电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)Stable Matching

Stable Matching
Stable Matching

Matching Residents to Hospitals Goal.Given a set of preferences among hospitals and medical school students,design a self-reinforcing admissions process. Unstable pair:applicant x and hospital y are unstable if: x prefers y to its assigned hospital. y prefers x to one of its admitted students. Stable assignment.Assignment with no unstable pairs. Natural and desirable condition. Individual self-interest will prevent any applicant/hospital deal from being made
3 Matching Residents to Hospitals Goal. Given a set of preferences among hospitals and medical school students, design a self-reinforcing admissions process. Unstable pair: applicant x and hospital y are unstable if: x prefers y to its assigned hospital. y prefers x to one of its admitted students. Stable assignment. Assignment with no unstable pairs. Natural and desirable condition. Individual self-interest will prevent any applicant/hospital deal from being made
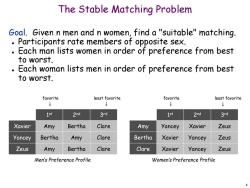
The Stable Matching Problem Goal.Given n men and n women,find a "suitable"matching. Participants rate members of opposite sex. Each man lists women in order of preference from best to worst. 。 Each woman lists men in order of preference from best to worst. favorite least favorite favorite least favorite 1st 2nd 3rd 1st 2nd 3rd Xavier Amy Bertha Clare Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Men's Preference Profile Women's Preference Profile 4
4 The Stable Matching Problem Goal. Given n men and n women, find a "suitable" matching. Participants rate members of opposite sex. Each man lists women in order of preference from best to worst. Each woman lists men in order of preference from best to worst. Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Xavier Amy Bertha Clare 1 st 2nd 3rd Men’s Preference Profile favorite least favorite Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus 1 st 2nd 3rd Women’s Preference Profile favorite least favorite

The Stable Matching Problem Perfect matching:everyone is matched monogamously. Each man gets exactly one woman. Each woman gets exactly one man. Stability:no incentive for some pair of participants to undermine assignment by joint action. In matching M,an unmatched pair m-w is unstable if man m and woman w prefer each other to current partners. Unstable pair m-w could each improve by eloping. Stable matching:perfect matching with no unstable pairs. Stable matching problem.Given the preference lists of n men and n women,find a stable matching if one exists. 5
5 The Stable Matching Problem Perfect matching: everyone is matched monogamously. Each man gets exactly one woman. Each woman gets exactly one man. Stability: no incentive for some pair of participants to undermine assignment by joint action. In matching M, an unmatched pair m-w is unstable if man m and woman w prefer each other to current partners. Unstable pair m-w could each improve by eloping. Stable matching: perfect matching with no unstable pairs. Stable matching problem. Given the preference lists of n men and n women, find a stable matching if one exists
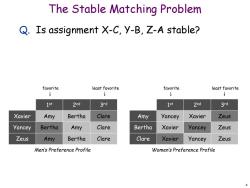
The Stable Matching Problem Q.Is assignment X-C,y-B,Z-A stable? favorite least favorite favorite least favorite 1st 2nd 3rd 1st 2nd 3rd Xavier Amy Bertha Clare Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Men's Preference Profile Women's Preference Profile 6
6 The Stable Matching Problem Q. Is assignment X-C, Y-B, Z-A stable? Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Xavier Amy Bertha Clare 1 st 2nd 3rd Men’s Preference Profile Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus 1 st 2nd 3rd Women’s Preference Profile favorite least favorite favorite least favorite
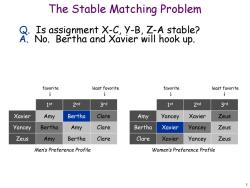
The Stable Matching Problem Is assignment X-C,y-B,Z-A stable? A.No.Bertha and Xavier will hook up. favorite least favorite favorite least favorite ↓ 1st 2nd 3rd 1st 2nd 3rd Xavier Amy Bertha Clare Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Men's Preference Profile Women's Preference Profile 7
7 The Stable Matching Problem Q. Is assignment X-C, Y-B, Z-A stable? A. No. Bertha and Xavier will hook up. Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Xavier Amy Bertha Clare Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus 1 st 2nd 3rd 1 st 2nd 3rd favorite least favorite favorite least favorite Men’s Preference Profile Women’s Preference Profile
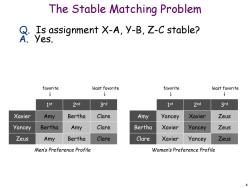
The Stable Matching Problem Q.Is assignment X-A,Y-B,Z-C stable? A.Yes. favorite least favorite favorite least favorite 1st 2nd 3rd 1st 2nd 3rd Xavier Amy Bertha Clare Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Men's Preference Profile Women's Preference Profile 8
8 The Stable Matching Problem Q. Is assignment X-A, Y-B, Z-C stable? A. Yes. Zeus Amy Bertha Clare Yancey Bertha Amy Clare Xavier Amy Bertha Clare Clare Xavier Yancey Zeus Bertha Xavier Yancey Zeus Amy Yancey Xavier Zeus 1 st 2nd 3rd 1 st 2nd 3rd favorite least favorite favorite least favorite Men’s Preference Profile Women’s Preference Profile
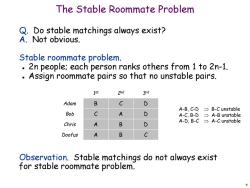
The Stable Roommate Problem Q.Do stable matchings always exist? A.Not obvious. Stable roommate problem. 2n people;each person ranks others from 1 to 2n-1. Assign roommate pairs so that no unstable pairs. 1st 2nd 3rd Adam B A-B,C-D三B-C unstable Bob C A-C,B-D A-B unstable A-D,B-C A-C unstable Chris A B Doofus A B c Observation.Stable matchings do not always exist for stable roommate problem. 9
9 The Stable Roommate Problem Q. Do stable matchings always exist? A. Not obvious. Stable roommate problem. 2n people; each person ranks others from 1 to 2n-1. Assign roommate pairs so that no unstable pairs. Observation. Stable matchings do not always exist for stable roommate problem. B Bob Chris Adam C A B D D Doofus A B C D C A 1 st 2nd 3rd A-B, C-D B-C unstable A-C, B-D A-B unstable A-D, B-C A-C unstable

