厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules

What's a chemical bond? Chemical Bonding
What’s a chemical bond? Chemical Bonding

Quantum mechanical theory for description of molecular structures and chemical bondings Molecular Orbital (MO)Theory a)Proposed by Hund,Mulliken,Lennard-Jones et al.in 1930s. b)Further developments by Slater,Huckel and Pople et al c)MO-based softwares are widely used nowaday,e.g.,Gaussian Valence Bond (VB)Theory a)Proposed by Heitler and London 1930s,further developments by Pauling and Slater et al. b)Programmed in later 1980s,e.g.,latest development--XMVB! Density Functional Theory a)Proposed by Kohn et al. b)DFT-implemented QM softwares are widely used,e.g.,Gaussian
Quantum mechanical theory for description of molecular structures and chemical bondings • Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory a) Proposed by Hund, Mulliken, Lennard-Jones et al. in 1930s. b) Further developments by Slater, Hückel and Pople et al. c) MO-based softwares are widely used nowaday, e.g., Gaussian • Valence Bond (VB) Theory a) Proposed by Heitler and London 1930s, further developments by Pauling and Slater et al. b) Programmed in later 1980s, e.g., latest development--XMVB! • Density Functional Theory a) Proposed by Kohn et al. b) DFT-implemented QM softwares are widely used, e.g., Gaussian

Slater Pauling Kohn 卢嘉锡
Slater Pauling Kohn 卢嘉锡
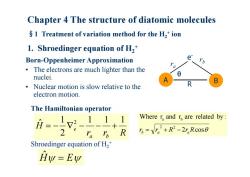
Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules $1 Treatment of variation method for the H,+ion 1.Shroedinger equation of H,* Born-Oppenheimer Approximation e The electrons are much lighter than the 0 nuclei. Nuclear motion is slow relative to the R electron motion. The Hamiltonian operator 月=-12-111 Where r and r are related by: 2 ra I R 5=V.2+R2-2r.Rc0s0 Shroedinger equation of H2 Hy=Ew
Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules §1 Treatment of variation method for the H 2 + ion 1. Shroedinger equation of H 2 + Born-Oppenheimer Approximation • The electrons are much lighter than the nuclei. • Nuclear motion is slow relative to the electron motion. r r R H a b e 1 1 1 2 1 ˆ 2 The Hamiltonian operator 2 cos Where r and r are related by : 2 2 a b rb ra R ra R A B e- r b r a R Hˆ E Shroedinger equation of H 2 +
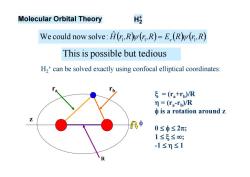
Molecular Orbital Theory H歧 We could now solve:H(,R(,R)=E.(R(r,R) This is possible but tedious H,+can be solved exactly using confocal elliptical coordinates: ξ=(Ta+rp)/R =(ra-rp)/R φis a rotation around z A中 0≤φ≤2; 1≤5≤0; -1≤m≤1
H2+ can be solved exactly using confocal elliptical coordinates: ra rb z = (ra+rb)/R = (ra-rb)/R is a rotation around z 0 2; 1 ; -1 1 R Molecular Orbital Theory H2 Hr,R r,R E R r,R 1 1 e 1 ˆ We could now solve: Thisis possible but tedious

Ψelee=F(传,n)(2π)l/neim吨 where m=0,±1,±2,±3, The associated quantum number is A.>orbital angular momentum 入=ml Each electronic level with m 0 is doubly degenerate,i.e.+ml,-m atoms:=0,1,2....and the atomic orbitals are called:s.p.d,etc. diatomics:入=0,l,2,.and the molecular orbitals are:o,元,δ,etc H2*:ro=2 Bohr letter Ep 2.71 eV
elec = F(,) (2)-1/2 eim where m=0, ±1, ±2, ±3, … The associated quantum number is . orbital angular momentum =|m| Each electronic level with m 0 is doubly degenerate, i.e. + |m|,-|m| atoms: = 0,1,2,... and the atomic orbitals are called: s,p,d, etc. diatomics: = 0,1,2, ... and the molecular orbitals are: , , , etc. 0 12 3 4 letter H2+ : r0 = 2 Bohr Eb = 2.71 eV

2.The Variation Theorem For any well-behaved wavefunction the average energy from the Hamiltonian of the system is always greater or close to the exact ground state energy (Eo)for that Hamiltonian, E-9≥E ∫p"pdr
2. The Variation Theorem For any well-behaved wavefunction , the average energy from the Hamiltonian of the system is always greater or close to the exact ground state energy (E 0) for that Hamiltonian, * 0 * ˆ E d H d E
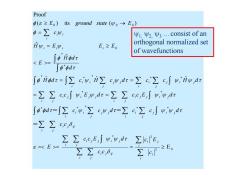
Proof p(e≥Eo)its ground state(wo→Eo) p=∑cw Ψ1,Ψ2,Ψ3.consist of an A,=E,Ψ, E,≥E orthogonal normalized set of wavefunctions 「pidz = 「ppdx ∫idr=∑ciw,iΣc",dr=∑c∑c∫w,iwar =∑∑ccw,E",dr=∑∑cc,E,∫w,,d fpdr=∫∑cw,∑cw,dr=∑c,∑c∫g,w,dr =∑∑cc6, ∑∑cc,Ew,"dr∑efE E== ΣΣccA ∑s ≥E
2 0 * 2 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * 0 0 0 0 E ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ( ) its ( ) Proof i i j i i i j ij i j i j j i j i j i j ij i j j i j j i i j j j i i i i j j i j i j i j i j j i j j i j j i i j j j i i i i i i i i i i c c E c c c c E d E c c d c c d c c d c c E d c c E d H d c H c d c c H d d H d E H E E E c E ground state E = = = 1, 2, 3 …consist of an orthogonal normalized set of wavefunctions

