电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)04 NP and Computational Intractability

Design and Analysis of Algorithms 4.NP and Computational Intractability Mingyu XIAO School of Computer Science and Engineering University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
Design and Analysis of Algorithms 4. NP and Computational Intractability Mingyu XIAO School of Computer Science and Engineering University of Electronic Science and Technology of China

Algorithm Design Patterns and Anti-Patterns Algorithm design patterns. Ex. Greedy. O(n log n)interval scheduling. Divide-and-conquer. O(n log n)FFT. Dynamic programming. O(n2)edit distance. Duality. O(n3)bipartite matching. Reductions. Algorithm design anti-patterns. NP-completeness. O(nc)algorithm unlikely. PSPACE-completeness. O(nc)certification algorithm unlikely. Undecidability. No algorithm possible. 3
2 Algorithm Design Patterns and Anti-Patterns Algorithm design patterns. Ex. Greedy. O(n log n) interval scheduling. Divide-and-conquer. O(n log n) FFT. Dynamic programming. O(n2) edit distance. Duality. O(n3) bipartite matching. Reductions. Algorithm design anti-patterns. NP-completeness. O(nc ) algorithm unlikely. PSPACE-completeness. O(nc ) certification algorithm unlikely. Undecidability. No algorithm possible

4.1 Polynomial-Time Reductions
4.1 Polynomial-Time Reductions

Classify Problems According to Computational Requirements Q.Which problems will we be able to solve in practice? A working definition.[von Neumann 1953,Godel 1956,Cobham 1964,Edmonds 1965,Rabin 1966] Those with polynomial-time algorithms. Yes Probably no Shortest path Longest path Matching 3D-matching Min cut Max cut 2-SAT 3-SAT Planar 4-color Planar 3-color Bipartite vertex cover Vertex cover
4 Classify Problems According to Computational Requirements Q. Which problems will we be able to solve in practice? A working definition. [von Neumann 1953, Godel 1956, Cobham 1964, Edmonds 1965, Rabin 1966] Those with polynomial-time algorithms. Yes Probably no Shortest path Longest path Min cut Max cut 2-SAT 3-SAT Matching 3D-matching Planar 4-color Planar 3-color Bipartite vertex cover Vertex cover

Classify Problems Classes.Classify problems according to those that can be solved in polynomial-time and those that cannot. Frustrating news.Huge number of fundamental problems have defined classification for decades. This chapter.Show that these fundamental problems are "computationally equivalent"and appear to be different manifestations of one really hard problem. 5
5 Classify Problems Classes. Classify problems according to those that can be solved in polynomial-time and those that cannot. Frustrating news. Huge number of fundamental problems have defined classification for decades. This chapter. Show that these fundamental problems are "computationally equivalent" and appear to be different manifestations of one really hard problem

Polynomial-Time Reduction don't confuse with reduces from Reduction.Problem X polynomial reduces to problem y if arbitrary instances of problem X can be solved using: Polynomial number of standard computational steps,plus Polynomial number of calls to oracle that solves problem y. Notation.X≤py. computational model supplemented by special piece of hardware that solves instances of y in a single step Questions. Any requirement on the input size of y? 6
6 Polynomial-Time Reduction Reduction. Problem X polynomial reduces to problem Y if arbitrary instances of problem X can be solved using: Polynomial number of standard computational steps, plus Polynomial number of calls to oracle that solves problem Y. Notation. X P Y. don't confuse with reduces from computational model supplemented by special piece of hardware that solves instances of Y in a single step Questions. Any requirement on the input size of Y?

Polynomial-Time Reduction Purpose.Classify problems according to relative difficulty. Design algorithms.If X sp y and y can be solved in polynomial-time, then X can also be solved in polynomial time. Establish intractability.If Xsp y and X cannot be solved in polynomial-time,then y cannot be solved in polynomial time. Establish equivalence..IfX≤y and y≤pX,we use notation X≡py. \ up to cost of reduction 7
7 Polynomial-Time Reduction Purpose. Classify problems according to relative difficulty. Design algorithms. If X P Y and Y can be solved in polynomial-time, then X can also be solved in polynomial time. Establish intractability. If X P Y and X cannot be solved in polynomial-time, then Y cannot be solved in polynomial time. Establish equivalence. If X P Y and Y P X, we use notation X P Y. up to cost of reduction

Reduction By Simple Equivalence Basic reduction strategies. Reduction by simple equivalence. Reduction from special case to general case. Reduction by encoding with gadgets
Reduction By Simple Equivalence Basic reduction strategies. Reduction by simple equivalence. Reduction from special case to general case. Reduction by encoding with gadgets
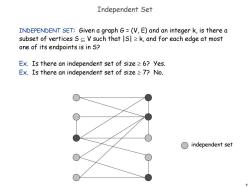
Independent Set INDEPENDENT SET:Given a graph G=(V,E)and an integer k,is there a subset of vertices sc V such that s>k,and for each edge at most one of its endpoints is in S? Ex.Is there an independent set of size≥6?yes. Ex.Is there an independent set of size≥7?No. ○independent set 9
9 Independent Set INDEPENDENT SET: Given a graph G = (V, E) and an integer k, is there a subset of vertices S V such that |S| k, and for each edge at most one of its endpoints is in S? Ex. Is there an independent set of size 6? Yes. Ex. Is there an independent set of size 7? No. independent set
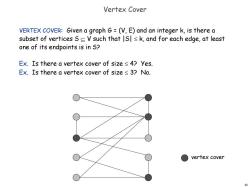
Vertex Cover VERTEX COVER:Given a graph G=(V,E)and an integer k,is there a subset of vertices S V such that ISI s k,and for each edge,at least one of its endpoints is in S? Ex.Is there a vertex cover of size≤4?yes. Ex.Is there a vertex cover of size≤3?No. vertex cover 10
10 Vertex Cover VERTEX COVER: Given a graph G = (V, E) and an integer k, is there a subset of vertices S V such that |S| k, and for each edge, at least one of its endpoints is in S? Ex. Is there a vertex cover of size 4? Yes. Ex. Is there a vertex cover of size 3? No. vertex cover
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)03 Maximum Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)02 Basics of algorithm design & analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)Stable Matching.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)01 Introduction(肖鸣宇).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《数据库系统原理 An Introduction to Database System》课程教学资源(电子教案,颜清).doc
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 分支限界法(Branch and Bound Method).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 回朔法(Backtracking Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 动态规划 Dynamic Programming.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 递归与分治策略.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 算法概述 Algorithm Introduction(刘瑶、陈佳).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(FP-growth Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(Apriori Algorithm、Improve of Apriori Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Clustering Analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis and Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis(Logistic Regression).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.1-2.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.5-2.7).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)05 Approximation Algorithms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(李发根).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 古典密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 流密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 分组密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 Hash函数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(一)6.1-6.4.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(二)6.5-6.9.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 数字签名.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 密码协议.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(主讲:曾凡平).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 基础知识.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 密码学基础.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 虚拟专用网络(VPN)技术.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:An adaptive trust model based on recommendation filtering algorithm for the Internet of Things systems.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Automatic Generation of Capability Leaks’ Exploits for Android Applications.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Adaptive Random Testing for XSS Vulnerability.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:A Novel Hybrid Model for Task Dependent Scheduling in Container-based Edge Computing.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Capability Leakage Detection Between Android Applications Based on Dynamic Feedback.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Multi-platform Application Interaction Extraction for IoT Devices.pdf