The Propose-And-Reject Algorithm Propose-and-reject algorithm.[Gale-Shapley 1962]Intuitive method that guarantees to find a stable matching. Initialize each person to be free. while (some man is free and hasn't proposed to every woman){ Choose such a man m w 1st woman on m's list to whom m has not yet proposed if (w is free) assign m and w to be engaged else if (w prefers m to her fiance m') assign m and w to be engaged,and m'to be free else w rejects m 0
Propose-and-reject algorithm. [Gale-Shapley 1962] Intuitive method that guarantees to find a stable matching. 10 The Propose-And-Reject Algorithm Initialize each person to be free. while (some man is free and hasn't proposed to every woman) { Choose such a man m w = 1st woman on m's list to whom m has not yet proposed if (w is free) assign m and w to be engaged else if (w prefers m to her fiancé m') assign m and w to be engaged, and m' to be free else w rejects m }

Proof of Correctness:Termination Observation 1.Men propose to women in decreasing order of preference. Observation 2.Once a woman is matched,she never becomes unmatched;she only "trades up.' Claim.Algorithm terminates after at most n2 iterations of while loop. Pf.Each time through the while loop a man proposes to a new woman.There are only n2 possible proposals. 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th Victor A B D E Amy W Wyatt B E Bertha Xavier E Clare Yancey B C E Diane Zeus B D E Erika W X Z n(n-1)+1 proposals required 11
11 Proof of Correctness: Termination Observation 1. Men propose to women in decreasing order of preference. Observation 2. Once a woman is matched, she never becomes unmatched; she only "trades up." Claim. Algorithm terminates after at most n2 iterations of while loop. Pf. Each time through the while loop a man proposes to a new woman. There are only n2 possible proposals. ▪ Wyatt Victor 1 st A B 2nd C D 3rd C B Zeus A Yancey Xavier C D A B B A D C 4th E E 5th A D E E D C B E Bertha Amy 1 st W X 2nd Y Z 3rd Y X Erika V Diane Clare Y Z V W W V Z X 4th V W 5th V Z X Y Y X W Z n(n-1) + 1 proposals required
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)01 Introduction(肖鸣宇).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《数据库系统原理 An Introduction to Database System》课程教学资源(电子教案,颜清).doc
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 分支限界法(Branch and Bound Method).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 回朔法(Backtracking Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 动态规划 Dynamic Programming.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 递归与分治策略.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 算法概述 Algorithm Introduction(刘瑶、陈佳).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(FP-growth Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(Apriori Algorithm、Improve of Apriori Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Clustering Analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis and Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis(Logistic Regression).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.1-2.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.5-2.7).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Overview Data Analysis and Data Mining(李晓瑜).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子降维算法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子神经网络(Neural Network,NN).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)02 Basics of algorithm design & analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)03 Maximum Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)04 NP and Computational Intractability.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)05 Approximation Algorithms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(李发根).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 古典密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 流密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 分组密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 Hash函数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(一)6.1-6.4.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(二)6.5-6.9.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 数字签名.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 密码协议.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(主讲:曾凡平).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 基础知识.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 密码学基础.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 虚拟专用网络(VPN)技术.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:An adaptive trust model based on recommendation filtering algorithm for the Internet of Things systems.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Automatic Generation of Capability Leaks’ Exploits for Android Applications.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Adaptive Random Testing for XSS Vulnerability.pdf
