mandell,Douglas and Bennett’s Principales and Practice of Infectious Diseasea.Vol-2, 2001 edited by Gerald L.Mandell,Jone E.Bennett,Raphael Dolin, publishing by Harcourt Ansia and Churchill Livingstone. 2、4th Edition Kelley’s Textbook of Internal Medicine 2004 edited by H.David Humes, publishing by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Inc. 教研 室意 见 教学组长: 教研室主任: 年 月 日
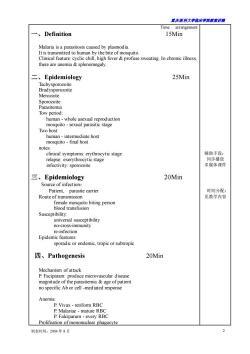
置庆医科大学脑床半院载未讲满 Time arrangement 、Definition 15Min asitosis caused by plasmodia 0 there are an emia splenomegaly 二、Epidemiology 25Min Tachysporozoite Bradysporozoite Merozoite whole Two host. ediate hos mosquito-final host notes clinical symptoms:erythrocytic stage 辅助手段: relapse:exerythrocytic stage 同步播放 infectivity:sporozoite 多媒体课件 三、Epidemiology 20Min Source of infection Patient. paras 时间分配. Rou 见教学内容 blood transfusion to biting person Susceptibility universal susceptibility no-cross-immunity re-infection Epidemic features: sporadic or endemic,tropic or subtropic 四、Pathogenesis 20Min Mechanism ofattack P.Faciparam:produce microvascular disease magnitude ofthe parasitemia&age of patient no specific Ab or cell-mediated response Anemia -retiform RBC P.Falcipar um every RBC Prolifeation of mononuclear phagocvte 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 2 Time arrangement 一、Definition 15Min Malaria is a parasitosis caused by plasmodia. It is transmitted to human by the bite of mosquito. Clinical feature: cyclic chill, high fever & profuse sweating. In chronic illness, there are anemia & splenomegaly. 二、Epidemiology 25Min Tachysporozoite Bradysporozoite Merozoite Sporozoite Parasitemia Tow period: human - whole asexual reproduction mosquito - sexual parasitic stage Two host: human - intermediate host mosquito - final host notes: clinical symptoms: erythrocytic stage relapse: exerythrocytic stage infectivity: sporozoite 三、Epidemiology 20Min Source of infection: Patient, parasite carrier Route of transmission female mosquito biting person blood transfusion Susceptibility: universal susceptibility no-cross-immunity re-infection Epidemic features: sporadic or endemic, tropic or subtropic 四、Pathogenesis 20Min Mechanism of attack P. Faciparam: produce microvascular disease magnitude of the parasitemia & age of patient no specific Ab or cell -mediated response Anemia: P. Vivax - retiform RBC P. Malariae - mature RBC P. Falciparum - every RBC Prolifeation of mononuclear phagocyte 辅助手段: 同步播放 多媒体课件 时间分配: 见教学内容

君庆医科大学脑床半院表来讲测 hepatomegaly enomegaly Cerebral edema congestion 五、Clinical manifestation 20Min Ihetiiht2430d tertian malaria:13~15 day malignant malaria:7~12 day Typical attack Chill:abrupt onset,shivering,pale face,cyanosis.Last 10 min or 1~2hr. High fever.T rise to 40oC with malaise,myalgia,thirsty.Last 2-6 Hr. 装ye Sings anemia splenomegaly hepatomegaly,ALTelevate Pemiciouse attack:cause by P.Falciparum bral malaria high fev er,headache,vomiting,convulsion delirum,respiratory failure Relapse:early relapse-6m Malaria caused by transfusion incubation period:7~10 day no exerythrogenic phase,no relapse 六、Complications 20Min Black-water-fever: cause:I/inadequate G-6-PD 2/The toxin release by malarial parasite 3/Allergic reaction to anti-malarial /dark redor black urine Acute glom 七、Laboratory Findings 20Min Blood picture:decrease in RBC&Hb blood film for parasite serological examination 制表时间.2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 3 hepatomegaly splenomegaly Cerebral edema & congestion 五、Clinical manifestation 20Min Incubation period: quartan malaria: 24-30 day tertian malaria: 13~15 day malignant malaria: 7~12 day Typical attack Chill: abrupt onset, shivering, pale face,cyanosis. Last 10 min or 1~2hr. High fever: T rise to 40oC with malaise, myalgia, thirsty. Last 2~6 Hr. Sweating: profuse sweating with restlessness regular 48 hr. or 72 hr. Cycle Sings anemia splenomegaly hepatomegaly, ALT elevate Perniciouse attack: cause by P. Falciparum cerebral malaria high fever, headache, vomiting, convulsion delirum, respiratory failure hyperpyrexia type T> 420C, convulsion, delirium Relapse: early relapse - 6m Malaria caused by transfusion incubation period: 7~10 day no exerythrogenic phase, no relapse 六、Complications 20Min Black- water- fever: cause:1/inadequate G-6-PD 2/The toxin release by malarial parasite 3/Allergic reaction to anti-malarial drugs feature:1/chill & fever 2/dark red or black urine 3/severe hemolytic anemia Acute glomerulonephritis 七、Laboratory Findings 20Min Blood picture: decrease in RBC & Hb blood film for parasite serological examination

