《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)applied and industrial microbiology

Chapter 28 Applied and Industrial Microbiology
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 28 Applied and Industrial Microbiology

Foods are preserved by: 。 Drying Osmotic pressure(salt or sugar) 。Fermentation
Foods are preserved by: • Drying • Osmotic pressure (salt or sugar) • Fermentation

Industrial Food Canning ⊙@ Washing, sorting, blanching Steam box Can ③Steaming ④Can sealed ⑤Sterilization Cans ⑦Labeling, filling to exhaust cooled storage, air Retort(see Figure 28.2) and delivery Figure 28.1
Industrial Food Canning Figure 28.1

Commercial Sterilization to Destroy C.botulinum Endospores 12D treatment kills 1012 endospores Surviving endospores of thermophilic anaerobes cause spoilage with gas Or flat-sour spoilage
• 12D treatment kills 1012 endospores • Surviving endospores of thermophilic anaerobes cause spoilage with gas • Or flat-sour spoilage Commercial Sterilization to Destroy C. botulinum Endospores

Food Preservation Presterilized materials assembled into packages and aseptically filled (Aseptic packaging) 。Gamma radiation kills bacteria,insects,and parasitic worms High-energy electrons Figure 28.4
• Presterilized materials assembled into packages and aseptically filled (Aseptic packaging) • Gamma radiation kills bacteria, insects, and parasitic worms • High-energy electrons Food Preservation Figure 28.4

Cheese Curd:solid casein from lactic acid bacteria and rennin 。 Whey:liquid separated from curd 。Hard cheeses produced by lactic acid bacteria (a)The milk has been coagulated by the action of rennin Semisoft cheeses (forming curd)and is inoculated with ripening bacteria for flavor and acidity.Here the workers are cutting the ripened by Penicillium curd into slabs. on surface Figure 28.8a
Cheese Figure 28.8a • Curd: solid casein from lactic acid bacteria and rennin • Whey: liquid separated from curd • Hard cheeses produced by lactic acid bacteria • Semisoft cheeses ripened by Penicillium on surface

lonizing Radiation Product Purpose Wheat,wheat flour Insect disinfestation White potatoes Sprout inhibition Pork Trichinella spiralis control Enzymes (dehydrated) Microbial control Frvit Insect disinfestation, ripening delay Vegetables,fresh Insect disinfestation Herbs Microbial control Spices Microbial control Vegetable seasonings Microbial control Poultry,fresh or frozen Microbial control Meat,frozen,packaged Sterilization Animal feed and pet food Salmonella control Meat,uncooked,chilled Microbial control Meat,uncooked,frozen Microbial control "For meats used solely in the National Aeronautics and Space Administration space flight programs. Table 28.2
Ionizing Radiation Table 28.2

Alcoholic Beverages and Vinegar Beer and ale are fermented starch 。 Malting:Germinating barley converts starch to maltose and glucose Yeast ferment sugars to ethyl alcohol +CO2
• Beer and ale are fermented starch • Malting: Germinating barley converts starch to maltose and glucose • Yeast ferment sugars to ethyl alcohol + CO2 Alcoholic Beverages and Vinegar
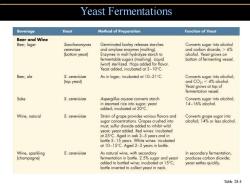
Yeast Fermentations Beverage Yeast Method of Preparation Function of Yeast Beer and Wine Beer,lager Saccharomyces Germinated barley releases starches Converts sugar into alcohol cerevisae and amylase enzymes(malting). and carbon dioxide;>6% (bottom yeast) Enzymes in malt hydrolyze starch to alcohol.Yeast grows on fermentable sugars (mashing).Liquid bottom of fermenting vessel. (wort)sterilized.Hops added for flavor. Yeast added,incubated at 3-10C. Beer,ale S.cerevisiae As in lager;incubated at 10-21C. Converts sugar into alcohol; (top yeast) and CO2;<4%alcohol. Yeast grows at top of fermentation vessel. Sake S.cerevisiae Aspergillus oryzae converts starch Converts sugar into alcohol; in steamed rice into sugar;yeast 14-16%alcohol. added;incubated at 20C Wine,natural S.cerevisiae Strain of grape provides various flavors and Converts grape sugar into sugar concentrations.Grapes crushed into alcohol;14%or less alcohol. must;sulfur dioxide added to inhibit wild yeast;yeast added.Red wines:incubated at 25C.Aged in oak 3-5 years and in bottle 5-15 years.White wines:incubated at 10-15C.Aged 2-3 years in bottle. Wine,sparkling S.cerevisiae As natural wine,with secondary In secondary fermentation, (champagne) fermentation in bottle.2.5%sugar and yeast produces carbon dioxide; added to botled wine;incubated at 15C; yeast settles quickly. bottle inverted to collect yeast in neck. Table 28.4
Yeast Fermentations Table 28.4
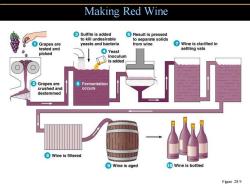
Making Red Wine ③Sulfite is added ⑥Result is pressed to kill undesirable to separate solids ①Grapes are yeasts and bacteria from wine ⑦Wine is clarified in tested and picked Yeast settling vats inoculum is added ②Grapes are 5 Fermentation crushed and occurs destemmed ⑧Wine is filtered Wine is aged 1Wine is bottled Figure 28.9
Making Red Wine Figure 28.9
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)antimicrobial drugs 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)antimicrobial drugs 1/2.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 微生物的生长和环境条件.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 真核微生物.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物的生态.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 原核生物.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 细菌的遗传和变异.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 病毒.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)绪论(主讲:刘雅婷).ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 微生物的营养和代谢.ppt
- 云南农业大学:《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 微生物的细胞.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 微生物生态.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 传染与免疫.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 微生物的遗传变异和育种.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四、五章 微生物的营养与培养基.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 微生物的生长繁殖及其控制.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 真核微生物.ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 病毒和类病毒(亚病毒).ppt
- 《微生物学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 原核生物.ppt
- 《植物生殖生物学》课程教学资源(课件讲稿)植物雄性不育性 Plant male sterility.pdf
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)biotechnology and recombinant DNA 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)biotechnology and recombinant DNA 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)chemical principles 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)chemical principles 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)classification of microrganisms 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)classification of microrganisms 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)disorders associated with the immune system 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)disorders associated with the immune system 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 1/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 2/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 3/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 4/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)domains bacteria archaea 5/5.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 1/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 2/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)environmental microbiology 3/3.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 1/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)functional anatomy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2/2.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 1/4.ppt
- 《微生物学 Microbiology》课程PPT教学课件(英文版)fungi algae protozoa and helminths 2/4.ppt
