复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Physiology——INTRODUCTION

Chapter 1 INTRODUCT ION 1.Physiology its research field Definition of physiology The task of physiological research *How *Why Influence of environment Adaptation and regulation
Chapter 1 § 1. Physiology & its research field • Definition of physiology • The task of physiological research * How * Why * Influence of environment * Adaptation and regulation INTRODUCTION

Relationship between medicine physiology Physiology is one of basic medical sciences Three levels of physiological research Cellular molecular level Organic systemic level Integrative level Methods of physiological research Acute and chronic animal experiment in vitro in vivo experiment molecular biological experiment
• Relationship between medicine & physiology * Physiology is one of basic medical sciences • Three levels of physiological research * Cellular & molecular level * Organic & systemic level * Integrative level • Methods of physiological research * Acute and chronic animal experiment * in vitro & in vivo experiment * molecular biological experiment

2.Internal environment of the body Body fluid (60%of body weight) Intracellular fluid (40%) Extracellular fluid (20%) Plasma (5%) Interstitial fluid (15%) Lymph (<1%) Cerebrospinal fluid (<1%) Aqueous humor (<1%) etc
§ 2. Internal environment of the body • Body fluid (60% of body weight) * Intracellular fluid (40%) * Extracellular fluid (20%) Plasma (5%) Interstitial fluid (15%) Lymph (<1%) Cerebrospinal fluid (<1%) Aqueous humor (<1%) etc

(占体重的40%) 人体外 Distribution transfusion of body fluid
Distribution & transfusion of body fluid

Concept of internal environment ('1870) By Claude Bernard (1813-1878) milieu interne [mi:ljo:into:n]French Concept of homeostasis ('1920) By W.B.Cannon (1871-1945) Importance of maintaining the homeostasis Enough nutritional substances O2 Low level of metabolic products CO2 Water,electrolyte,acid-base balance Temperature,osmotic pressure,etc. Homeostasis is a dynamic equilibrium Regulation of homeostasis Involve all systems,especially the lung kidney
• Concept of internal environment (’1870) By Claude Bernard (1813-1878) milieu interne [`mi:lj: `int:n] [French] • Concept of homeostasis (’1920) By W. B. Cannon (1871-1945) • Importance of maintaining the homeostasis * Enough nutritional substances & O2 * Low level of metabolic products & CO2 * Water, electrolyte, acid-base balance * Temperature, osmotic pressure, etc. • Homeostasis is a dynamic equilibrium • Regulation of homeostasis * Involve all systems, especially the lung & kidney

3.Regulation of physiological function ●Nervous regulation Definition the characteristics Reflex reflex arc ●Humoral regulation Definition the characteristics Hormone its secretory forms Telecrine,paracrine,neurosecretion,etc. ●Autoregulation Definition the characteristics
§ 3. Regulation of physiological function • Nervous regulation * Definition & the characteristics * Reflex & reflex arc • Humoral regulation * Definition & the characteristics * Hormone & its secretory forms Telecrine, paracrine, neurosecretion, etc. • Autoregulation * Definition & the characteristics

传入神经元 突触-- 人传入纤维 中间神经元 ●一感受器 突触 传出神经元 传出年雄人入 oi- 一-一二效应器 图1013反射弧 Reflex reflex arc
Reflex & reflex arc

4.Automatic control system in the body Non-automatic control system Open loop system Feedback control system Closed loop system,Automatic control Negative feedback system Positive feedback system Feed-forward control system More quickly,less oscillated foresighted
§ 4. Automatic control system in the body • Non-automatic control system Open loop system • Feedback control system * Closed loop system, Automatic control * Negative feedback system * Positive feedback system • Feed-forward control system More quickly, less oscillated & foresighted
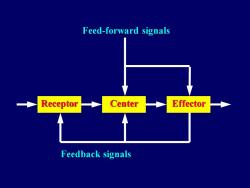
Feed-forward signals Receptor Center Effector Feedback signals
Receptor Center Effector Feed-forward signals Feedback signals
按次数下载不扣除下载券;
注册用户24小时内重复下载只扣除一次;
顺序:VIP每日次数-->可用次数-->下载券;
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Functions of the Nervous System.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)ENERGY METABOLISM & BODY TEMPERATURE.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)digestion and absorption.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第三章 血液 blood.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)BASIC FUNCTIONS OF THE CELL.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第二章 遗传的细胞和分子基础.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十章 肿瘤遗传学 Cancer(Tumor)Genetics.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第一章 医学遗传学概论.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第六章 染色体病.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第五章 多基因遗传与常见复杂疾病(多基因遗传的特点).ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十一章 基因诊断 Gene diagnosis.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第十二章 基因治疗.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第七章 基因操作.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 单基因病 Mendelian Inheritance.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 人类疾病的生化和分子遗传学——先天性代谢病.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 人类疾病的分子遗传学——血红蛋白病.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 人类基因组计划.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)教学大纲_医学遗传学.doc
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)基因操作技术_医学遗传学第七章.doc
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第九章 感觉器官的功能.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Physiology of Reproduction.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)Physiology of the Endocrine System.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)RESPIRATION.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——从噪声中提取有用信息.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——传导(播)速度和流速测定.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——信号的时域测量.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理原则和方法——医学信号概述.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——医学图像处理基础.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第八章 尿的生成和排出.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——散点图与双信息图.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——数字信号预处理.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——模拟信号的数字化.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——生物信号的频域分析.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)生理学信号的记录和分析——生物信号的摘取.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)医学信号处理的原理和方法——生理学实验实例.ppt
- 复旦大学:《生理学》课程教学资源(PPT课件)第四章 血液循环 CIRCULATION.ppt
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)分子病与先天代谢病(2)医学遗传学第三章.doc
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)分子病与先天代谢病(1)医学遗传学第三章.doc
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)单基因病_医学遗传学第四章.doc
- 中国医科大学:《医学遗传学》课程教学资源(教案讲义)参考资料——中英文词汇_医学遗传学.doc
