电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 06 Classification

Lecture 6 Classification Dr.李晓瑜Xiaoyu Li Email:xiaoyuuestc@uestc.edu.cn http://blog.sciencenet.cn/u/uestc2014xiaoyu 2019-Spring SunData Group http://www.sundatagroup.org School of Information and Software Engineering,UESTC 1966 Copyright2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Dr.李晓瑜 Xiaoyu Li Email:xiaoyuuestc@uestc.edu.cn http://blog.sciencenet.cn/u/uestc2014xiaoyu 2019-Spring Lecture 6 Classification SunData Group http://www.sundatagroup.org/ School of Information and Software Engineering, UESTC Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 1

Gunbata Groun Content (6H) 。6.1 Basic Concepts 6.2 Decision Tree Induction .6.3 Bayes Classification Methods .6.4 Rule-Based Classification .6.5 Model Evaluation and Selection 6.6 Techniques to Improve Classification accuracy 2 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Content(6H) 6.1 Basic Concepts 6.2 Decision Tree Induction 6.3 Bayes Classification Methods 6.4 Rule-Based Classification 6.5 Model Evaluation and Selection 6.6 Techniques to Improve Classification Accuracy Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 2

Basic Concepts 3 DATA Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 3 Basic Concepts

1 What's Classification? .A bank loans officer loan application>safe or risky A marketing manager judge customer buy a new PC Medical researchers>breast cancer data>treatment 。→Data analysis task is Classification Classification is a form of data analysis that extracts models describing important data classes. Such models,called classifiers,predict categorical (discrete,unordered)class labels. ATA 4 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 4 1 What’s Classification? A bank loans officer → loan application→ safe or risky A marketing manager → judge customer buy a new PC Medical researchers→ breast cancer data→ treatment → Data analysis task is Classification Classification is a form of data analysis that extracts models describing important data classes. Such models, called classifiers, predict categorical (discrete, unordered) class labels

1 What's Classification? Prediction problems .(1)Classification .(2)Numeric Prediction DATA 5 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 5 1 What’s Classification? Prediction Problems (1) Classification (2) Numeric Prediction

2 General Approach to Classification ·Two-step process: Step 1:Learning Step /Training Phase Supervised Learning V.S.Unsupervised Learning (e.g.Clustering) a classification model is constructed .Step 2:Classification Step the model is used to predict class labels for given data ATA 6 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 6 2 General Approach to Classification Two-step process: Step 1: Learning Step / Training Phase Supervised Learning V.S. Unsupervised Learning (e.g. Clustering) a classification model is constructed Step 2:Classification Step the model is used to predict class labels for given data
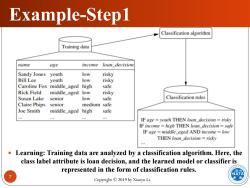
Example-Step1 Classification algorithm Training data name age income loan decision Sandy Jones youth low risky Bill Lee youth low risky Caroline Fox middle_aged high safe Rick Field middle_aged low risky Susan Lake senior low safe Classification rules Claire Phips senior medium safe Joe Smith middle_aged high safe 4年0 IF age youth THEN loan_decision risky IF income high THEN loan_decision safe IF age middle_aged AND income low THEN loan_decision risky .Learning:Training data are analyzed by a classification algorithm.Here,the class label attribute is loan decision,and the learned model or classifier is represented in the form of classification rules. ATA Copyright2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 7 Example-Step1 Learning: Training data are analyzed by a classification algorithm. Here, the class label attribute is loan decision, and the learned model or classifier is represented in the form of classification rules
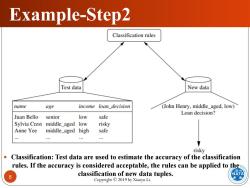
Example-Step2 Classification rules Test data New data name age income loan_decision (John Henry,middle_aged,low) Loan decision? Juan Bello senior low safe Sylvia Crest middle_aged low risky Anne Yee middle_aged high safe risky Classification:Test data are used to estimate the accuracy of the classification rules.If the accuracy is considered acceptable,the rules can be applied to the 8 classification of new data tuples. DATA Copyright2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 8 Example-Step2 Classification: Test data are used to estimate the accuracy of the classification rules. If the accuracy is considered acceptable, the rules can be applied to the classification of new data tuples

3 Training Set .A Training Set made up of database tuples and their associated class labels. A tuple,X,is represented by an n-dimensional attribute vector,X=(xI,x2,...,xn),depicting n measurements made on the tuple from n database attributes, respectively,A1,42,...,An. Each tuple,X,is assumed to belong to a predefined class as determined by another database attribute called the class label attribute. DATA 9 Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 9 3 Training Set A Training Set made up of database tuples and their associated class labels. A tuple, X, is represented by an n-dimensional attribute vector, X=(x1, x2,…, xn), depicting n measurements made on the tuple from n database attributes, respectively, A1, A2,…, An. Each tuple, X, is assumed to belong to a predefined class as determined by another database attribute called the class label attribute

4 Test set .A Test Set made up of test tuples and their associated class labels. Test Set is independent of the training tuples, meaning that they were not used to construct the classifier. 10 DATA Copyright 2019 by Xiaoyu Li
Copyright © 2019 by Xiaoyu Li. 10 4 Test set A Test Set made up of test tuples and their associated class labels. Test Set is independent of the training tuples, meaning that they were not used to construct the classifier
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(FP-growth Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 04 Association Rules of Data Reasoning(Apriori Algorithm、Improve of Apriori Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 05 Clustering Analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis and Classification.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 03 Regression Analysis(Logistic Regression).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.1-2.4).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 02 Raw Data Analysis and Pre-processing(2.5-2.7).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Lecture 01 Overview Data Analysis and Data Mining(李晓瑜).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子降维算法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子神经网络(Neural Network,NN).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子机器学习(量子K-means算法).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)隐马尔科夫算法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)降维算法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)分类算法(朱钦圣).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)聚类算法.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)量子力学.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)决策树.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《数据分析与数据挖掘 Data Analysis and Data Mining》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)线性模型.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第一章 算法概述 Algorithm Introduction(刘瑶、陈佳).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第二章 递归与分治策略.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第三章 动态规划 Dynamic Programming.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第四章 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第五章 回朔法(Backtracking Algorithm).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Algorithms Design and Analysis》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六章 分支限界法(Branch and Bound Method).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《数据库系统原理 An Introduction to Database System》课程教学资源(电子教案,颜清).doc
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)01 Introduction(肖鸣宇).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)Stable Matching.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)02 Basics of algorithm design & analysis.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)03 Maximum Flow.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)04 NP and Computational Intractability.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《算法设计与分析 Design and Analysis of Algorithms》研究生课程教学资源(课件讲稿,英文版)05 Approximation Algorithms.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第1章 概述(李发根).pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第2章 古典密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第3章 流密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第4章 分组密码.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第5章 Hash函数.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(一)6.1-6.4.pdf
- 电子科技大学:《现代密码理论 Modern Cryptographic Theory》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第6章 公钥密码(二)6.5-6.9.pdf