置庆医科大学床半院藏讲满 ELISA for P.antigen DNA hybridization 八、Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis 10Min Epidemiological data endemic zone rosis 九、Treatment 10Min Anti-malarial drugs Chloroquine-susceptable infection chloroquine:1g/d,for 3 day.p.o. primaquine:for 8day,p.o. Chloroquine-resistant infection mefloguine: artemisinine ng/kg iv dr ese10 ng/kg iv0o吧ph2hr (3 day)+primaquine (8 day) 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 4 ELISA for P. antigen DNA hybridization 八、Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis 10Min Epidemiological data endemic zone blood transfusion Clinical manifestation Laboratory findings Diagnostic treatment: chloroqunine for 3 days Typhoid fever Septicemia Leptospirosis Encephalitis B 九、Treatment 10Min Anti-malarial drugs Chloroquine-susceptable infection chloroquine : 1g /d, for 3 day, p.o. primaquine: for 8day, p.o. Chloroquine-resistant infection mefloguine: artemisinine Pernicious attack Chloroquine: 10mg/kg iv drop in 4 hr. Then 5mg/kg, iv drop in 2 hr. Quinine: 500mg iv drop in 4 hr. Radical therapy Chloroquine (3 day) + primaquine ( 8 day)

君庆医科大学脑床半院表来讲测 Malaria is a parasitosis caused by plasmodia. It is transmitted to human by the bite of mosquito. Clinical feature:cyclic chill,high fever profuse sweating.In chronic illness, 小结 there are anemia splenomegaly. 1.Defination of Malaria 2、Clinical of Malaria 教案讲稿质量评价表 制表时间:2004年8月
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 5 小结 Malaria is a parasitosis caused by plasmodia. It is transmitted to human by the bite of mosquito. Clinical feature: cyclic chill, high fever & profuse sweating. In chronic illness, there are anemia & splenomegaly. 思考 题及 预习 1、 Defination of Malaria 2、Clinical of Malaria 3、Treatment of Malaria. 教案讲稿质量评价表
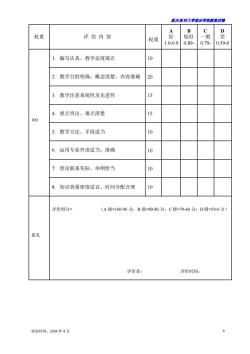
重庆医科大半临床半院载案讲满 B C 权重 评估内容 一般 权重 好较好 1.0-0.90.89- 0.79.0.59-0 编写认真、教学态度端正 2. 教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 教学注意系统性及先进性 4. 重点突出、难点清楚 15 100 5.教学方法、手段适当 6.运用专业外语适当、准确 0 7,理论联系实际、举例恰当 o 8.知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 评价得分= (A级=100-90分:B级=89-80分:C级=79-60分:D级=59-0分) 意见 评价者: 评价时间: 制表时间:2004年8月 6
重庆医科大学临床学院教案讲稿 制表时间:2004 年 8 月 6 权重 评 估 内 容 权重 A 好 1.0-0.9 B 较好 0.89- C 一般 0.79- D 差 0.59-0 100 1. 编写认真、教学态度端正 10 2. 教学目的明确、概念清楚、内容准确 20 3. 教学注意系统性及先进性 15 4. 重点突出、难点清楚 15 5. 教学方法、手段适当 10 6. 运用专业外语适当、准确 10 7. 理论联系实际、举例恰当 10 8. 知识容量密度适宜、时间分配合理 10 意见 评价得分= (A 级=100-90 分;B 级=89-80 分;C 级=79-60 分;D 级=59-0 分) 评价者: 评价时间:
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)流脑(英文).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)细菌性痢疾 Bacillary dysentery.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)艾滋病(AIDS).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)霍乱 Cholera.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)肝炎(英文).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)总论(英文).doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)艾滋病.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)禽流感.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)严重急性呼吸综合征.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)败血症.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)流行性出血热.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)霍乱.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)伤寒.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)病毒性肝炎.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)流脑.doc
- 重庆医科大学:《传染病学》课程教学资源(教案讲稿)总论.doc
- 《运动解剖学》课程教学资源(授课教案)运动解剖学完整讲义.docx
- 《运动解剖学》课程基本功大赛复习题及答案(共300题).docx
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学大纲.docx
- 重庆医科大学:《精神病学》课程教学资源(讲稿)精神科急诊与护理.pdf
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(实验指导)病毒性肝炎.doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(实验指导)发热待查.doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(实验指导)腹泻.doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(实验指导)消毒与隔离.doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)总论(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)传染性非典型肺炎(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)病毒性肝炎(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)败血症(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)伤寒、副伤寒(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)流行性乙型脑炎(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)霍乱(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)课后习题(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(作业习题)艾滋病(含参考答案).doc
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)严重急性呼吸综合征(severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)人禽流感 human avian influenza(重庆医科大学:邓蕙).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流行性出血热.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)艾滋病 Acquired Immune deficiency Syndrome.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)伤寒与副伤寒 Typhoid Fever and Paratyphoid Fever.ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)传染病总论(重庆医科大学:袁喆).ppt
- 《传染病学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)流行性脑脊髓膜炎 meningococcal meningitis.ppt
