《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 2/3

Chapter 27,part B Environmental Microbiology
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 27, part B Environmental Microbiology

Decomposition by Microbes (a)Solid municipal wastes being turned by a specially (b)Compost made from municipal wastes awaiting trucks designed machine. to spread on agricultural fields. Figure 27.10
Decomposition by Microbes Figure 27.10
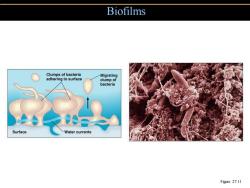
Biofilms Clumps of bacteria Migrating adhering to surface clump of bacteria Surface Water currents Figure 27.11
Biofilms Figure 27.11
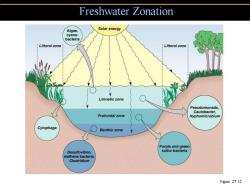
Freshwater Zonation Algae, Solar energy cyano- bacteria Littoral zone Littoral zone Limnetic zone Pseudomonads, Caulobacter, Profundal zone Hyphomicrobium Cytophaga Benthic zone Purple and green Desulfovibrio. sulfur bacteria methane bacteria Clostridium Figure 27.12
Freshwater Zonation Figure 27.12

Bioluminescence Luciferase FMNH2 →FMN+photon Figure 27.13
Bioluminescence Figure 27.13 FMNH2 FMN + photon Luciferase

Water Quality Microbes are filtered from water that percolates into groundwater. Some pathogens are transmitted to human in drinking and recreational water. Resistant chemicals may be concentrated in the aquatic food chain. Mercury is metabolized by certain bacteria into a soluble compound,concentrated in animals
Water Quality • Microbes are filtered from water that percolates into groundwater. • Some pathogens are transmitted to human in drinking and recreational water. • Resistant chemicals may be concentrated in the aquatic food chain. • Mercury is metabolized by certain bacteria into a soluble compound, concentrated in animals
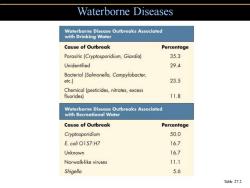
Waterborne Diseases Waterborne Disease Outbreaks Associated with Drinking Water Cause of Outbreak Percentage Parasitic(Cryptosporidium,Giardia) 35.3 Unidentified 29.4 Bacterial (Salmonella,Campylobacter, etc.) 23.5 Chemical (pesticides,nitrates,excess fluorides) 11.8 Waterborne Disease Outbreaks Associated with Recreational Water Cause of Outbreak Percentage Cryptosporidium 50.0 E.coli O157:H7 16.7 Unknown 16.7 Norwalk-like viruses 11.1 Shigella 5.6 Table 27.2
Waterborne Diseases Table 27.2
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 5/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 4/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 3/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 2/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 1/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)disorders associated with the immune system 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)disorders associated with the immune system 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)classification of microrganisms 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)classification of microrganisms 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)chemical principles 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)chemical principles 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)biotechnology and recombinant DNA 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)biotechnology and recombinant DNA 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)applied and industrial microbiology.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)antimicrobial drugs 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)antimicrobial drugs 1/2.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的生长和环境条件.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 真核微生物.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物的生态.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 1/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 2/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 3/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 4/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of digestive system 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of digestive system 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of digestive system 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the cardiovascalar and lymphatic systems 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the cardiovascalar and lymphatic systems 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the cardiovascalar and lymphatic systems 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the nervous system 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the nervous system 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the respiratory system 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the respiratory system 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the respiratory system 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the skin and eyes 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the skin and eyes 2/2.ppt
