厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 1 The Basic Knowledge of Quantum Mechanics(讲授:曹泽星、蒋亚琪)

Structural Chemistry 结构化学是研究原子、分子和晶体的微观结构,研究原子和分 子运动规律,研究物质的结和性能关系的科学 主要研究从原子、分子片、分子、超分子,到分子和原子的各种 不同尺度和不同复杂程度的聚集态和组装态的合成和反应,分离 和分析,结构和形态,物理性能和生物活性及其规律和应用的自 然科学 --- 徐光宪 1998年诺贝尔化学奖获得者Kohn和Pople认为: “量子化学已经发展成为广大化学家所使用的工具,将化学带入 一个新时代,在这个新时代里实验和理论能够共同协力探讨分子 体系的性质。化学不再是纯粹的实验科学了
Structural Chemistry 主要研究从原子、分子片、分子、超分子,到分子和原子的各种 不同尺度和不同复杂程度的聚集态和组装态的合成和反应,分离 和分析,结构和形态,物理性能和生物活性及其规律和应用的自 然科学 –-- 徐光宪 1998年诺贝尔化学奖获得者Kohn和Pople认为: “量子化学已经发展成为广大化学家所使用的工具,将化学带入 一个新时代,在这个新时代里实验和理论能够共同协力探讨分子 体系的性质。化学不再是纯粹的实验科学了” 结构化学是研究原子、分子和晶体的微观结构,研究原子和分 子运动规律,研究物质的结和性能关系的科学

The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1981 Martin Karplus,Michael Levitt,Arieh Warshel Fukui Hoffmann The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2013 ©Nobel Media AB Photo:Kellana via Martin Karplus Wikimedia Commons Michael Levitt Arieh Warshel QM/MM boundary The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2013 was awarded jointly to Martin Karplus, Solution Michael Levitt and Arieh Warshel "for the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems". 2013年诺贝尔化学奖获奖理由:复杂体系多尺度模型
2013年诺贝尔化学奖获奖理由:复杂体系多尺度模型 Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1981 Fukui & Hoffmann

Know-How about Structural Chemistry ◆3+2+1原则 3种理论:量子理论,化学键理论,点阵理论 3种结构:原子结构,分子结构,晶体结构 3个基础:量子化学基础,对称性原理基础,结晶化学基础 2个因素:电子因素,空间因素 1条主线:结构决定性能,性能反映结构 理解为主,记忆为辅(预习-复习--总结) ◆发展的观点 分子→超分子,微观→介观(纳米)→宏观,相对论? 光速不变?
Know-How about Structural Chemistry 3+2+1原则 3种理论:量子理论,化学键理论,点阵理论 3种结构:原子结构,分子结构,晶体结构 3个基础:量子化学基础,对称性原理基础,结晶化学基础 2个因素:电子因素,空间因素 1条主线:结构决定性能,性能反映结构 理解为主,记忆为辅(预习--- 复习--- 总结 ) 发展的观点 分子 →超分子,微观 →介观(纳米) →宏观,相对论? 光速不变? …

What is Chemistry The branch of natural science that deals with composition,structure, properties of substances and the changes they undergo. Chemistry Chem is try
What is Chemistry The branch of natural science that deals with composition, structure, properties of substances and the changes they undergo. Chemistry = Chem + is + try ?

Structure vs.Properties The structure determines properties Properties reflect the structure
The structure determines properties Properties reflect the structure Structure vs. Properties

Types of substances Atoms Geometric Structure Molecules Clusters Size Congeries makes the difference Nano materials Electronic Structure Bulk materials
Types of substances Atoms Molecules Clusters Congeries Nano materials Bulk materials Geometric Structure Size makes the difference Electronic Structure

Basic Units Atom The basic building block of all matter.The smallest particle of an element that has the same properties as the element. Composed of an electron cloud and a central nucleus
Atom The basic building block of all matter. The smallest particle of an element that has the same properties as the element. Composed of an electron cloud and a central nucleus. Basic Units

