《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)disorders associated with the immune system 2/2

Chapter 19,part B Disorders Associated with the Immune System
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 19, part B Disorders Associated with the Immune System

Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) 。1981 In U.S.,cluster of Pneumocystis and Kaposi's sarcoma in young homosexual men discovered.The men showed loss of immune function. 。1983 Discovery of virus causing loss of immune function
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) • 1981 In U.S., cluster of Pneumocystis and Kaposi's sarcoma in young homosexual men discovered. The men showed loss of immune function. • 1983 Discovery of virus causing loss of immune function
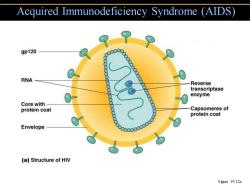
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) 9p120 RNA Reverse transcriptase enzyme Core with protein coat Capsomeres of protein coat Envelope (a)Structure of HIV Figure 19.12a
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) Figure 19.12a

The Origin of AIDS Crossed the species barrier into humans in Africa in the 1930s Patient who died in 1959 in Congo is the oldest known case Spread in Africa as a result of urbanization Spread in world through modern transportation and unsafe sexual practices Norwegian sailor who died in 1976 is the first known case in Western world
• Crossed the species barrier into humans in Africa in the 1930s • Patient who died in 1959 in Congo is the oldest known case • Spread in Africa as a result of urbanization • Spread in world through modern transportation and unsafe sexual practices • Norwegian sailor who died in 1976 is the first known case in Western world The Origin of AIDS
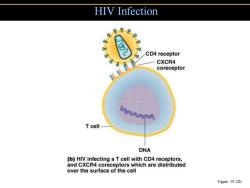
HIV Infection 89分 CD4 receptor CXCR4 coreceptor T cell DNA (b)HIV infecting a T cell with CD4 receptors, and CXCR4 coreceptors which are distributed over the surface of the cell Figure 19.12b
HIV Infection Figure 19.12b
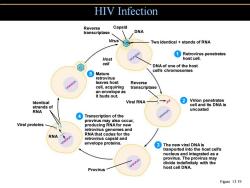
HIV Infection Reverse Capsid transcriptase DNA Virus Two identical stands of RNA Retrovirus penetrates Host host cell. cell DNA of one of the host 5Mature cell's chromosomes retrovirus leaves host Reverse cell,acquiring transcriptase an envelope as it buds out. Identical Viral RNA 2Virion penetrates cell and its DNA is strands of RNA uncoated 4 Transcription of the provirus may also occur, Viral proteins producing RNA for new retrovirus genomes and RNA RNAthat codes for the retrovirus capsid and envelope proteins. 3 The new viral DNA is tranported into the host cell's nucleus and integrated as a provirus.The provirus may divide indefinitely with the Provirus host cell DNA. Figure 13.19
HIV Infection Figure 13.19 Retrovirus penetrates host cell. Virion penetrates cell and its DNA is uncoated The new viral DNA is tranported into the host cell’s nucleus and integrated as a provirus. The provirus may divide indefinitely with the host cell DNA. 1 2 3 DNA Transcription of the provirus may also occur, producing RNA for new retrovirus genomes and RNA that codes for the retrovirus capsid and envelope proteins. 4 Mature retrovirus leaves host cell, acquiring an envelope as it buds out. 5 Reverse Capsid transcriptase Virus Two identical + stands of RNA DNA of one of the host cell’s chromosomes Provirus Host cell Reverse transcriptase Viral RNA RNA Viral proteins Identical strands of RNA

HIV Infection CD4 receptors CXCR4 Proviral DNA coreceptors Proviral DNA -T Cell Viral RNA mRNA 0 0 Core with Envelope viral RNA Chromosomal DNA Progeny HIV 0 39 Virus budding from T cell (a)Latent infection (b)Active infection Figure 19.13
HIV Infection Figure 19.13

HIV Infection Proviral DNA Macrophage 688 Vacuole Chromosomal DNA -HIV (a)Latent infection Proviral DNA 八 a88 Viral mRNA RNA Core with viral RNA b】Active infection Figure 19.14
HIV Infection Figure 19.14

The Stages of HIV Infection Category A Asymptomatic or persistent lymphadenopathy Category B Persistent Candida albicans infections Category C Clinical AlDS.CMV,TB, Pneumocystis,toxoplasmosis, Kaposi's sarcoma
• Category A Asymptomatic or persistent lymphadenopathy • Category B Persistent Candida albicans infections • Category C Clinical AIDS. CMV, TB, Pneumocystis, toxoplasmosis, Kaposi's sarcoma The Stages of HIV Infection

The Stages of HIV Infection Category A:Asymptomatic Category B:Symptomatic.Early Category C:AIDS or chronic lymphadenopathy. indications of immune failure. indicator conditions. 1200 12 1-2 months following initial infection, 1100 the population of HIV in blood peaks 11 at about 10,000,000/ml. 1000 ③Seroconversion. 10 Antibodies against HIV appear. 900 HIV population in blood crashes. 800 8 700 6Huge but indefinite numbers of 1 HIV in lymphoid tissue,in latent or 600 proviral form (see Figure 19.13).At least 6 8 21-2 months following initial 100 billion HIV generated each day 500 infection,population of for years,mostly by infected T cells. 5 CD4 T-cells plunges. (Darker color below line indicates viral 400 5CD4 T-cell load in lymphatic tissue.) HIV population in blood population 300 declines steadily 3 Rise of HIV in blood 3 as immune system 200 breaks down. HIV in blood stabilizes 2 at steady state of 100 1000to10,000/ml. ⑦Clinical AIDS:cD4Tcel population 200/mm3 2 4 5 7 8 10 1-2 months Years Figure 19.15
The Stages of HIV Infection Figure 19.15
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)disorders associated with the immune system 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)classification of microrganisms 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)classification of microrganisms 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)chemical principles 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)chemical principles 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)biotechnology and recombinant DNA 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)biotechnology and recombinant DNA 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)applied and industrial microbiology.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)antimicrobial drugs 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)antimicrobial drugs 1/2.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的生长和环境条件.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 真核微生物.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物的生态.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 原核生物.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 细菌的遗传和变异.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 病毒.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论(主讲:刘雅婷).ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 微生物的营养和代谢.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 微生物的细胞.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物生态.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 1/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 2/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 3/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 4/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 5/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 1/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 2/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 3/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 4/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of digestive system 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of digestive system 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of digestive system 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the cardiovascalar and lymphatic systems 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the cardiovascalar and lymphatic systems 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)microbial diseases of the cardiovascalar and lymphatic systems 3/3.ppt
