电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)05 Approximation Algorithms

Design and Analysis of Algorithms 5.Approximation Algorithms Mingyu XIAO School of Computer Science and Engineering University of Electronic Science and Technology of China
Design and Analysis of Algorithms 5. Approximation Algorithms Mingyu XIAO School of Computer Science and Engineering University of Electronic Science and Technology of China

Approximation Algorithms Q.Suppose I need to solve an NP-hard problem.What should I do? A.Theory says you're unlikely to find a poly-time algorithm. Must sacrifice one of three desired features. Solve problem to optimality. Solve problem in poly-time. Solve arbitrary instances of the problem. p-approximation algorithm. Guaranteed to run in poly-time. Guaranteed to solve arbitrary instance of the problem Guaranteed to find solution within ratio p of true optimum. Challenge.Need to prove a solution's value is close to optimum,without even knowing what optimum value is! 2
2 Approximation Algorithms Q. Suppose I need to solve an NP-hard problem. What should I do? A. Theory says you're unlikely to find a poly-time algorithm. Must sacrifice one of three desired features. Solve problem to optimality. Solve problem in poly-time. Solve arbitrary instances of the problem. -approximation algorithm. Guaranteed to run in poly-time. Guaranteed to solve arbitrary instance of the problem Guaranteed to find solution within ratio of true optimum. Challenge. Need to prove a solution's value is close to optimum, without even knowing what optimum value is!

5.1 Load Balancing
5.1 Load Balancing

Load Balancing Input.m identical machines;n jobs,job j has processing time tj. Job j must run contiguously on one machine. A machine can process at most one job at a time. Def.Let J(i)be the subset of jobs assigned to machine i.The load of machine i is Li=>jeJ(i)fj. Def.The makespan is the maximum load on any machine L max;Li. Load balancing.Assign each job to a machine to minimize makespan
4 Load Balancing Input. m identical machines; n jobs, job j has processing time tj . Job j must run contiguously on one machine. A machine can process at most one job at a time. Def. Let J(i) be the subset of jobs assigned to machine i. The load of machine i is Li = j J(i) tj . Def. The makespan is the maximum load on any machine L = maxi Li . Load balancing. Assign each job to a machine to minimize makespan
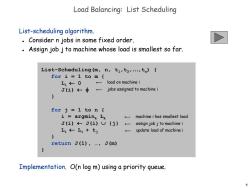
Load Balancing:List Scheduling List-scheduling algorithm. Consider n jobs in some fixed order. D Assign job j to machine whose load is smallest so far. List-Scheduling(m,n,t1,t2,...,tn){ for i=1 to m 工1←0 load on machine i J(i)←中- jobs assigned to machine i } for j=1 to n i=argmink Lk machine i has smallest load J(i)←J(i)U{} assign job j to machine i 工:←工:+t与 update load of machine i return J(1),…,J(m) Implementation.O(n log m)using a priority queue. 5
5 List-scheduling algorithm. Consider n jobs in some fixed order. Assign job j to machine whose load is smallest so far. Implementation. O(n log m) using a priority queue. Load Balancing: List Scheduling List-Scheduling(m, n, t1,t2,…,tn) { for i = 1 to m { Li 0 J(i) } for j = 1 to n { i = argmink Lk J(i) J(i) {j} Li Li + tj } return J(1), …, J(m) } jobs assigned to machine i load on machine i machine i has smallest load assign job j to machine i update load of machine i