Atomic Structure All the matter around you is made of atoms,and all atoms are made of only three types of subatomic particle, ②electron(-l protons,electrons,and neutrons. proton (+ All protons are exactly the same,all neutron (0) neutrons are exactly the same,and all electrons are exactly the same. There are many elements in the PERIODIC TABLE.Over 100! The thing that makes those elements different is the number of electrons,protons,and neutrons
All the matter around you is made of atoms, and all atoms are made of only three types of subatomic particle, protons, electrons, and neutrons. All protons are exactly the same, all neutrons are exactly the same, and all electrons are exactly the same. Atomic Structure There are many elements in the PERIODIC TABLE. Over 100! The thing that makes those elements different is the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons

Dalton (1803) History of Thomson(1904) positive and negative charges) Atomic models Rutherford(1911) (the nucleus) Understanding Bohr(1913) atomic structure is a (energy levels) first step to understand structure of the matter Schrodinger(1926) (electron cloud model)
History of Atomic Models Understanding atomic structure is a first step to understand structure of the matter
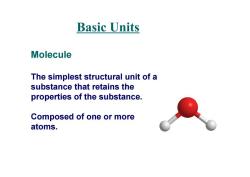
Basic Units Molecule The simplest structural unit of a substance that retains the properties of the substance. Composed of one or more atoms
Molecule The simplest structural unit of a substance that retains the properties of the substance. Composed of one or more atoms. Basic Units
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 9 多原子的半经验方法 Semi-experimental method for polyatomic molecular.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 8 共轭分子的结构与性能 Ab initio technique for polyatomic molecular.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 7 简单分子轨道理论 Elementary molecular orbital(MO)theory.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 6 分子的对称性与对称群 Molecular symmetry and symmetric group.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 5 原子结构 Atomic structure.pdf
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 4 角动量与自旋 Angle momentum and spin.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 3 矩阵与算符 Matrix and operator.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 2 简单量子力学体系 Rudimental quantum mechanics system.ppt
- 厦门大学:《量子化学 Quantum Chemistry》课程电子教案(教学课件)Chapter 1 Schrödinger 方程 Schrodinger equation.ppt
- 中国科学技术大学:《高分子化学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)第六、七、八、九章 离子聚合、开环聚合、链式共聚合反应、配位聚合、聚合物的化学反应(主讲:刘世勇).pdf
- 和频光谱在生物膜等生物界面中的应用 In situ molecular level studies on membrane related peptides and proteins in real time using sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二十二章 镧系元素和锕系元素.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二十一章 过渡元素(二).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第二十章 过渡元素(一).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十八章 铜、锌副族.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十七章 碱金属与碱土金属.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十四章 氮族元素.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十五章 碳族元素(碳、硅、硼).pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十二章 卤素.pdf
- 上饶师范学院:《无机化学》课程电子教案(课件讲稿)第十三章 氧族元素.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 2 Atomic Structure.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 Molecular symmetry and symmetry point group.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 5 The structure of polyatomic molecules.pdf
- 厦门大学:《结构化学 Structural Chemistry》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 6 Polyatomic molecules(II).pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Group Theory and Its Application to Quantum Chemistry - Introduction(主讲:曹泽星).pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Part I 群论基础 Chapter 1 基本概念 Chapter 2 抽象群的结构.pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 3 群的类分解 Chapter 4 商群与同态(Factor group & Homomorphism)Chapter 5 群的直积(Direct Product)Chapter 6 置换群(Permutation group/Symmetric group).pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 7 Cayley定理 Chapter 8 线性向量空间(Linear vector spaces)Chapter 9 线性算符(Linear Operator)Chapter 10 群的表示.pdf
- 厦门大学:《群论及其在化学中的应用》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)Chapter 11 酉空间(Unitary Space)Chapter 12 表示的约化及其判据 Chapter 13 正交定理 The Orthogonality Relations Chapter 14 直积群的表示 Chapter 15 表示的分解 Chapter 16 投影算符(Projection Operator).pdf
- 《普通化学》课程电子教案(PPT教学课件)第9章 仪器分析基础.pptx
- 山西师范大学:《生物化学》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 山西师范大学:《生物化学实验》课程教学大纲.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)绪论(主讲:任浩).pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第四章 分子结构.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第一章 量子力学基础.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第二章 运动的量子理论.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第六章 固体.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第三章 原子结构和原子光谱.pdf
- 中国石油大学(华东):《结构化学》课程电子教案(教学课件)第五章 对称性.pdf