Example:Devise a trial variation function for the particle in a one-dimensional box of length I. A simple function that has the properties of the ground state is the parabolic function: 中=x(1-x) for0sx≤I 21 6m 0-a= -J "Hodr 5h2 >h2 8m12
Example: Devise a trial variation function for the particle in a one-dimensional box of length l. 0 l A simple function that has the properties of the ground state is the parabolic function: x(l x) for 0x l m l lx x dx dx d lx x m H d l 6 ( ) ( ) 2 ˆ 2 3 2 2 2 0 2 2 * 30 ( ) 5 2 0 2 * l d x l x dx l 2 8 2 2 2 4 2 5 * * ˆ ml h ml h d H d E
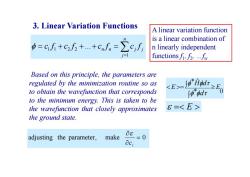
3.Linear Variation Functions A linear variation function is a linear combination of =cf+c方++cnn=∑c,f n linearly independent functionsf2... Based on this principle,the parameters are regulated by the minimization routine so as to obtain the wavefunction that corresponds 82司 J0"odr to the minimum energy.This is taken to be the wavefunction that closely approximates 6= the ground state. adjusting the parameter, make 08 =0 aci
Based on this principle, the parameters are regulated by the minimization routine so as to obtain the wavefunction that corresponds to the minimum energy. This is taken to be the wavefunction that closely approximates the ground state. * 0 * ˆ E d H d E adjusting the parameter, make 0 i c E 3. Linear Variation Functions n j n n j j c f c f c f c f 1 1 1 2 2 ... A linear variation function is a linear combination of n linearly independent functions f1, f2, …fn
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Molecular symmetry and symmetry point group.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 The Basic Knowledge of Quantum Mechanics(讲授:曹泽星、蒋亚琪).pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 9 多原子的半经验方法 Semi-experimental method for polyatomic molecular.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 8 共轭分子的结构与性能 Ab initio technique for polyatomic molecular.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 7 简单分子轨道理论 Elementary molecular orbital(MO)theory.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 6 分子的对称性与对称群 Molecular symmetry and symmetric group.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 5 原子结构 Atomic structure.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 4 角动量与自旋 Angle momentum and spin.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 3 矩阵与算符 Matrix and operator.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 2 简单量子力学体系 Rudimental quantum mechanics system.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 1 Schrödinger 方程 Schrodinger equation.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《高分子化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六、七、八、九章 离子聚合、开环聚合、链式共聚合反应、配位聚合、聚合物的化学反应(主讲:刘世勇).pdf
- 和频光谱在生物膜等生物界面中的应用 In situ molecular level studies on membrane related peptides and proteins in real time using sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二十二章 镧系元素和锕系元素.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二十一章 过渡元素(二).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二十章 过渡元素(一).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十八章 铜、锌副族.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十七章 碱金属与碱土金属.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十四章 氮族元素.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 The structure of polyatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Polyatomic molecules(II).pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Group Theory and Its Application to Quantum Chemistry - Introduction(主讲:曹泽星).pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Part I 群论基础 Chapter 1 基本概念 Chapter 2 抽象群的结构.pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 群的类分解 Chapter 4 商群与同态(Factor group & Homomorphism)Chapter 5 群的直积(Direct Product)Chapter 6 置换群(Permutation group/Symmetric group).pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 7 Cayley定理 Chapter 8 线性向量空间(Linear vector spaces)Chapter 9 线性算符(Linear Operator)Chapter 10 群的表示.pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 酉空间(Unitary Space)Chapter 12 表示的约化及其判据 Chapter 13 正交定理 The Orthogonality Relations Chapter 14 直积群的表示 Chapter 15 表示的分解 Chapter 16 投影算符(Projection Operator).pdf
- 《普通化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第9章 仪器分析基础.pptx
- 山西师范大学:《生物化学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 山西师范大学:《生物化学实验》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)绪论(主讲:任浩).pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第四章 分子结构.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第一章 量子力学基础.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第二章 运动的量子理论.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第六章 固体.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第三章 原子结构和原子光谱.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第五章 对称性.pdf
- 安徽建筑大学:材料与化学工程学院应用化学专业培养方案(2019版).doc
- 安徽建筑大学:材料与化学工程学院《高分子化学实验》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 山东农业大学:《生物化学实验B》课程教学大纲.pdf