Load Balancing:List Scheduling Analysis Theorem.[Graham,1966]Greedy algorithm is a 2-approximation. First worst-case analysis of an approximation algorithm. Need to compare resulting solution with optimal makespan L*. Lemma 1.The optimal makespan L*maxj tj. Pf.Some machine must process the most time-consuming job. Lemma2.The optimal makespan L*≥a∑,t,: Pf. The total processing time is >jtj. One of m machines must do at least a 1/m fraction of total work. 6
6 Load Balancing: List Scheduling Analysis Theorem. [Graham, 1966] Greedy algorithm is a 2-approximation. First worst-case analysis of an approximation algorithm. Need to compare resulting solution with optimal makespan L*. Lemma 1. The optimal makespan L* maxj tj . Pf. Some machine must process the most time-consuming job. ▪ Lemma 2. The optimal makespan Pf. The total processing time is j tj . One of m machines must do at least a 1/m fraction of total work. ▪ L * 1 m t j j
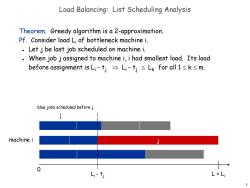
Load Balancing:List Scheduling Analysis Theorem.Greedy algorithm is a 2-approximation. Pf.Consider load Li of bottleneck machine i. Let j be last job scheduled on machine i. When job j assigned to machine i,i had smallest load.Its load before assignment is Li-tj→Li-tj≤Lk for all1≤k≤m. blue jobs scheduled before j machine i Li-tj L=L: 7
7 Load Balancing: List Scheduling Analysis Theorem. Greedy algorithm is a 2-approximation. Pf. Consider load Li of bottleneck machine i. Let j be last job scheduled on machine i. When job j assigned to machine i, i had smallest load. Its load before assignment is Li - tj Li - tj Lk for all 1 k m. j 0 Li L = Li - tj machine i blue jobs scheduled before j
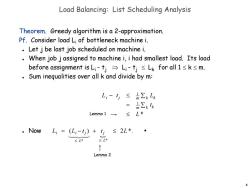
Load Balancing:List Scheduling Analysis Theorem.Greedy algorithm is a 2-approximation. Pf.Consider load Li of bottleneck machine i. Let j be last job scheduled on machine i. When job j assigned to machine i,i had smallest load.Its load before assignment is Li-tj→Li-tj≤Lk for all1≤k≤m. Sum inegualities over all k and divide by m: L,-4≤a∑kL h∑k Lemma 1 ≤L* ·NowL;=(L,-4)+t) ≤2L*. ≤L* ≤L米 1 Lemma 2 8
8 Load Balancing: List Scheduling Analysis Theorem. Greedy algorithm is a 2-approximation. Pf. Consider load Li of bottleneck machine i. Let j be last job scheduled on machine i. When job j assigned to machine i, i had smallest load. Its load before assignment is Li - tj Li - tj Lk for all 1 k m. Sum inequalities over all k and divide by m: Now ▪ Li t j 1 m k Lk 1 m t k k L * Li (Li t j ) L* t j L* 2L *. Lemma 2 Lemma 1
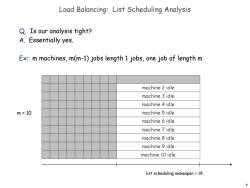
Load Balancing:List Scheduling Analysis Q.Is our analysis tight? A.Essentially yes. Ex:m machines,m(m-1)jobs length 1 jobs,one job of length m machine 2 idle machine 3 idle machine 4 idle m=10 machine 5 idle machine 6 idle machine 7 idle machine 8 idle machine 9 idle machine 10 idle list scheduling makespan 19 9
9 Load Balancing: List Scheduling Analysis Q. Is our analysis tight? A. Essentially yes. Ex: m machines, m(m-1) jobs length 1 jobs, one job of length m machine 2 idle machine 3 idle machine 4 idle machine 5 idle machine 6 idle machine 7 idle machine 8 idle machine 9 idle machine 10 idle list scheduling makespan = 19 m = 10
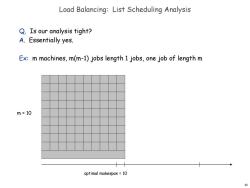
Load Balancing:List Scheduling Analysis Q.Is our analysis tight? A.Essentially yes. Ex:m machines,m(m-1)jobs length 1 jobs,one job of length m m=10 optimal makespan 10 10
10 Load Balancing: List Scheduling Analysis Q. Is our analysis tight? A. Essentially yes. Ex: m machines, m(m-1) jobs length 1 jobs, one job of length m m = 10 optimal makespan = 10
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)04 NP and Computational Intractability.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)03 Maximum Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)02 Basics of algorithm design & analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)Stable Matching.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)01 Introduction(肖鸣宇).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《数据库系统原理 An Introduction to Database System》课程教学资源(电子教案,颜清).doc
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 分支限界法(Branch and Bound Method).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 回朔法(Backtracking Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 动态规划 Dynamic Programming.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 递归与分治策略.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 算法概述 Algorithm Introduction(刘瑶、陈佳).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(FP-growth Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(Apriori Algorithm、Improve of Apriori Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Clustering Analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis and Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis(Logistic Regression).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.1-2.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(李发根).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 古典密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 流密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 分组密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 Hash函数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(一)6.1-6.4.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(二)6.5-6.9.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第7章 数字签名.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第8章 密码协议.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(主讲:曾凡平).pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 基础知识.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 密码学基础.pdf
- 中国科学技术大学:《网络安全》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 虚拟专用网络(VPN)技术.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:An adaptive trust model based on recommendation filtering algorithm for the Internet of Things systems.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Automatic Generation of Capability Leaks’ Exploits for Android Applications.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Adaptive Random Testing for XSS Vulnerability.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:A Novel Hybrid Model for Task Dependent Scheduling in Container-based Edge Computing.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Capability Leakage Detection Between Android Applications Based on Dynamic Feedback.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:Multi-platform Application Interaction Extraction for IoT Devices.pdf
- 《网络与系统安全》教学参考文献:RepassDroid - Automatic Detection of Android Malware Based on Essential Permissions and Semantic Features of Sensitive APIs.pdf
